- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
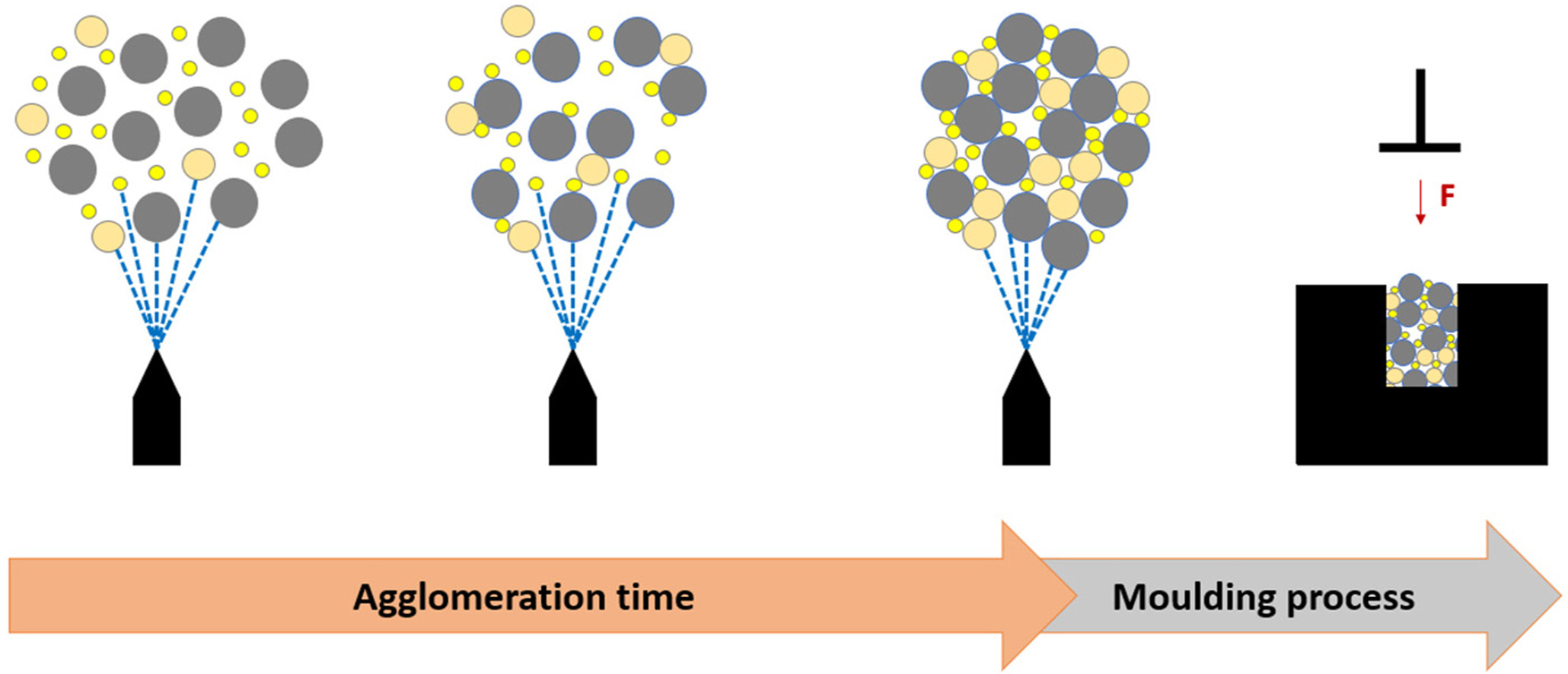
• A novel carbon granules formulation based on carbon and peroxide powder was developed.
• Influence of spraying parameters during agglomeration was understood and optimized.
• Through spraying parameters, a defined pore and volume structure in agglomerates and carbon tablets was achieved.
• Particle agglomeration was monitored throughout agglomeration cycle time.
• Through design of experiments, optimum carbon tablet strength was achieved based on spraying parameters.
Spraying parameters during particle agglomeration processes can affect the agglomeration kinetics and particle growth. This study was conducted to better understand the influence of the spraying parameters in a fluidized bed wet agglomeration process, and the influence on the stability characteristics of carbon tablets. A formulation based on fine carbon and peroxide powder, as well as carboxymethyl cellulose as a binder, was used to produce agglomerates in a first production step. Thereafter in a second production step carbon tablets with a high porosity were molded for the customer goods industry. The optimization of the compressive strength of these carbon tablets was the goal of the trials. Carbon agglomerates were produced with a laboratory scale granulator called “ProCell” and were compressed with a five-cavity mechanical press. The screening of the agglomeration process parameters and their influence on the agglomerates quality, as well as the performance characteristics of the carbon tablets, were investigated using a multilevel factorial design. The experimental runs were done by varying atomized air pressure and feed rate of the fluid. This was determined by the design model. The findings of the statistical trials showed that low atomized air pressure and a low feed rate lead to a higher tablet compressive strength.