- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
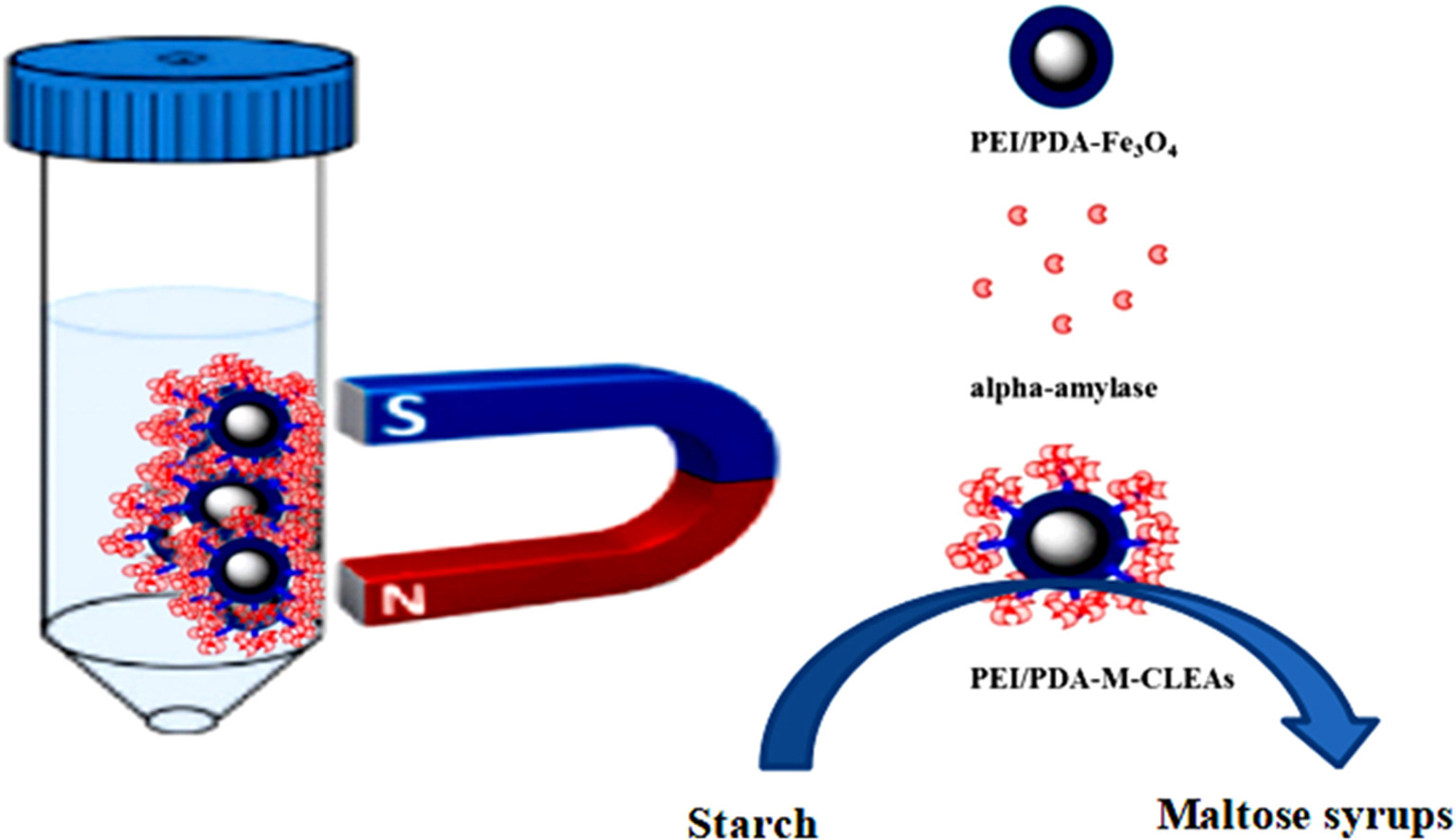
• Novel magnetic cross-linked α-amylase aggregates were successfully prepared.
• Resultant PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs and N-M-CLEAs exhibited excellent thermal stability, storage stability and pH stability.
• PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs and N-M-CLEAs exhibited higher starch hydrolysis efficiency than free α-amylase.
In this work α-amylase was immobilized on magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with polyethylenimine (PEI)/polydopamine (PDA) coating or 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane (APTES) for the first time via adsorption–precipitation–cross-linking. Compared with the free α-amylase, the resultant magnetic cross-linked α-amylase aggregates (PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs and N-M-CLEAs) exhibited excellent thermal and storage stability as well as pH stability. After storage at 25 °C for 60 days, free α-amylase only retained 60% of its initial activity, while PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs and N-M-CLEAs retained 80% and 78% of their initial activities, respectively. Furthermore, N-M-CLEAs and PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs showed good reusability. After 6 repeated uses, PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs and N-M-CLEAs still maintained 65% and 62% of their initial activities, respectively. Especially, PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs and N-M-CLEAs exhibited higher starch hydrolysis efficiency than free α-amylase. The maximum dextrose equivalent (DE) values of starch hydrolysis by PEI/PDA-M-CLEAs and N-M-CLEAs reached 29.24% and 28.79% within 90 min, respectively. However, the maximum DE values of starch hydrolysis by the free α-amylase was only 27.89% even in 150 min. The magnetic cross-linked α-amylase aggregates could be introduced as effective biocatalyst for industrial applications in production of maltose syrups.