- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
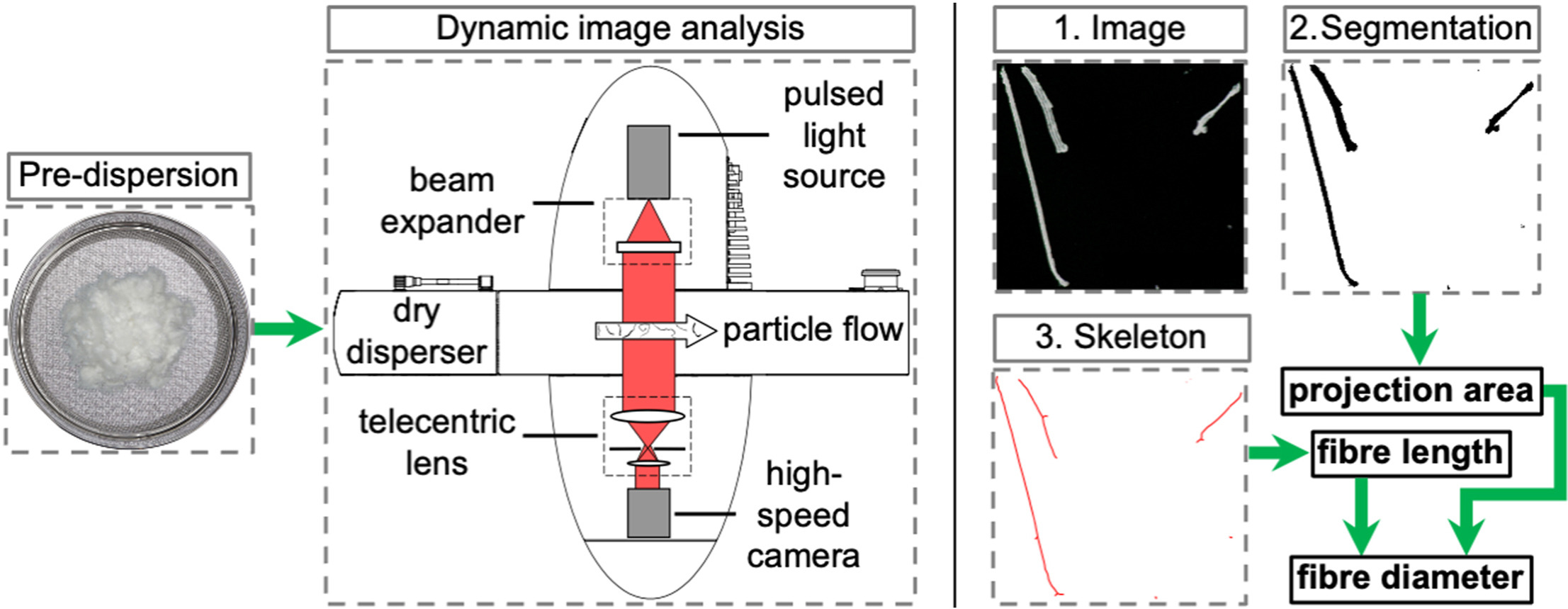
• Pre-dispersion step to singularise interlocking fibres.
• Dynamic image analysis to determine projection area, fibre length and diameter.
• Flow cell boundaries during wet dispersion minimise fibre orientation influence.
• Semi-automatic evaluation by ImageJ if automated image processing algorithms fail.
Dynamic image analysis provides an automated evaluation method to determine the size and shape of multiple particles. This method represents a common application for ordinary bulk material. The latest draft of ISO 13322–2:2021 describes the state of the art, but lacks instructions for handling fibrous bulk material. Interlocking fibres complicate the measurement conditions and require a disentanglement of fibrous samples during a pre-dispersion step. A further error source includes the fibre orientation inside the measurement zone of the device. If the thresholding algorithm fails to differentiate between the fibre projection area and the background, a subsequent image optimisation solves the problem. This article addresses the mentioned problems by analysing cotton cellulose and polyacrylonitrile fibres. Besides the execution of a pre-dispersion step, the experiments compare the discrepancies between dry and wet dispersion. Here, the software packages PAQXOS and ImageJ perform the image evaluation. In this case, the wet dispersion setup with a subsequent image evaluation by ImageJ provides comprehensible results.