- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
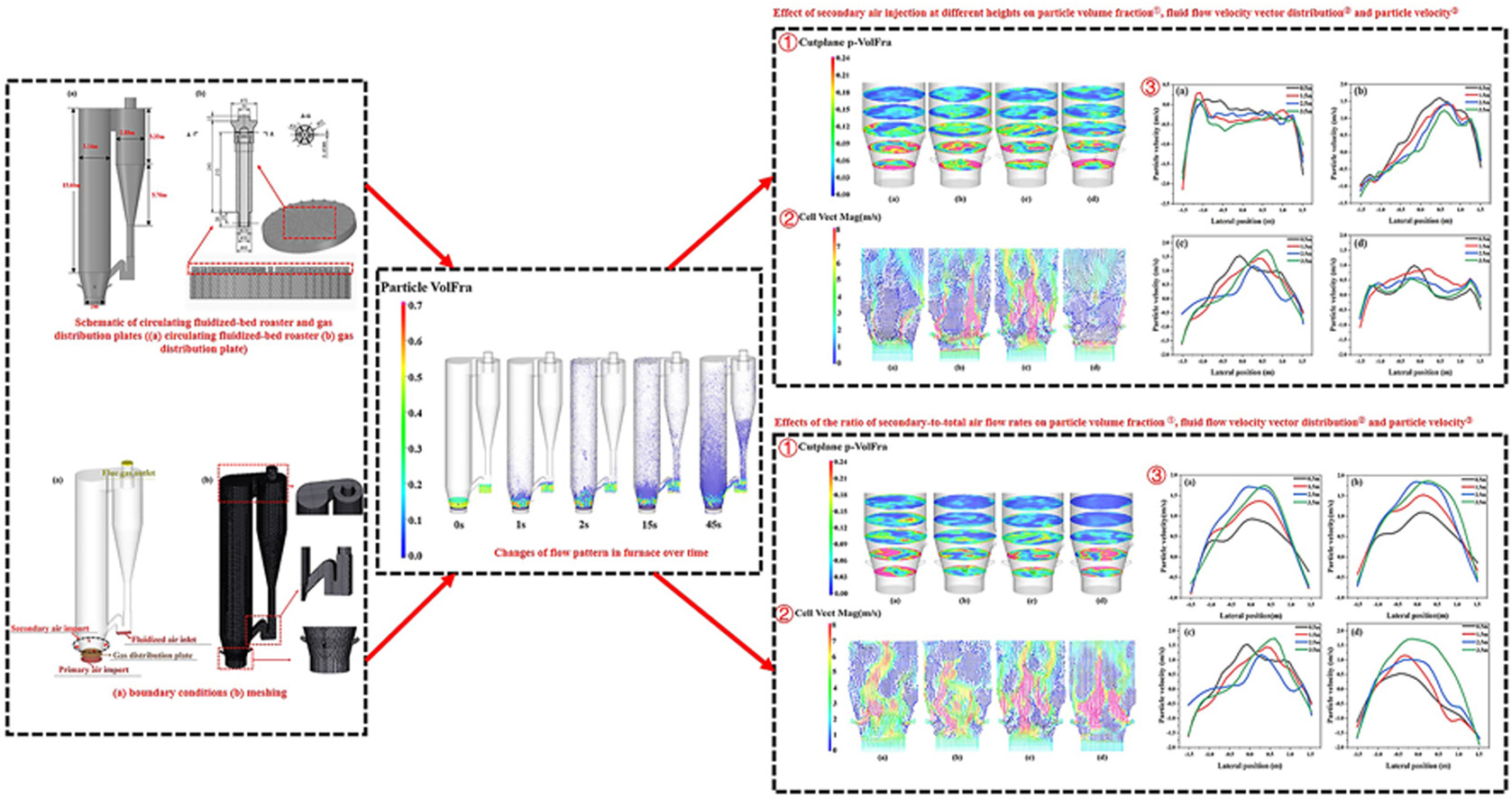
• A computational particle fluid dynamics simulation was performed to investigate a circulating fluidized bed roaster.
• Effect of the different secondary air positions on the gas–solid flow was explored.
• Effect of the different secondary air ratios on the gas–solid flow was explored.
• The optimal secondary air position and the secondary air ratio are obtained.
A full-cycle numerical simulation of a circulating fluidized bed (CFB) by the use of the computational particle fluid dynamics (CPFD) method has been developed. The effects of the presence or absence of the secondary air, different secondary air positions, and different secondary air ratios on the gas–solid flow characteristics were explored. The results show that the presence of the secondary air makes a core-annular structure of the velocity distribution of particles in the fluidized bed, which enhances the uniformity of particles’ distribution and the stability of fluidization. The position and the ratio of the secondary air have a significant impact on the particle distribution, particle flow rate, and gas flow rate in the fluidized bed. When the secondary air position and ratio are optimal, the particles, particle flow rate, and air flow rate in the CFB are evenly distributed, the gas–solid flow state is good, and the CFB can operate stably.