- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
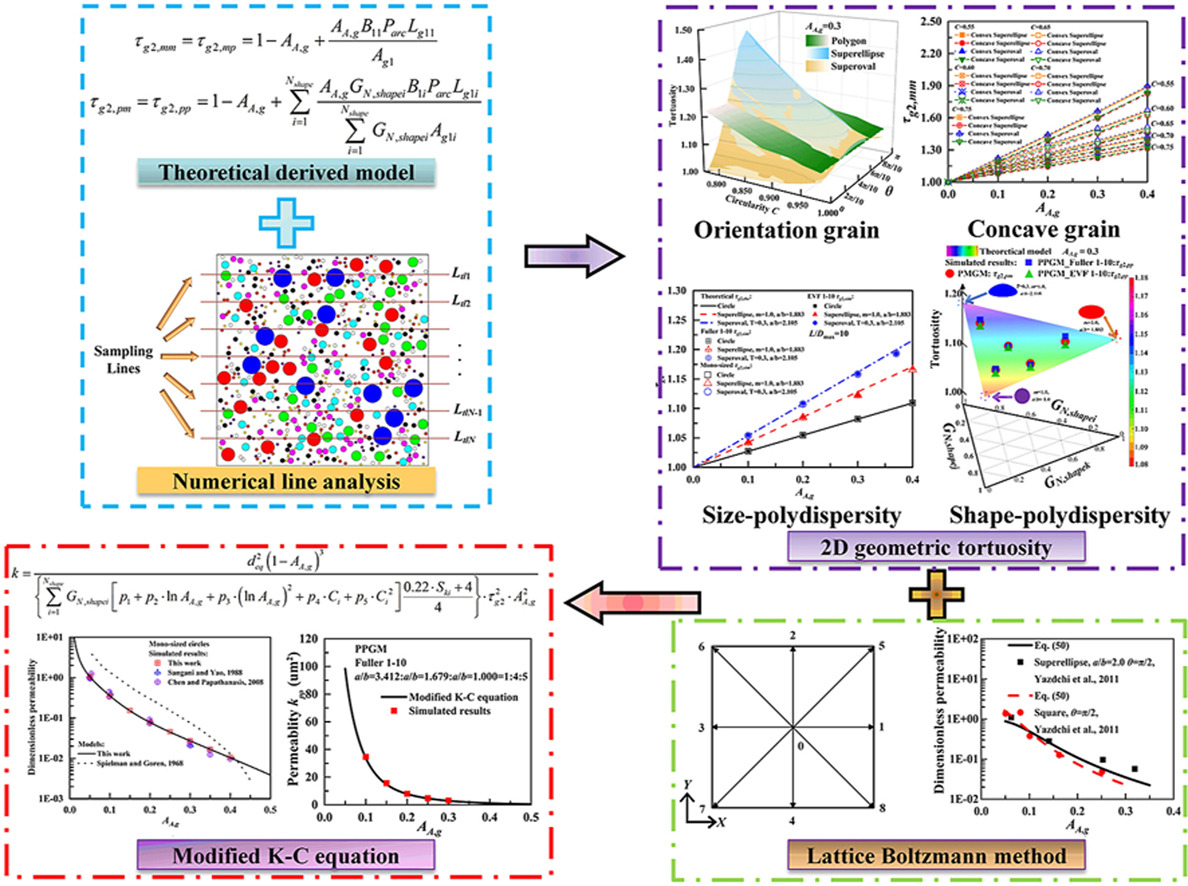
• 2D geometric tortuosities of various non-circular granular medias were derived.
• Effects of shape, orientation, and concavity on tortuosity were quantified.
• Shape and size polydispersities were included in modified Kozeny-Carman model.
• Grain composition's impact on 2D permeability was characterized.
The microstructure of granular media, including grain's shape- and size-polydispersities, orientation, and area fraction can potentially affect its permeability. However, few studies consider the coupling effects of these features. This work employs geometrical probability and stereology to establish quantitative relationships between the above microstructural features and the geometric tortuosity of the two-dimensional granular media containing superellipse, superoval, and polygon grains. Then the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) is used to determine the permeabilities of these granular media. By combining the tortuosity model and the LBM-derived permeabilities, modified K–C equations are formulated to predict the permeability and the shape factor, considering the grain's shape- and size-polydispersities, orientation, and area fraction. The reliability of these methods can be verified by comparing them with both our simulations and available experimental, theoretical, and numerical data reported in the literature. The findings implicate that the tortuosity and permeability of the granular media are strongly correlated with the grain's shape, orientation, and area fraction but unaffected by the size polydispersity and spatial arrangement of grains. Only circularity is not enough to derive a unified formula for considering the impact of grain shape on tortuosity and permeability, other shape parameters need to be explored in the future.