- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
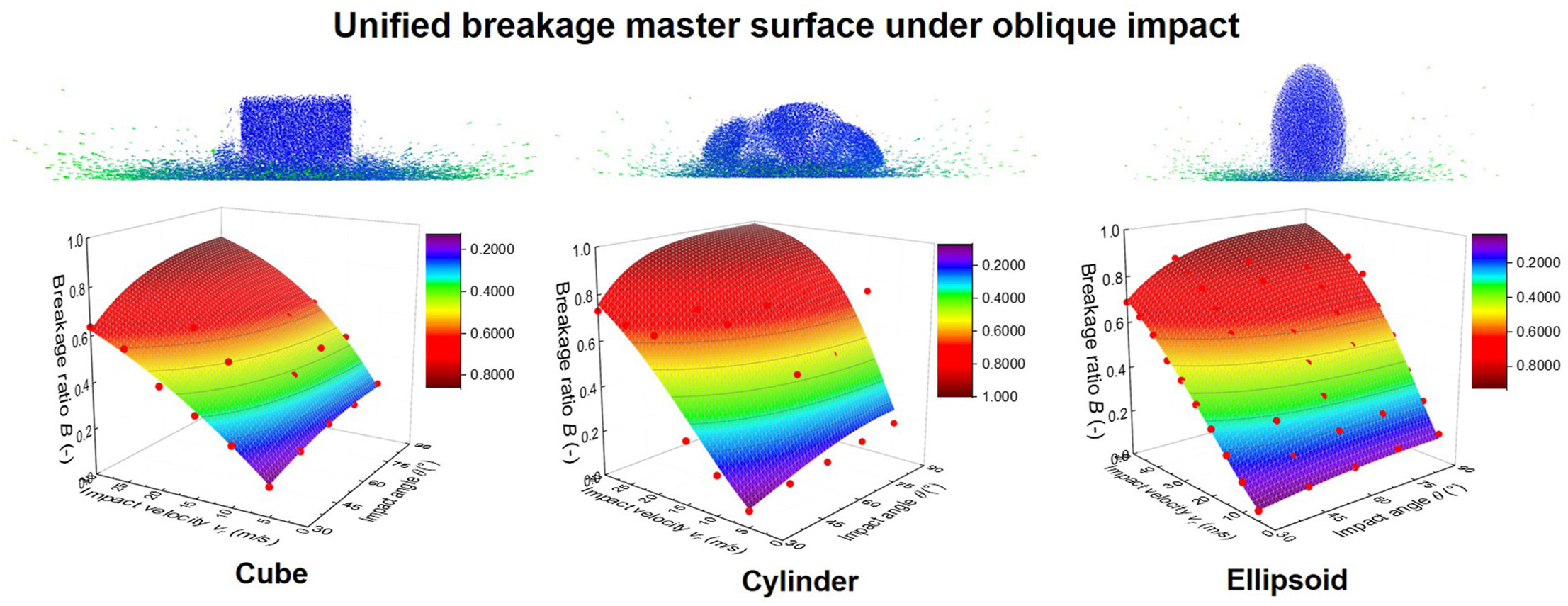
• Impact breakage of nonspherical particles is investigated by DEM under oblique impact.
• Investigation of impact orientation and tangential velocity on the breakage characteristics.
• Model calibration and validation for equivalent velocity.
• Unified breakage master surfaces for all the particle shapes are constructed.
Particle breakage commonly occurs during processing of particulate materials, but a mechanistic model of particle impact breakage is not fully established. This article presents oblique impact breakage characteristics of nonspherical particles using discrete element method (DEM) simulations. Three different particle shapes, i.e. spherical, cuboidal and cylindrical, are investigated. Constituent spheres are agglomerated with bridging bonds to model the breakage characteristics under impact conditions. The effect of agglomerate shapes on the breakage pattern, damage ratio, and fragment size distribution is fully investigated. By using a newly proposed oblique impact model, unified breakage master surfaces are theoretically constructed for all the particle shapes under oblique impact conditions. The developed approach can be applied to modelling particulate processes where nonspherical particles and oblique impact breakage are prevailing.