- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
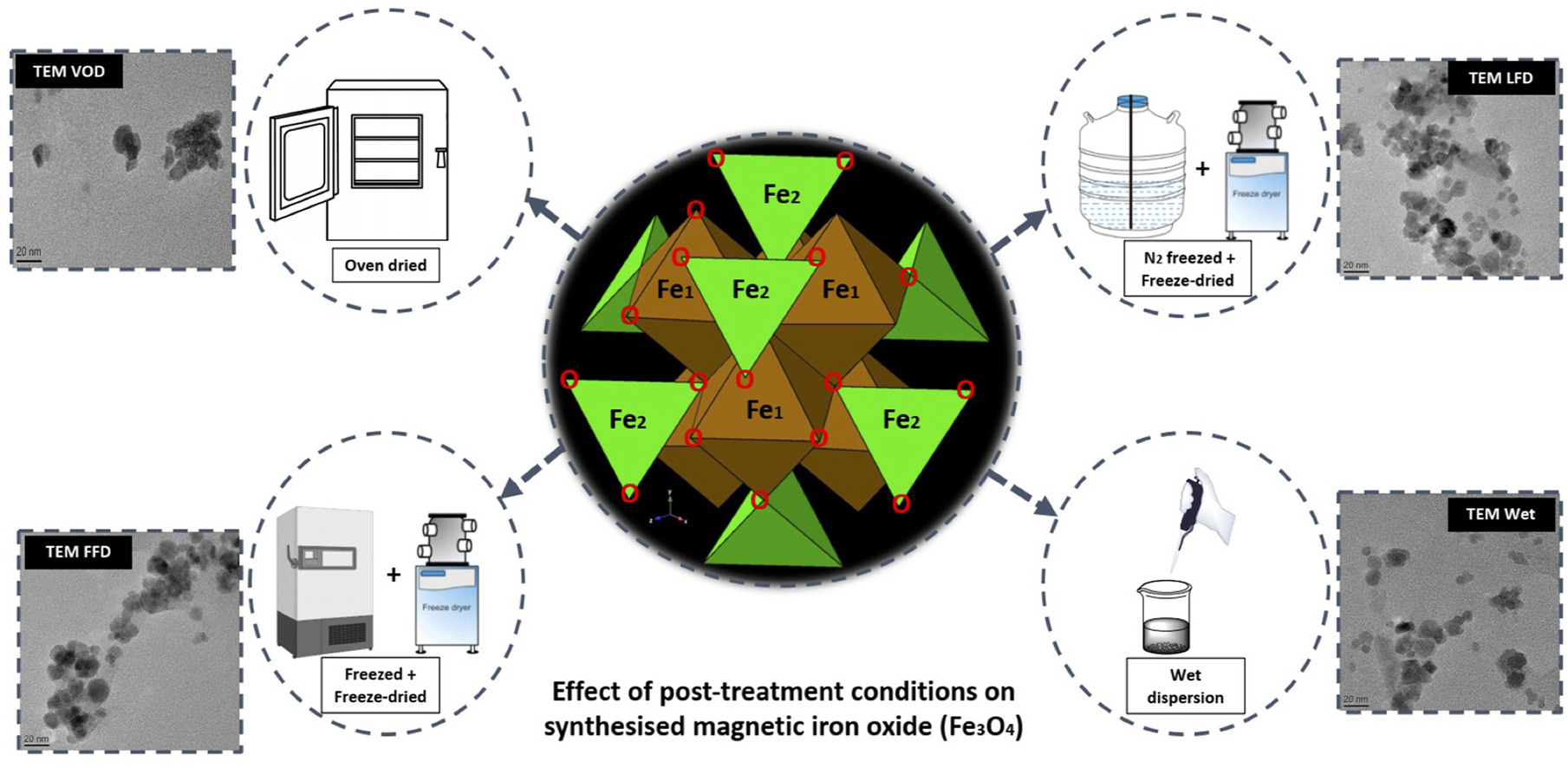
• Influence of synthesis and post-treatment methods on stability, dispersity, and magnetism of Fe3O4 NPs are investigated.
• Untreated Fe3O4 NPs (WET) has the best stability and dispersity at different temperatures.
• Liquid Nitrogen Freeze-dried (LFD) samples have the best stability and magnetism amongst post-treated samples.
Poor stability and dispersibility, as well as aggregation are considered as major challenges in clinical application of iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs). Several studies have shown that the synthesis parameters and post-synthesis treatments e.g., drying methods, have the capability to improve the particles' characteristics. Herein, we investigate the combined effect of synthesis and post-treatment parameters on the particle size, stability and magnetism of IONPs. Magnetite (Fe3O4) NPs were prepared via co-precipitation and post-treated using different methods, i.e. (i) freeze dried at –53 °C, 0.133 mbar for 48 h (liquid nitrogen frozen (LFD) and freezer frozen (FFD)), (ii) vacuum oven dried (VOD) at 60 °C for 24 h, and (iii) kept wet colloidal (WET), dispersed in deionized water. The Fe3O4 NPs’ chemical functional groups, size, shape, crystallinity, stability, aggregation, porosity, and magnetic properties were further analysed using different characterisation techniques. Analytical results showed that, while the WET sample had the best stability and significantly less aggregation at different temperatures, amongst post-treated Fe3O4 NPs, LFD sample exhibited the best stability (up to 37 °C), dispersion and smallest polydispersity index. Furthermore, all dried NPs had superparamagnetic characteristics, while, LFD Fe3O4 NPs had better magnetic properties and stability than other drying methods.