- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
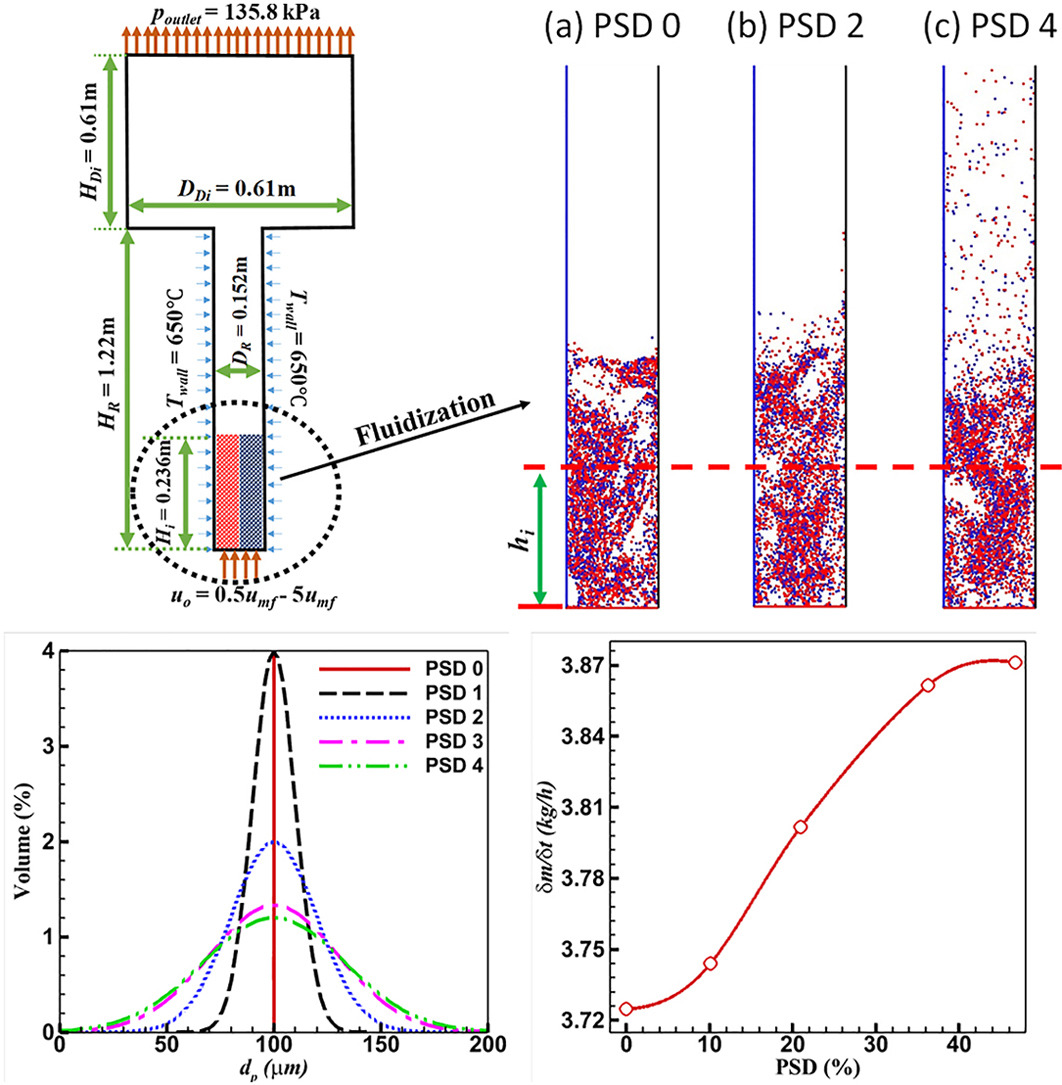
• A comprehensive CFD-DEM model for fluidized bed silane pyrolysis is developed.
• The effect of Si particle polydispersity on fluidisation and deposition rate is investigated.
• Broad particle size distributions (PSDs) expand beds more than narrow PSDs, which fluidize more smoothly.
• Broad PSDs lower net Si fines production and increase Si deposition by 4.3%.
A CFD-DEM model is developed for chemical vapour deposition of silane in a fluidized bed reactor to investigate the effect of polydispersity on local phase dynamics, mass and heat transport, as well as the rate of Si deposition. Both gas-phase fines formation and heterogeneous deposition on the seed particle, as well as the scavenging effect for Si particle growth, are incorporated. The method is first validated against the experimentally measured Si deposition rate, percentage of fine production and minimum fluidisation velocity. Subsequently, the properties, primarily particle intermixing, fluidisation behaviour and bubble dynamics along with the deposition process, are analyzed for several polydisperse beds under various operating conditions. The effect of polydispersity of the bed on a fraction of the bubble size, dense phase expansion and interchange coefficient between various phases is thoroughly investigated to establish a correlation with reactor performance. The results show that broad-Gaussian particle size distribution (PSD) exhibits excellent improvement in fluidisation behaviour, resulting in a high deposition rate, and minimum formation of Si fines.