- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
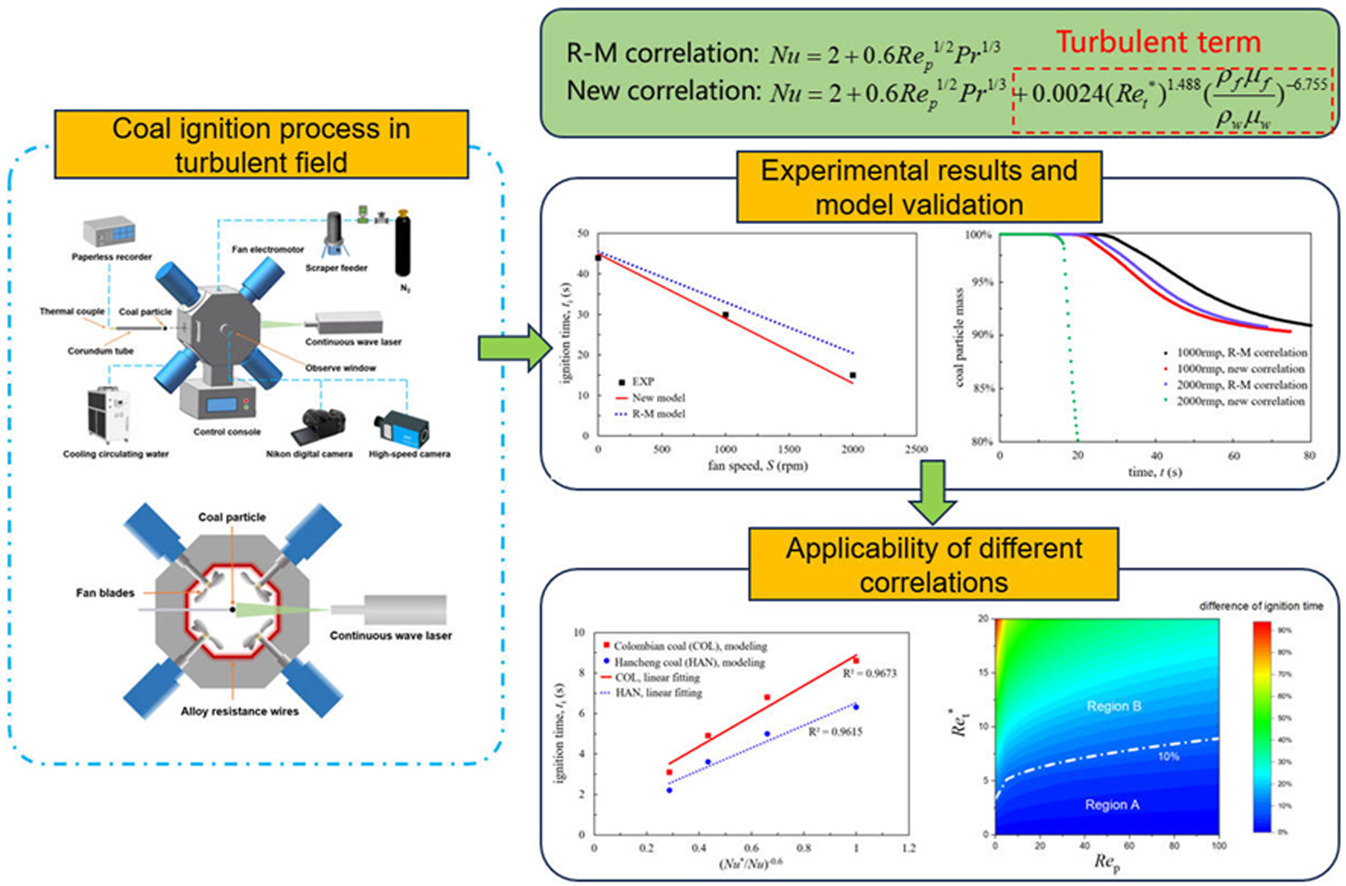
• Effect of fluctuation on the ignition of millimeter particles is studied.
• Ranz-Marshall correlation and new proposed correlation of Nusselt number are compared.
• Effects of temperature, diameter, particle distance and coal type are investigated.
Understanding the influencing mechanism of turbulent fluctuation on the ignition characteristics of millimeter coal particles is essential. In this work, to study the effect of turbulent fluctuation on ignition time, millimeter coal particles are subjected to a specific flow field, generated in a furnace with symmetric fans. A one-dimensional model with the new proposed correlation and the Ranz-Marshall (R-M) correlation for Nu (Nusselt number) is established to simulate the coal ignition process. In addition, the effects of fan speed, temperature, particle diameter, particle distance and coal type on the ignition time are investigated. It is found that an increase in fan speed from 0 to 3000 rpm leads to a particle Reynolds number Rep increase from 0 to 22.5, and a turbulent particle Reynolds number Ret∗ increase from 0 to 71.5. With a consideration of the fluctuation effect, the new correlation of Nu gives a better prediction of ignition time compared to the R-M correlation. Moreover, the ignition time is revealed to decrease with an increasing fan speed and an elevating temperature. While the ignition time shows merely an initial boost with enlarging particle distance, it exhibits a linearity with the term of particle diameter dp1.3–1.7 and Reynolds numbers (Nu∗/Nu)–0.6 (Nu∗ is turbulent Nusselt number). Based on this relationship, the difference of predicted ignition time is calculated at different Rep and Ret∗. It is shown that at low Rep or high Ret∗ values, the new correlation should substitute for the R-M correlation.