- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
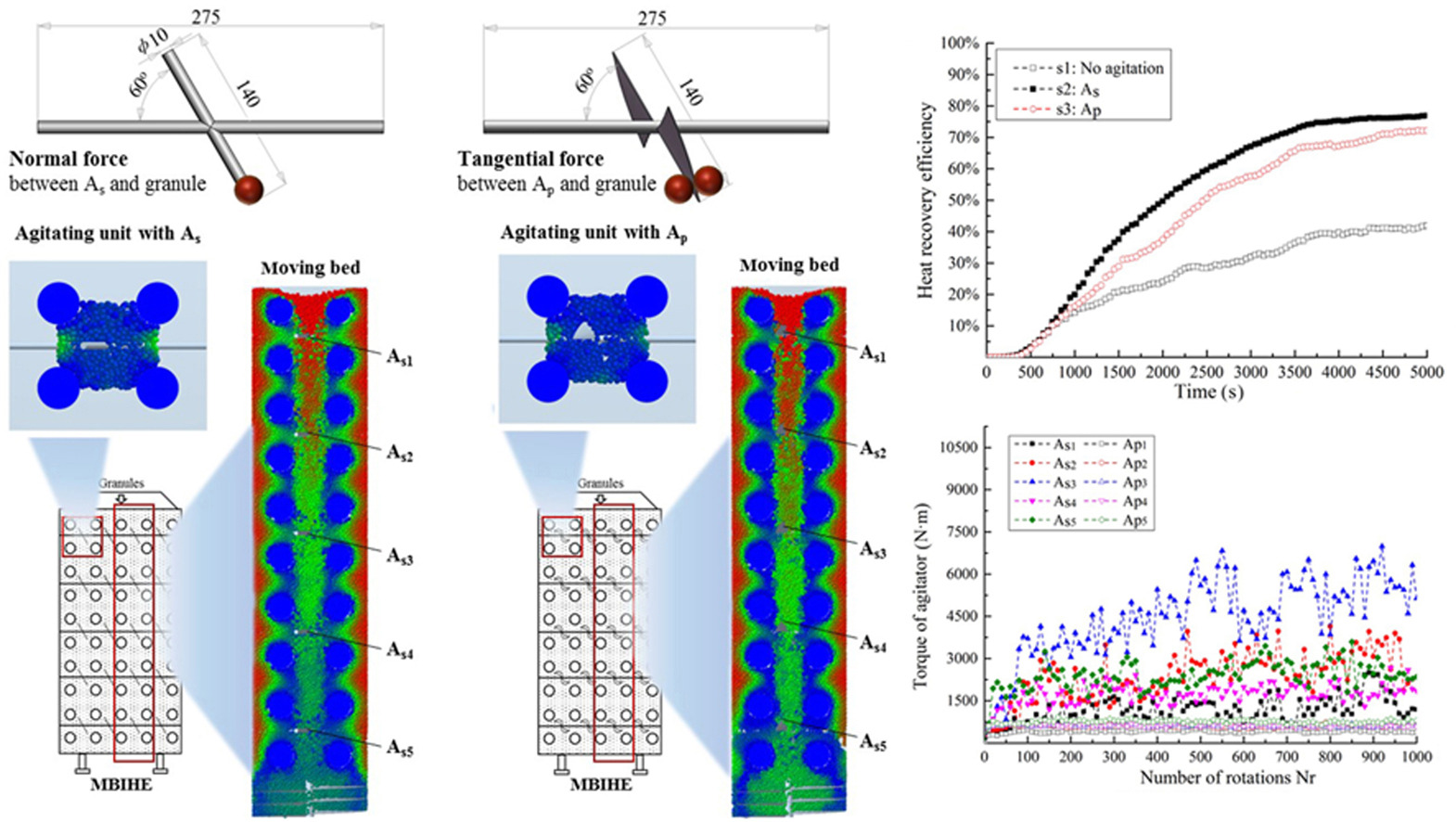
• Granule migration and heat transfer in moving bed is investigated by simulation.
• DEM coupled with CFD is adopted to analyze detailed heat transfer behavior.
• Heat transfer enhancement and the operating reliability of different agitators are compared.
• Agitator with plow-shaped surface is recommended for its better agitating reliability.
Waste heat recovery of high-temperature granules is one of the most promising sustainable energy supply and carbon reduction ways for industry. A moving bed indirect heat exchanger (MBIHE) with inner-migration was proposed for granular heat recovery. Granule migration and the enhanced heat transfer induced by two types of agitators (i.e., agitator with slanted stick As and with plow-shaped surface Ap) in the MBIHE are analyzed based on DEM coupled with CFD. Owing to the effective agitation, the average heat transfer coefficient in the granule side is enhanced to ∼3 times compared to that without agitation. The heat recovery efficiency in the moving bed reached more than 70% with the agitations of either As or Ap. The heat efficiency of As is ∼7% higher than that of Ap, but with at least 60% greater rotational torque. To ensure reliable agitation, the Ap is suggested to be adopted in the MBIHE to induce granule migration.