- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
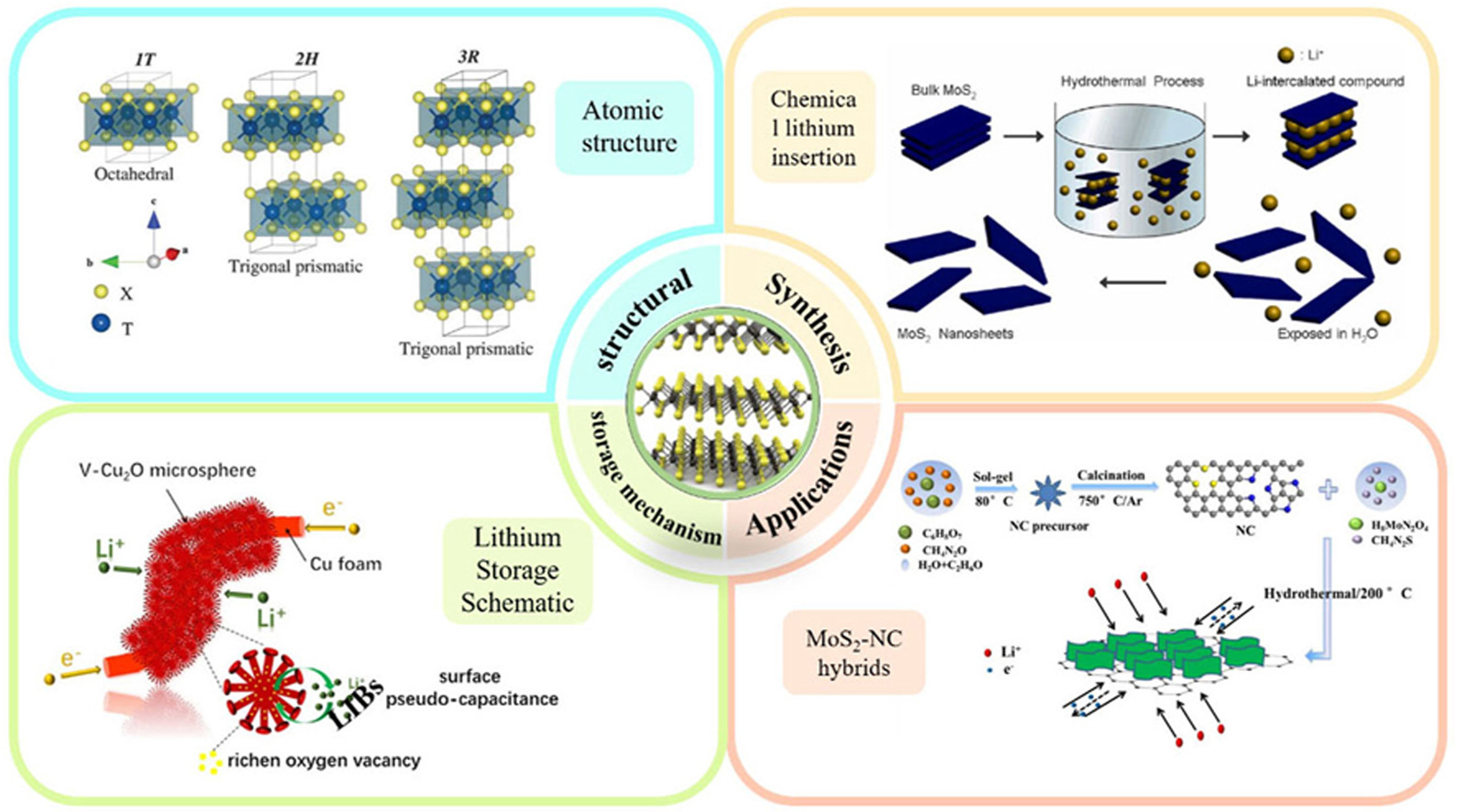
• Summarized how to distinguish metallic phase and semiconductor phase of MoS2.
• Four methods of preparing MoS2-based materials are summarized.
• Study of MoS2 lithium storage mechanism using DFT calculations and other methods.
• MoS2 defect engineering was studied to adjust its physicochemical properties.
• Emerging applications of MoS2-based electrode materials in LIBs.
In recent years, significant progress has been achieved in the creation of innovative functional materials for energy storage and conversion. Due to their distinct physicochemical characteristics, ultrathin nanosheets composed of common layered transition metal sulfide materials (MoS2) have demonstrated promise as high-capacity anode materials for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). Nevertheless, their practical application is severely limited by the tendency of monolayer nanosheets to restack due to strong van der Waals forces, dramatic volume changes during successive cycles, and low intrinsic conductivity. Recent research advances have shown that composite structures and nanowire morphologies with specific morphologies effectively overcome these issues. This paper reviews the recent research progress on molybdenum disulfide-based composites as anode materials for LIBs and discusses in detail the structural characteristics of pure molybdenum disulfide and other composite forms of molybdenum disulfide. In addition, the phase engineering, defect engineering, and lithium storage mechanisms of molybdenum disulfide and the synthesis of molybdenum disulfide-based nanocomposites by different preparation methods are focused on. Finally, we review the design (structure), recent developments, and challenges of novel anode materials and consider their electrochemical performance in Li-ion batteries.