- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
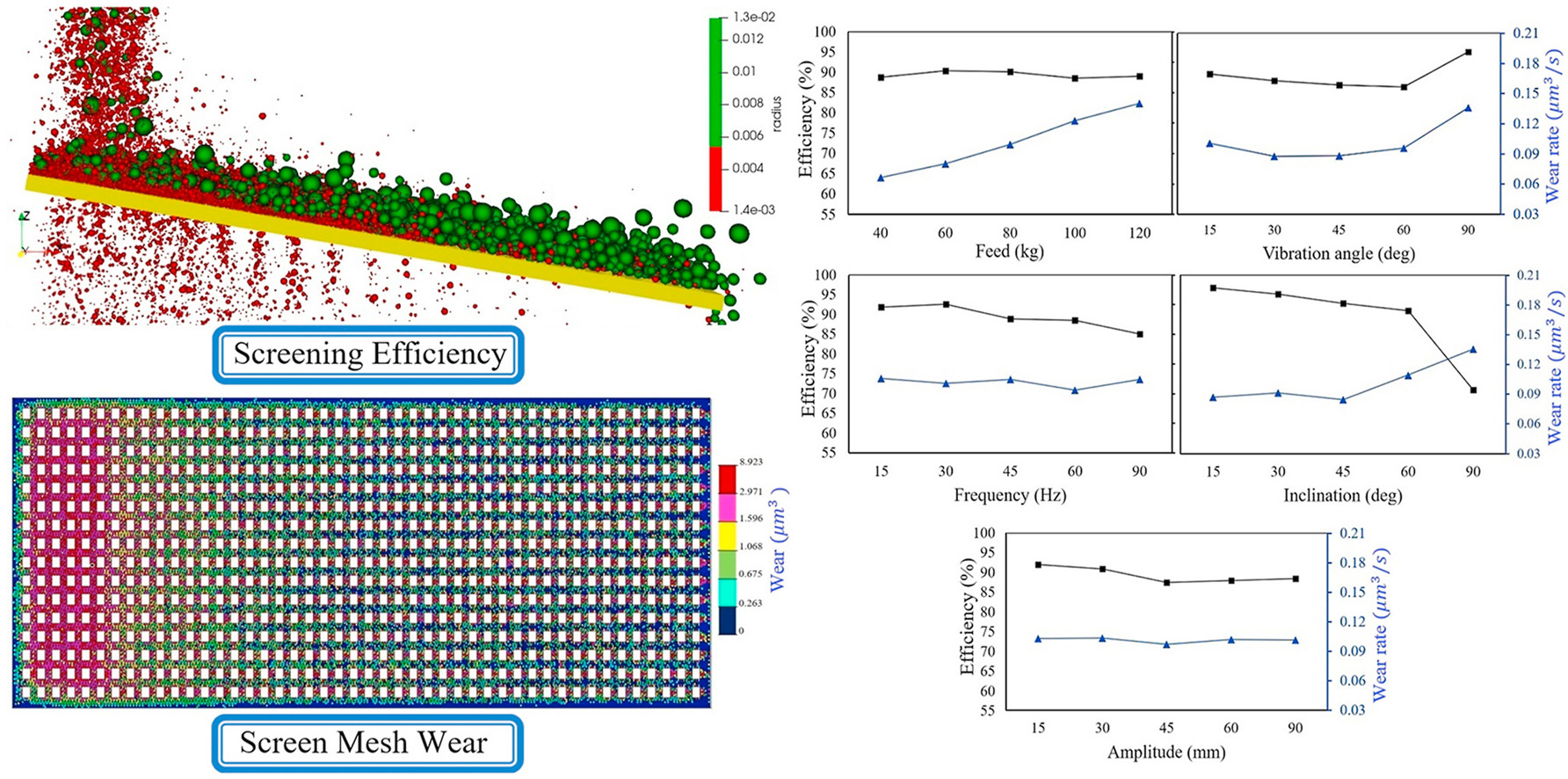
• Vibrating screen was numerically studied using the discrete element method.
• Optimal values for maximising efficiency and minimising mesh wear were determined.
• Screening efficiency and particles average velocity were inversely related.
• The most effective parameter on screening efficiency was the inclination angle.
• The most influential parameter on screen mesh wear rate was the feed rate.
This article investigates the combined effect and the order of influence of feed rate, inclination angle, vibration amplitude, frequency, and angle on the efficiency and mesh wear rate of a linear vibrating screen, as well as the average velocity, and mass of the accumulated particles. The discrete element modeling simulations were conducted using LIGGGHTS open-source code to analyze particles behaviour. The Taguchi method was employed to evaluate the combined effect of the parameters. Finally, the simulation results were analyzed using analysis of variance. The optimal values of the parameters for maximising efficiency and minimising mesh wear were determined using grey relational analysis. The results indicated that the most effective parameters on screening efficiency and average velocity of particles were the inclination angle, vibration angle, frequency, amplitude, and feed rate, respectively. The most influential parameters on screen mesh wear rate were feed rate, inclination angle, vibration angle, frequency, and amplitude, respectively.