- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
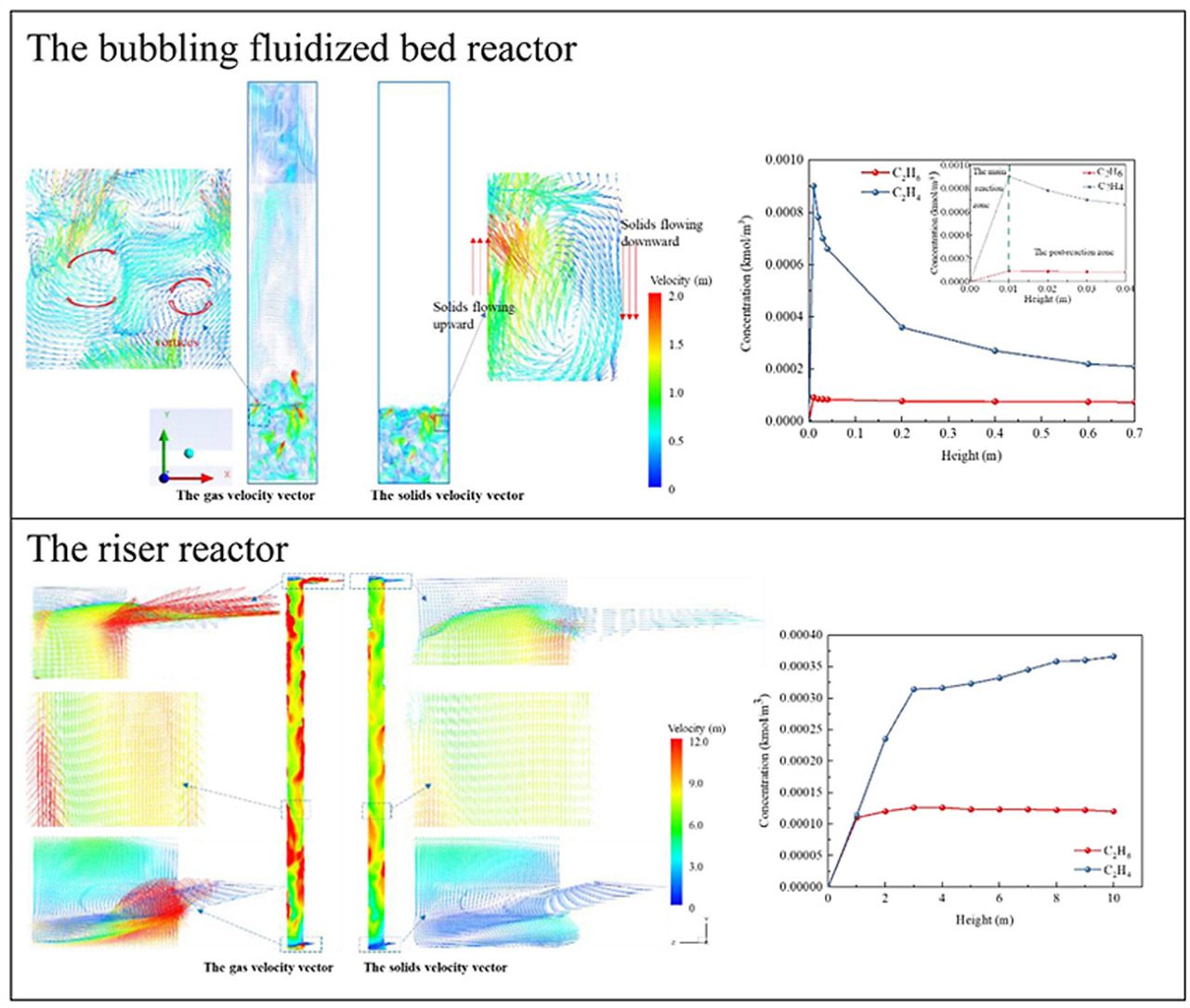
• Riser reactor can achieve isothermal operation for the OCM process.
• Consecutive reactions of ethylene are negligible due to the plug flow structure and low solids holdup in the riser.
• C2 yield of 21.1% is obtained in the riser reactor, increasing by 5.8% than that in the BFB.
• In the BFB, the C2H4 concentration quickly increases and then sharply declines with H.
The reasonable reactor design is of great importance for increasing the C2 yield (C2H4 and C2H6) of the oxidative coupling of methane (OCM), and the OCM reactor should remove the heat released in reactions quickly and efficiently and minimize the consecutive reaction of ethylene to carbon oxides. The fluidized bed reactor is characterized by excellent heat transfer, superior mass transport, and large handling capacity, while fewer studies focused on large-scale fluidized bed reactors for the OCM reaction. Therefore, large cold-model experiments and computational fluid dynamics simulations were conducted to investigate hydrodynamics and the OCM reaction performance in a large-scale bubbling fluidized bed (BFB) and a large-scale riser. In the BFB reactor, consecutive reactions of ethylene are acute because of the strong gas back-mixing, high solids holdup, and non-uniform solids distribution. While the consecutive reactions of ethylene are negligible due to the plug flow structure and low solids holdup in the riser reactor. Further, both reactors can achieve isothermal operation for the OCM process. The C2 selectivity of 45.4% and C2 yield of 21.1% are obtained in the riser reactor, increasing by 20.3% and 5.8% individually than that in the BFB reactor. This study provides useful information and reference to the OCM reactor design and commercialization.