- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
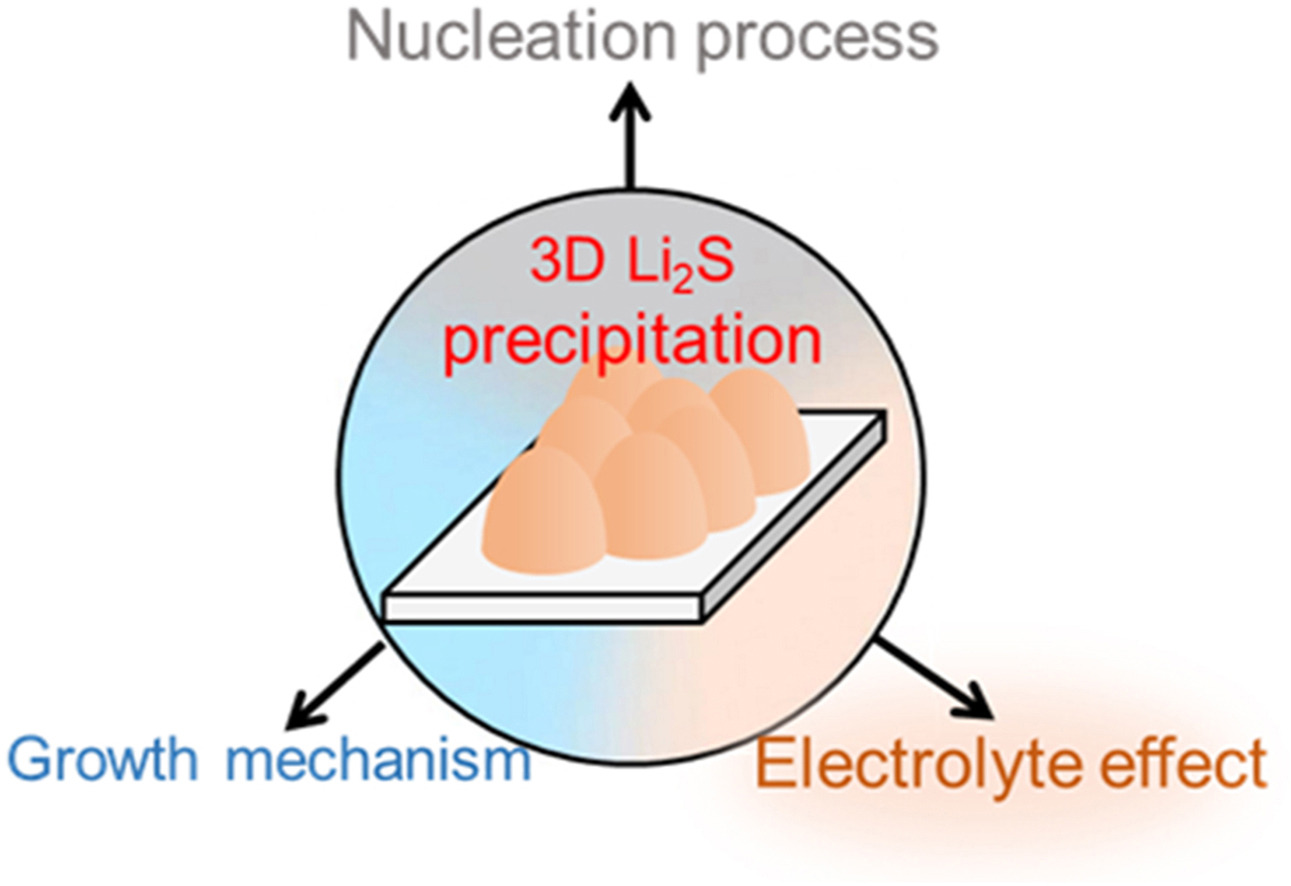
• Mechanism of Li2S deposition in macroscopic and microscopic scale is summarized.
• Polysulfide solubility and solvation in regulating the deposition models are underscored.
• Process, model, and characterization of Li2S deposition are discussed.
• General directions of developing long-life and high-rate Li–S batteries are proposed.
Lithium–sulfur (Li–S) batteries stand out the energy storage systems because of extremely high energy density (2600 W h Kg−1) and low-cost sulfur cathode. Unfortunately, the sluggish deposition from liquid Li polysulfides (LiPSs) to solid Li2S leads to mild power density and short cycle life. Understanding and regulating Li2S2/Li2S deposition are conceived to be importance to deliver second-plateau capacity in acceptable kinetics, which has the potential to operation Li–S batteries under electrolyte-lean conditions. This perspective aims to summarize the proposed models that can describe the nucleation and propagation of three-dimensional Li2S2/Li2S, as well as affords critical views how electrolyte dictates LiPS conversion from liquid to solid. It hopes to encourage necessary scaffold strategies and electrolyte formulations to further improve energy density and life span of Li–S batteries.