- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
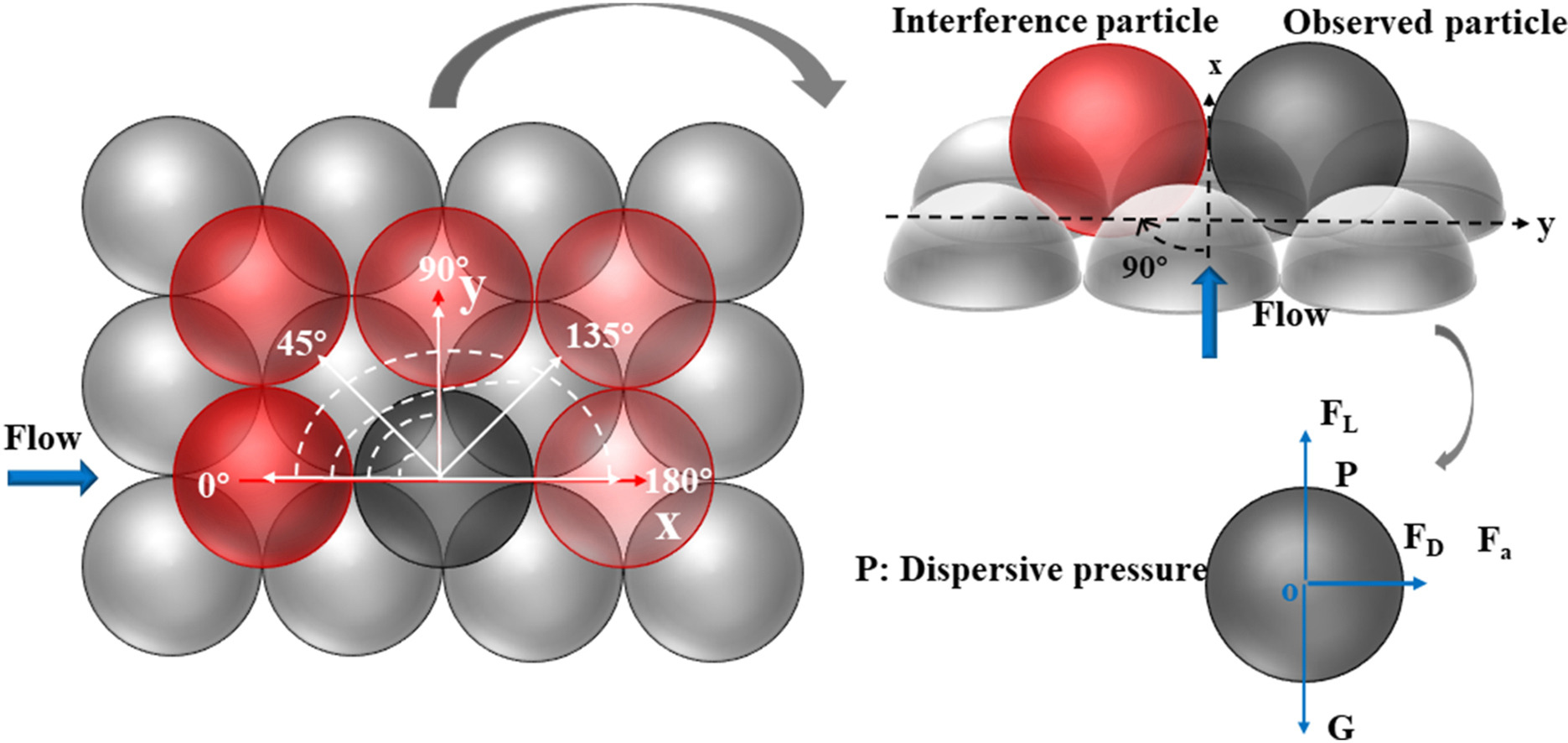
• The incipient velocity equation is conceived by the rolling instability mechanism.
• A series of 240 experiments were carried out on particle motion.
• Determination of drag and lift coefficients on the incipient velocity equation.
• Dispersive pressure will reduce the velocity by promoting particle motion.
• The particle arrangements affect particle motion.
The sediment particles play a huge role in shaping the bed load transport. In this research, 240 water-tunnel experiments are carried out to investigate the incipient velocity of the observation particles in two particle arrangements. To accurately predict the incipient velocity of the observation particles, the equation is conceived by the rolling instability mechanism. The incipient velocity equations and experimental data are used to analyze the trend of dispersive pressure and the effect of arrangement position on velocity. We find that it is appropriate to choose the coefficient of drag as 0.261 and the coefficient of lift as 0.198 for the incipient velocity equation of spherical particles on the hemispherical bed surface. Furthermore, the dispersive pressure is closely related to the flow state, particle size, and particle arrangement, which leads to the incipient velocity of the observation particle being at a minimum when the interference particle angle is 45°. Finally, the particle spacing and the projected area changed with the arrangements, directly affecting the incipient velocity of the observed particle. The analysis of four aspects for the coefficients, dispersive pressure, different particle spacing, and projected area will facilitate the prediction of particle incipient velocity, especially on hemispherical beds.