- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
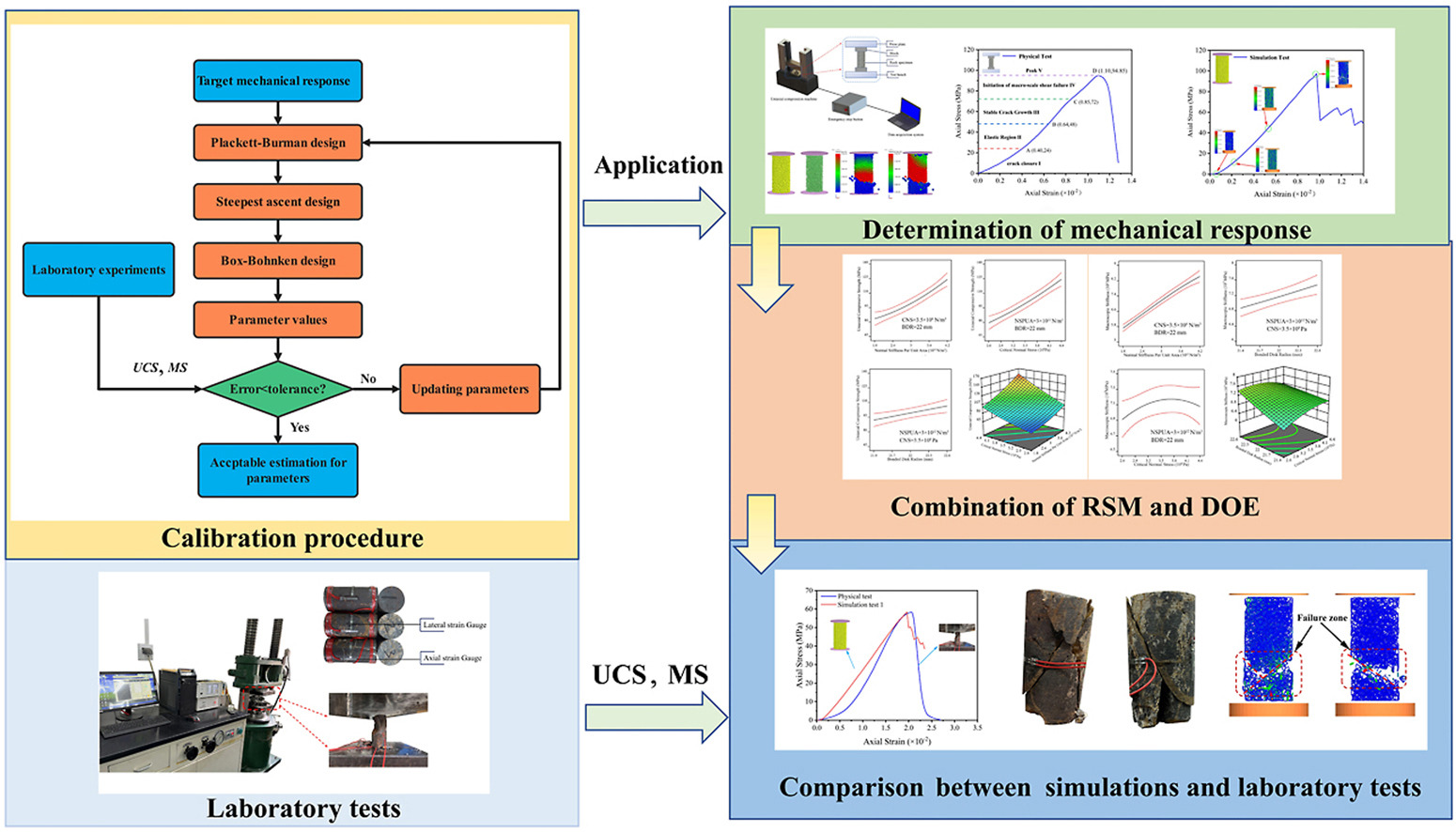
• A method of bonded-particle model calibration for ores is proposed.
• Connections between micro parameters and mechanical responses are determined.
• Sensitivities of micro parameters are explored by Plackett‒Burman design.
• Mathematical model is established.
The bonded-particle model (BPM) is commonly used in the numerical analysis of ore samples. To improve the accuracy of simulating the mechanical process of ore process of ore crushing in a crusher, the parameters of the BPM for the ore must be calibrated. In this study, a calibration method was proposed for the scientific determination of the parameters of the BPM for ore undergoing uniaxial compression. First, physical tests and simulations were conducted to determine the mechanical response (uniaxial compressive strength and macroscopic stiffness) of ore during uniaxial compression. Then, the sensitivity of the mechanical response to the values of microscopic parameters was tested using a Plackett‒Burman design. Next, the microscopic parameters with the greatest impact on the response were identified, and the range of parameters that met the target response was determined using a steepest ascent design; Second, a second-order model of the mechanical response was established using the sensitive parameters by combining a Box‒Behnken design with response surface methodology to obtain the optimal BPM parameters. Simulation tests showed that the normal stiffness per unit area, critical shear stress, and bonded disk radius had significant effects on the uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) and macroscopic stiffness (MS). To verify the validity of the proposed calibration method, laboratory tests were conducted. The consistency of the simulation results with experimental results indicated that response surface methodology with the Plackett‒Burman design, steepest ascent design, and Box‒Behnken design can be an effective method for calibrating the BPM of ores.