- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
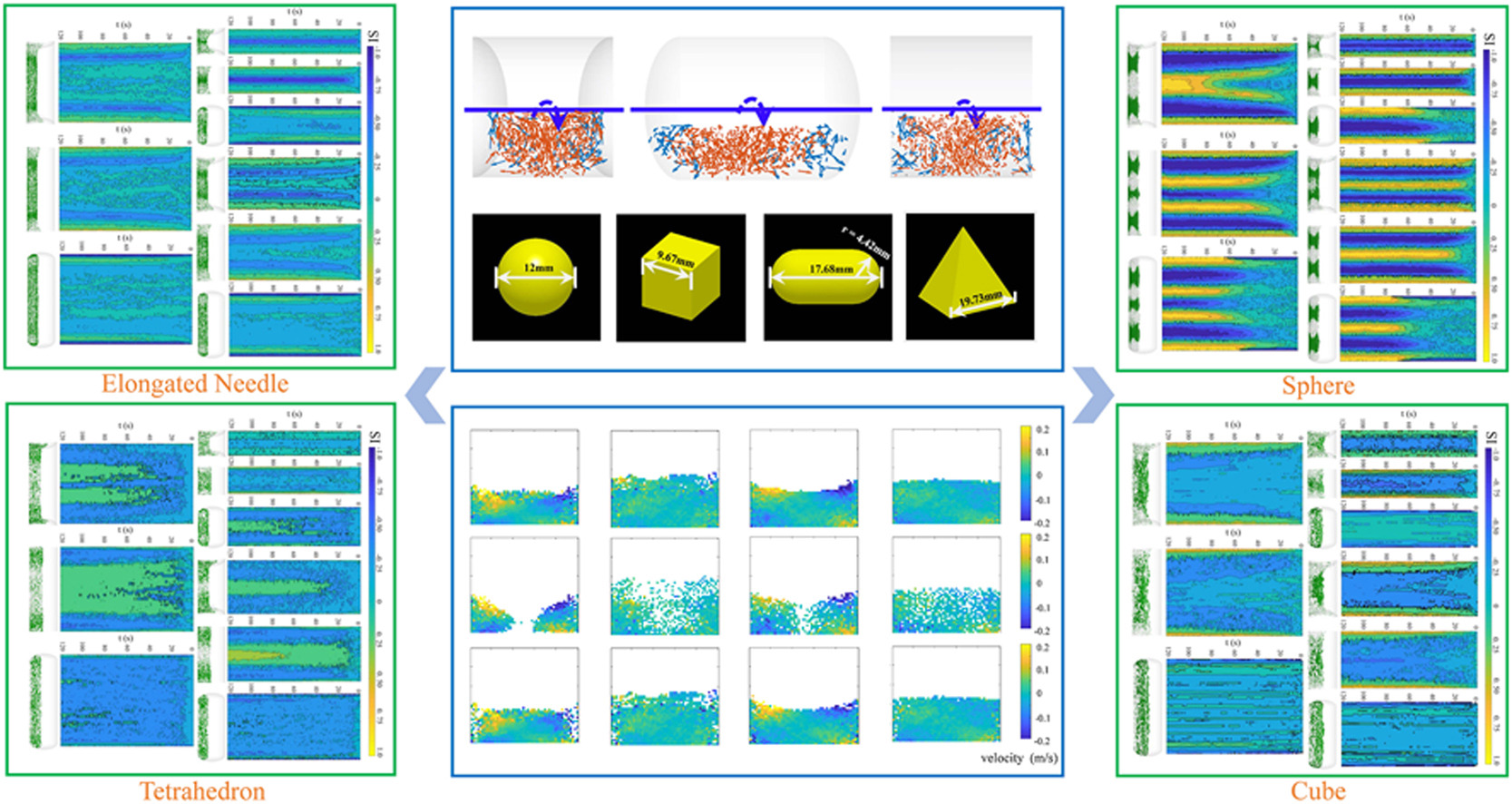
• A novel DEM rotary drum consisting of curved sidewalls was constructed.
• Axial flow rate is reduced significantly once particle angularity increases.
• Convex sidewalls enhance axial segregation while concave sidewalls inhibit.
• Non-spherical particles form no obvious multi-proportional segregation bands.
Particle mixing and segregation are common phenomena in rotary drums, which are challenging to be controlled and driven artificially in powder technology. In this work, the discrete element method (DEM) was applied to construct the novel rotary drum composed of different shaped curved sidewalls. By varying the operation parameters of particle and sidewall shapes as well as the length-to-diameter (L/D) ratio of drums, the axial mixing and segregation processes of binary size-induced particles were investigated. The results show that the axial flow velocity of the particle mixtures is noticeably weakened once the particle angularity increases, making the non-spherical particles to mix better in rotary drums compared to the spherical particles. Besides, in the short drums with size-induced spherical particles, the axial segregation characteristics are significantly enhanced by the convex sidewalls while suppressed by the concave sidewalls. However, for size-induced non-spherical particles, the axial segregation structure can be present in rotary drums with plane and concave sidewalls while not in drums with convex sidewalls. Moreover, the axial segregation band structure of spherical particles eventually increases proportionally with the increased drum L/D ratios. In contrast, the non-spherical particles cannot form obvious multi-proportional segregation bands.