- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
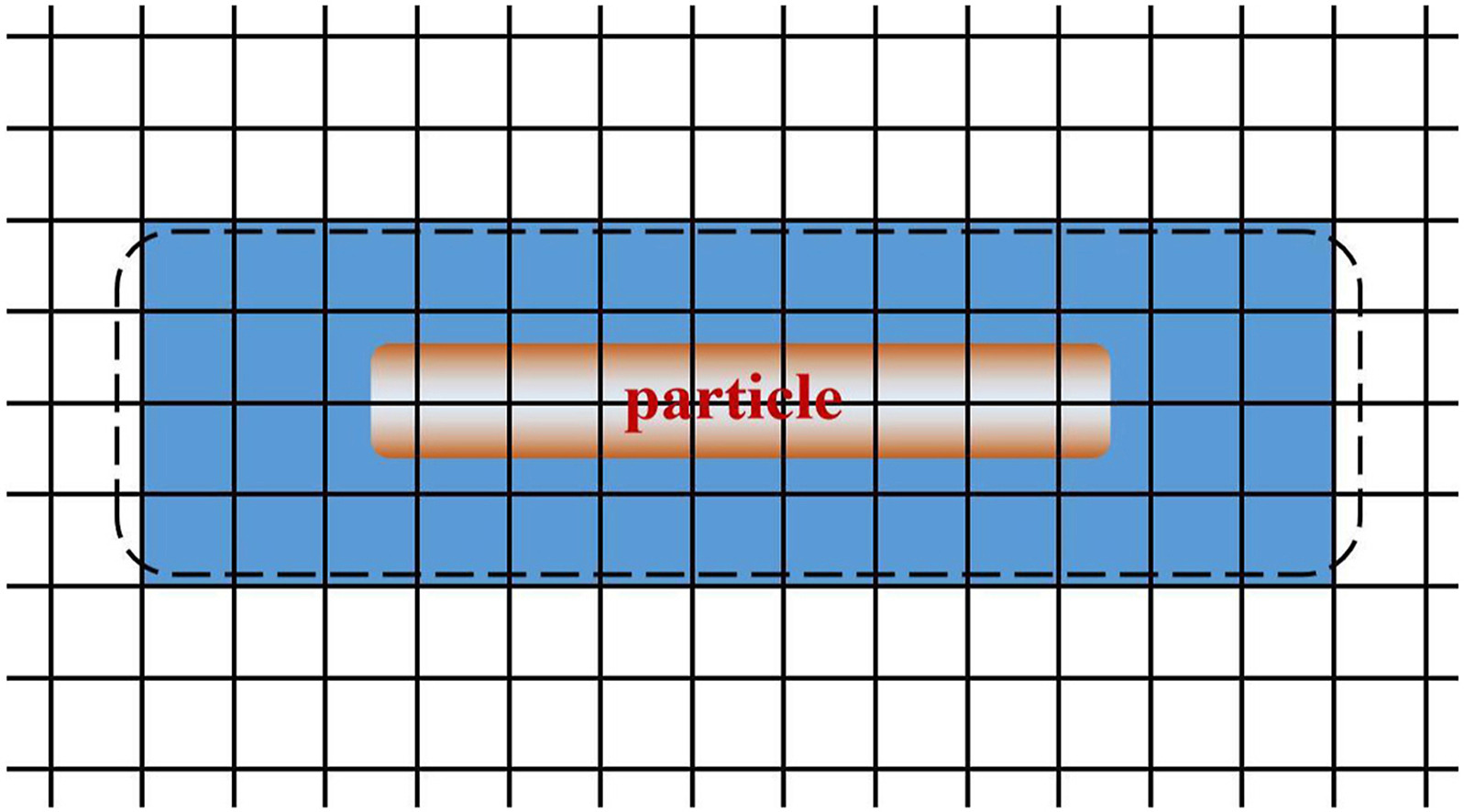
• Using minimum distance between fluid grid and particle boundary to evaluate effect of particle's drag force.
• Optimized semi-resolved CFD-DEM method is verified by a fluidized bed of rod-like particles.
• Semi-resolved CFD-DEM coupling algorithm exhibits mesh independence of fluid grid scale.
Based on a semi-resolved CFD-DEM coupling method, this study proposed a method that uses the minimum distance between the fluid grid and the particle boundary as a reference value to determine the degree of influence of the target fluid grid on the particle's drag force. A fluidized bed of rod-like particles was chosen as a typical case to investigate the effect of different fluid grid scales on various fluidized bed characteristic parameters. The calculation performance of the semi-resolved and unresolved CFD-DEM coupling algorithm on key fluidized bed characteristic parameters such as average pressure drop, particle frequency distribution with bed height, and particle orientation distribution were compared. It was found that the semi-resolved CFD-DEM coupling algorithm gradually obtained results with higher consistency with decreasing fluid grid scale for key parameters such as particle frequency distribution with bed height, particle orientation distribution, and time-history mixing index, exhibiting a phenomenon similar to grid independence in fluid simulation. By comparing with experimental results, it was verified that the semi-resolved CFD-DEM coupling algorithm can be applied to simulate multi-granular gas-solid systems with fluid grid scales equivalent to particle scales. This algorithm solves the limitation of fluid grid scale in the unresolved CFD-DEM coupling framework and improves the grid adaptability of the CFD-DEM coupling simulation algorithm.