- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
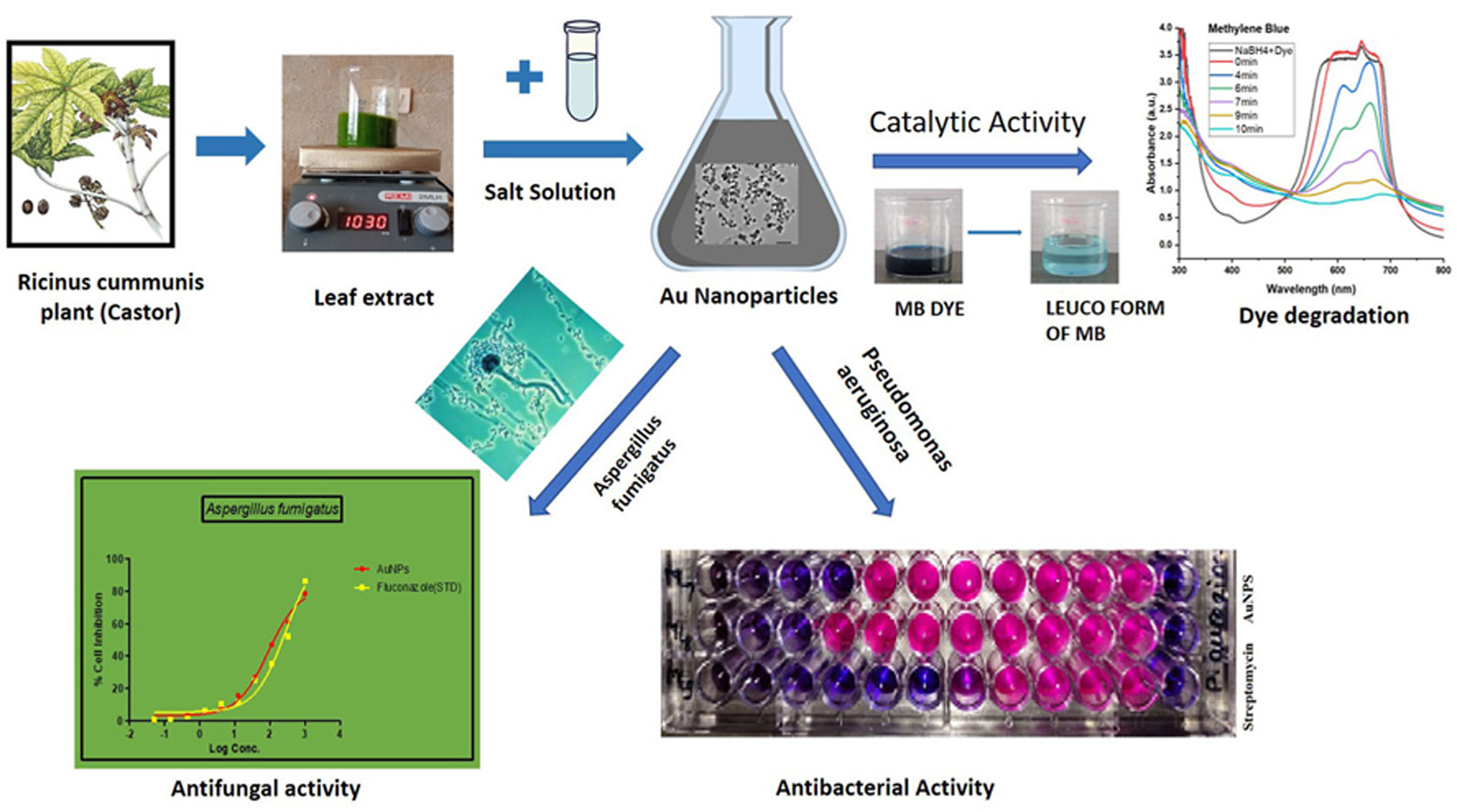
• Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Ricinus cummunis leaves.
• Reaction parameters effecting the formation of nanoparticles.
• Antifungal and antibacterial studies.
• Mechanism of organic dye degradation using biosynthesised nanoparticles.
In this study, biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) using aqueous extract of fresh leaves of Ricinus cummunis plant is reported without the use of any synthetic chemical in the reaction process. The prepared NPs are mostly spherical in shape with some particles having triangular or hexagonal structures. The average size of the particles as calculated using TEM data is 18 nm. The biosynthesised Au NPs were studied for their application in remediation of Congo Red, Methylene Blue, Reactive Red 120 and Rhodamine B dyes present in industrial effluents. The degradation of dyes was confirmed spectrophotometrically using UV–Vis Spectrophotometer. Reactive Red 120 and Congo red dyes were most effectively reduced with 88% degradation. The Au NPs were further studied for their potential as an effective antifungal agent against fungal strains namely Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus and antibacterial properties against Bacillus subtilis (Gram +ve) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Gram −ve) bacterial strains. The MIC values being 7.8 and 15.6 (μg/mL) for Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa respectively.