- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
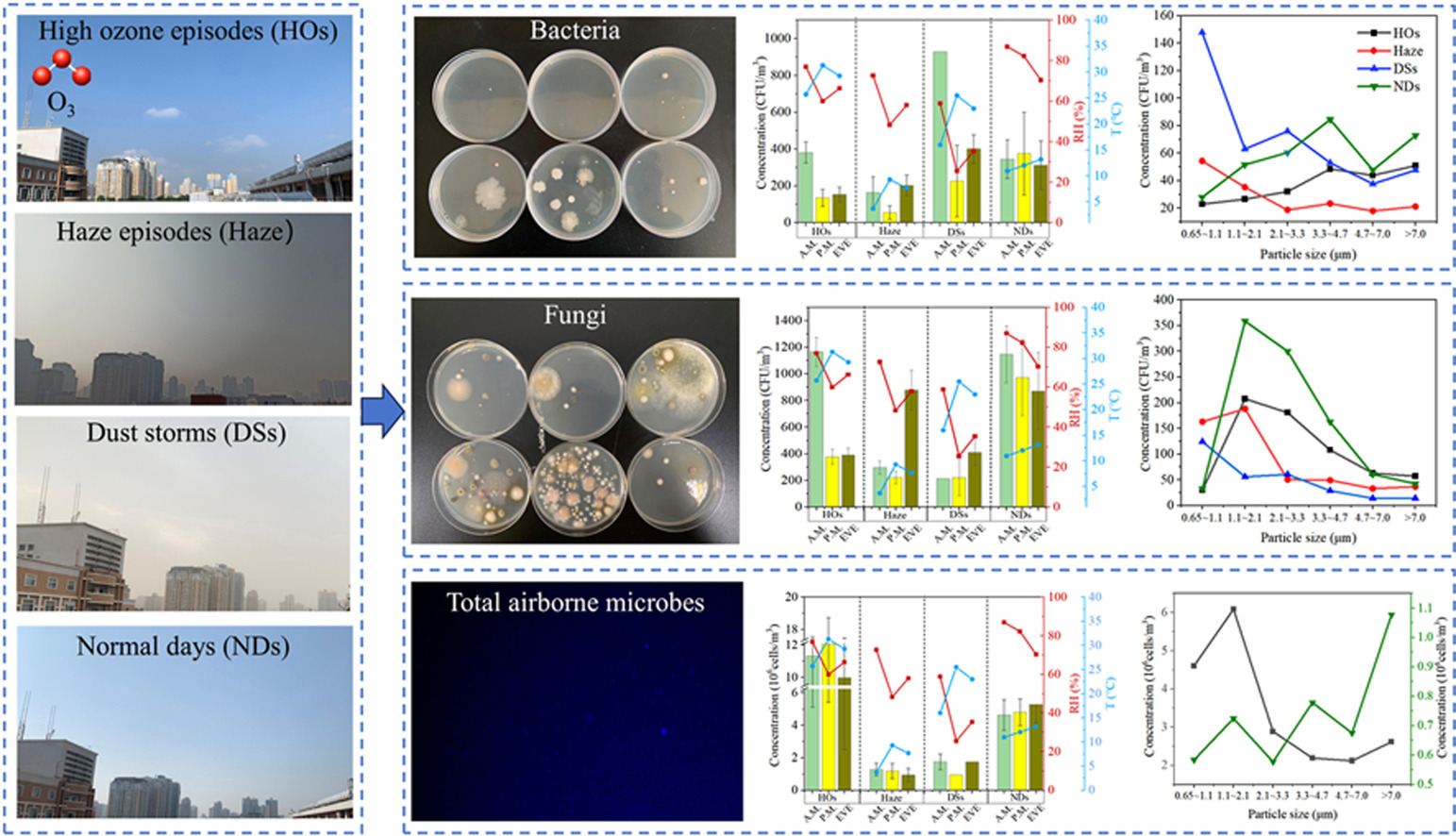
• Bacterial, fungal, and total airborne microbes were highest in dust storm, normal day, and high-O3 episodes, respectively.
• Similar diurnal variation trends were observed during three pollution events.
• Bacteria levels exhibited bimodal size distributions compared to unimodal-pattern fungi.
• Particulate matters show negative effects on fungal levels during dust storms.
• O3 and temperature were negative, but relative humidity was positive with fungal level during high-O3 episodes.
The characteristics of bioaerosols and their effects on human beings' health have become a major public concern in the recent years. This study compared the characteristics of bioaerosols under different types of pollution (high-ozone [HO] episodes, haze episodes, and dust storms [DSs]), with those of bioaerosols on normal days (NDs) in Xi'an, China. The concentrations, diurnal variations, and size distribution of bacteria, fungi, and total airborne microbes (TAMs) were investigated. The results showed that the bacterial and fungal concentrations were the highest during DSs and on NDs, reaching 425.2 and 956.9 colony-forming units/m3, respectively. The concentration of TAMs was the highest during HO episodes, reaching 10.7 × 106 cells/m3, which was significantly higher than that during the other events. The maximum concentrations of bacteria and fungi during HO episodes were observed in the morning, while they appeared separately in the morning and evening during haze episodes. Bacteria and TAMs during DSs reached peak concentrations in the morning and evening, which is opposite to the particulate matter (PM) distribution pattern. On NDs, temperature and relative humidity had significant effects on bioaerosols. The size distributions of airborne bacteria exhibited bimodal patterns, whereas unimodal distributions were observed for fungi. Fungi mainly attached in fine particles (<2.1 μm) with proportions of 67.4% and 60.5% during haze episodes and DSs, respectively, which means that fungi were easily penetrated into the human respiratory system. The evaluation of influence factors revealed that PM2.5 and PM10 had negative effects on fungal concentration during DSs, and ozone concentration and temperature were inversely correlated with fungal concentration during HO episodes. These results provide valuable reference data for elucidating the formation and evolution of bioaerosols under different types of pollution.