- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
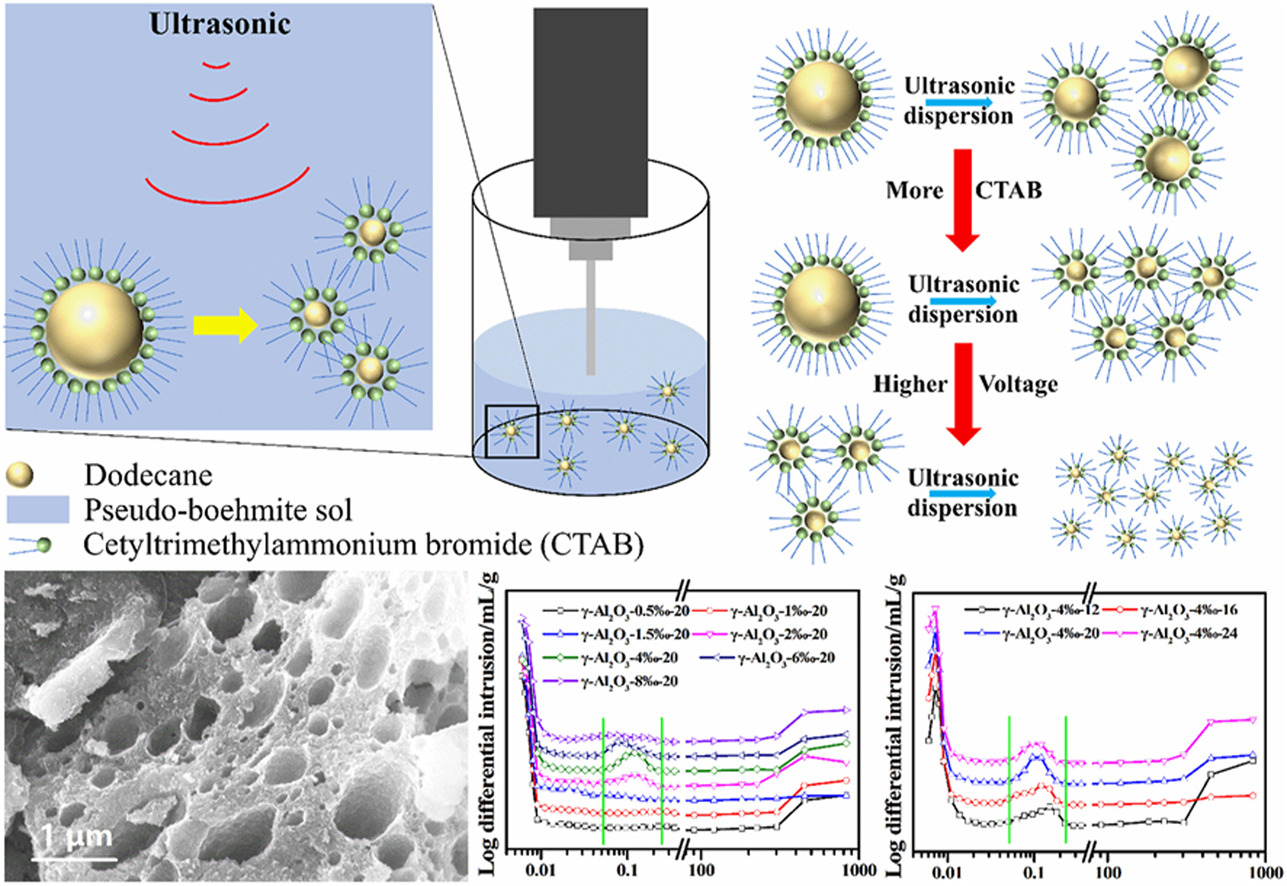
• Moderate use of surfactants can generate macroporous structures inside γ-Al2O3.
• Dodecane soft template dispersed into smaller emulsions under ultrasonic.
• Spherical γ-Al2O3 exhibits both mesoporous and macroporous structures.
• Spherical γ-Al2O3 display high hydrothermal stability.
The pore structure of spherical alumina supports is closely related to the dispersion of catalytically active components and the diffusion of reactants. Maintaining excellent pore structure under strict reaction conditions is of utmost importance. In this work, spherical γ-Al2O3 support with a bimodal pore structure, composed of macropores and mesopores, was successfully synthesized using dodecane as the pore-forming agent through the oil–ammonia column-shaping method. The morphology and internal pore structure of the alumina were found to be influenced by the amount of surfactant added and ultrasound treatment conditions. Notably, when concentration of surfactant was 4‰ and ultrasound voltage of 20 V was applied, the resulting γ-Al2O3-4‰-20 displayed a highly concentrated distribution of macropores with an average pore size of 100 nm, resulting in an impressive porosity of 69.21%. In contrast, the untreated sample of γ-Al2O3-0-0 only exhibited a mesoporous distribution with a porosity of 54.03%. Moreover, after being subjected to a hydrothermal treatment in a high temperature (600 °C) and high humidity (water vapor) environment for 120 h, the γ-Al2O3-4‰-20 sample maintained a high BET specific surface area of 170.9 m2 g−1 and mercury intrusion porosimetry specific surface area of 263.3 m2 g−1.