- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Full-loop simulations were conducted to study the L-valve in a CFB.
• Solid flow characteristics can be accurately predicted by the simulations.
• The effects of operating parameters on solid flow characteristics were obtained.
• The effects of geometric parameters were studied for the optimization of L-valve.
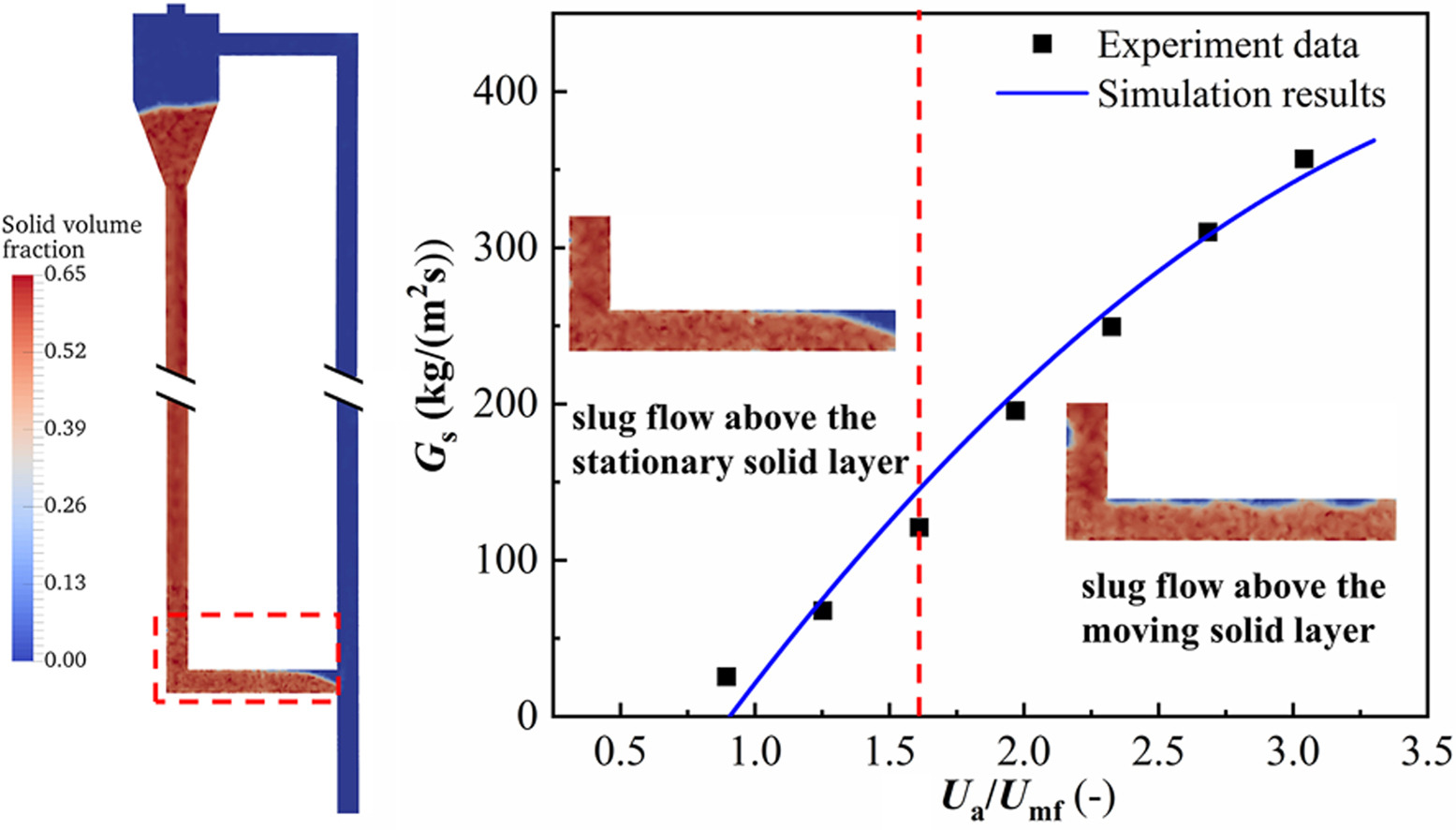
Stable and controllable solid flow is essential in circulating fluidized bed (CFB) systems. The L-valve is a typical non-mechanical valve that can provide flexible solid feeding. The investigation of the solid circulation rate and the hydrodynamic characteristics of the L-valve is crucial to its design and operation. The gas-solid flow in the L-valve of a full-loop CFB is studied with the coarse-grained discrete particle method (EMMS-DPM). Good agreements on the solid circulation rate and the pressure drop through the L-valve are achieved between the simulated and experimental data. The solid circulation rate increases linearly with the aeration velocity until the stable particle circulation of the CFB is destroyed. The flow patterns in the horizontal section of L-valve are gas-solid slug flow above the stationary solid layer and the moving solid layer, respectively. The effects of L-valve geometric parameters on the solid flow characteristics are also investigated. The results indicate that reducing the diameter and length of the horizontal section of L-valve can improve the solid transport efficiency, especially at low aeration velocity. Besides, the solid conveying capacity and flow stability are improved when the sharp bend of L-valve is modified to be a gradual bend.