- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
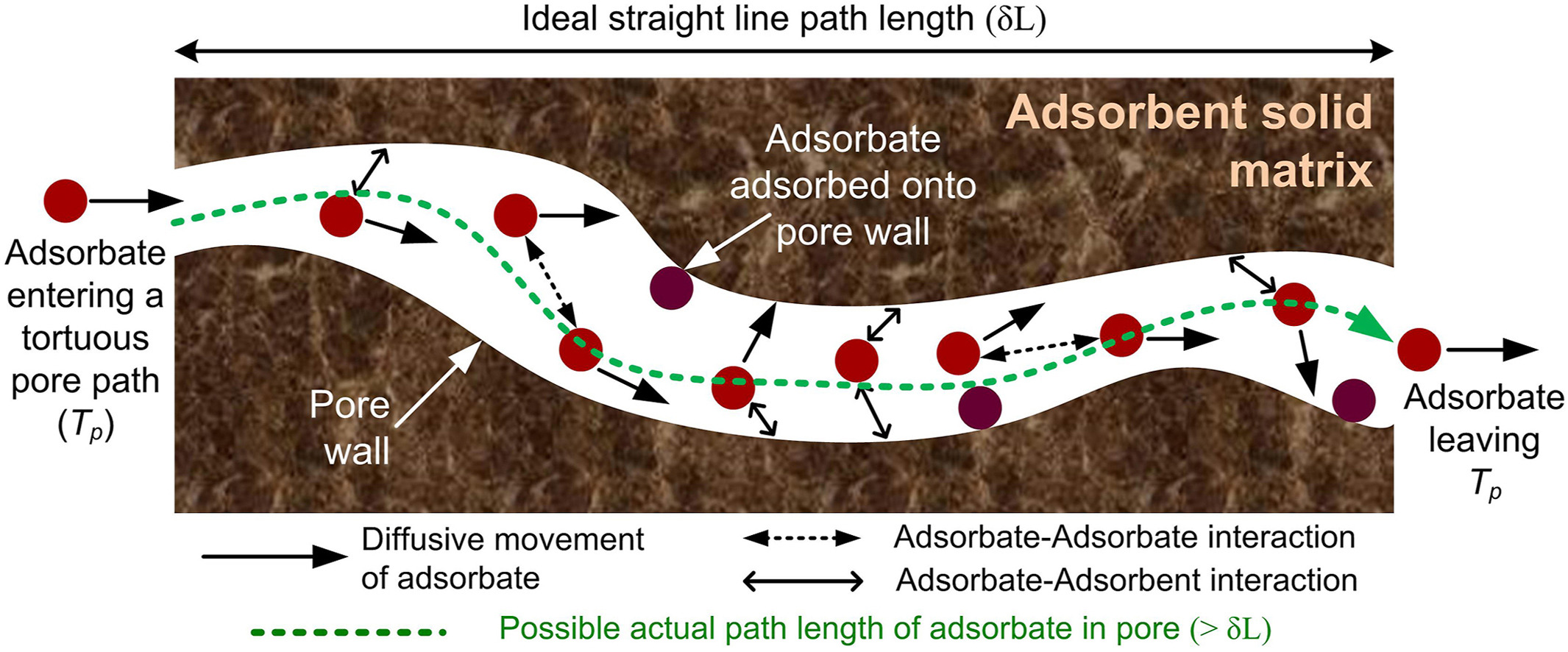
• Adsorbent tortuosity has been sporadically studied in aqueous-phase adsorptions.
• It seems inexact to give a single characteristic tortuosity value for an adsorbent.
• The analysis of adsorbent tortuosity in multicomponent aqueous systems is sparse.
Pore network, pore connectivity, and the resulting effective adsorbate pore diffusivity within an adsorbent are critical physical considerations in mass transport modeling of aqueous adsorption. Tied to these three adsorbent features are the adsorbent tortuosity and tortuosity factor concepts. These concepts encompass the collective hindrance to intra-adsorbent adsorbate transport arising because of a disorderly adsorbent porous topology. It is crucial for materials scientists, chemists, chemical engineers, and water treatment specialists to understand the complex and variable connections among adsorbate chemistry, adsorbent chemistry, adsorbent porosity, pore shape, size, and tortuosity, pore wall effect, adsorbate-adsorbent interactions, and adsorbate-adsorbate interactions in competitively contaminated aqueous environments. Adsorbent tortuosity has been sporadically studied in aqueous adsorption models. Despite the small population of these studies, insightful observations and inferences have been reported. However, as it appears, no review has been published to compile, compare, and contrast these aspects. Hence, this review concisely brings up those observations and interpretations around adsorbent tortuosity for aqueous adsorption systems. The notion of an adsorbent's tortuosity being single-valued is argued to be imprecise. Finally, perspectives are aired on possible research and development directions for elucidating the dynamic attributes of adsorbent tortuosity and applying them in real-scale adsorption-oriented water purification. The data acquired by filling in these research gaps can enable the design of adsorbents more adapted for real-scale water purification.