- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
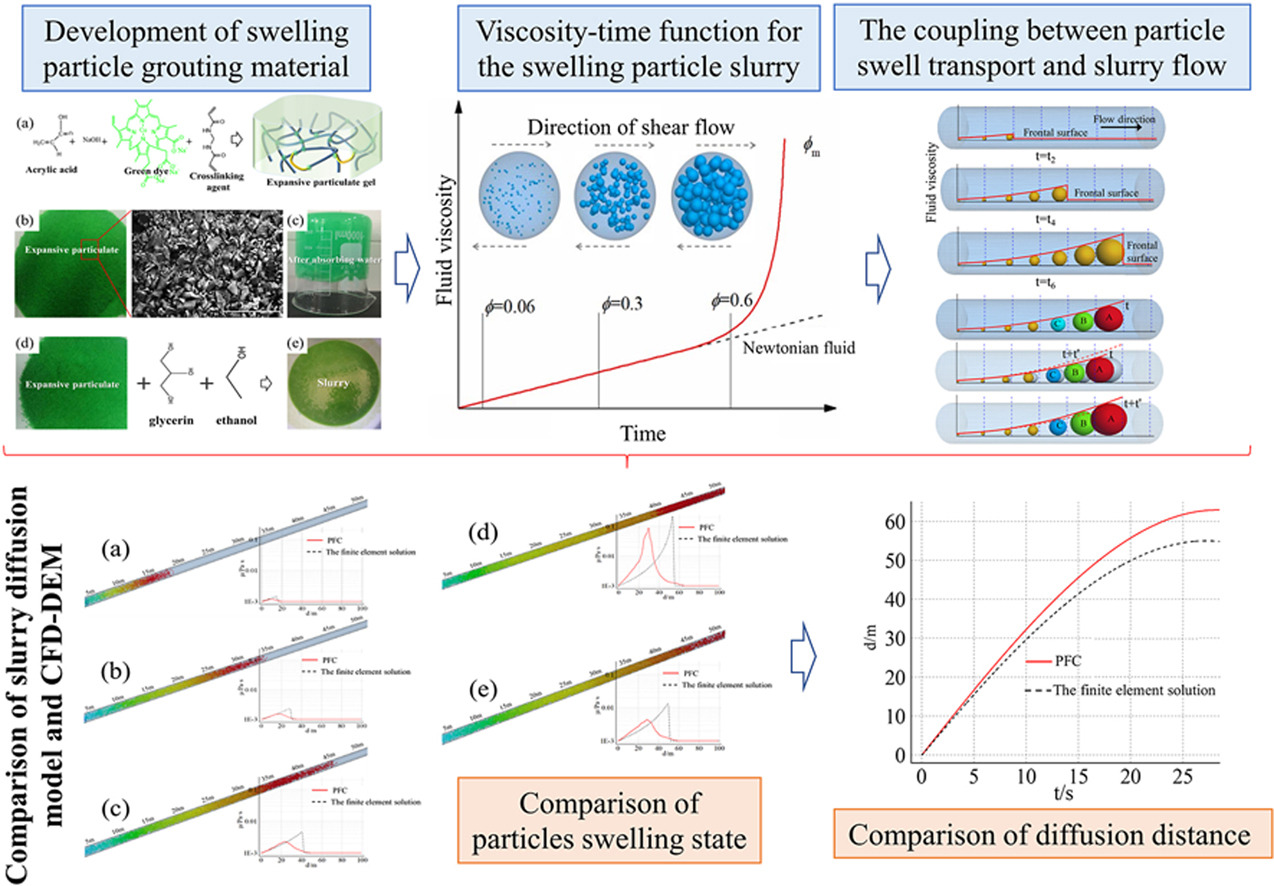
• A swelling particle grouting material has been developed and applied to treat burst water in karst pipelines.
• A constitutive model has been established to describe the swelling particle dynamic water diffusion process.
• A CFD-DEM coupling model of swelling particle slurry diffusion has been developed.
• The viscosity distribution obtained by theoretical analysis and numerical simulation are compared.
The swelling particle grouting material has demonstrated remarkable plugging effectiveness in high-pressure and large-flow burst water within karst pipelines. Currently, current research on the rheological model, flow computation theory, and plugging mechanism of this material is lacking. The conventional grouting slurry diffusion process, using the liquid-liquid two-phase flow method, fails to accurately simulate high solubility slurry and particle swelling. To address these limitations, this study established a precise constitutive model to describe the swelling particle slurry diffusion process in dynamic water. Additionally, a coupling calculation method was proposed to analyze the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of viscosity during slurry diffusion by considering the migration of slurry and the changes in viscosity. To investigate the interaction between particle swelling and flow field changes, a Computational Fluid Dynamics-Discrete Element Method (CFD-DEM) coupling model was developed for the diffusion of swelling particle slurry. It is demonstrated that slurry viscosity increases exponentially within the diffusion front as the particle swelling rate rises, and the drag force exhibits an intriguing behavior of initially increasing and then decreasing as the slurry flows through the pipeline. Furthermore, the CFD-DEM coupling model proved to be more accurate in describing viscosity distribution and diffusion distance compared to the finite element solution. The primary objective of this paper is to reveal the plugging mechanism and provide theoretical support for the engineering application of the swelling particle grouting material.