- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
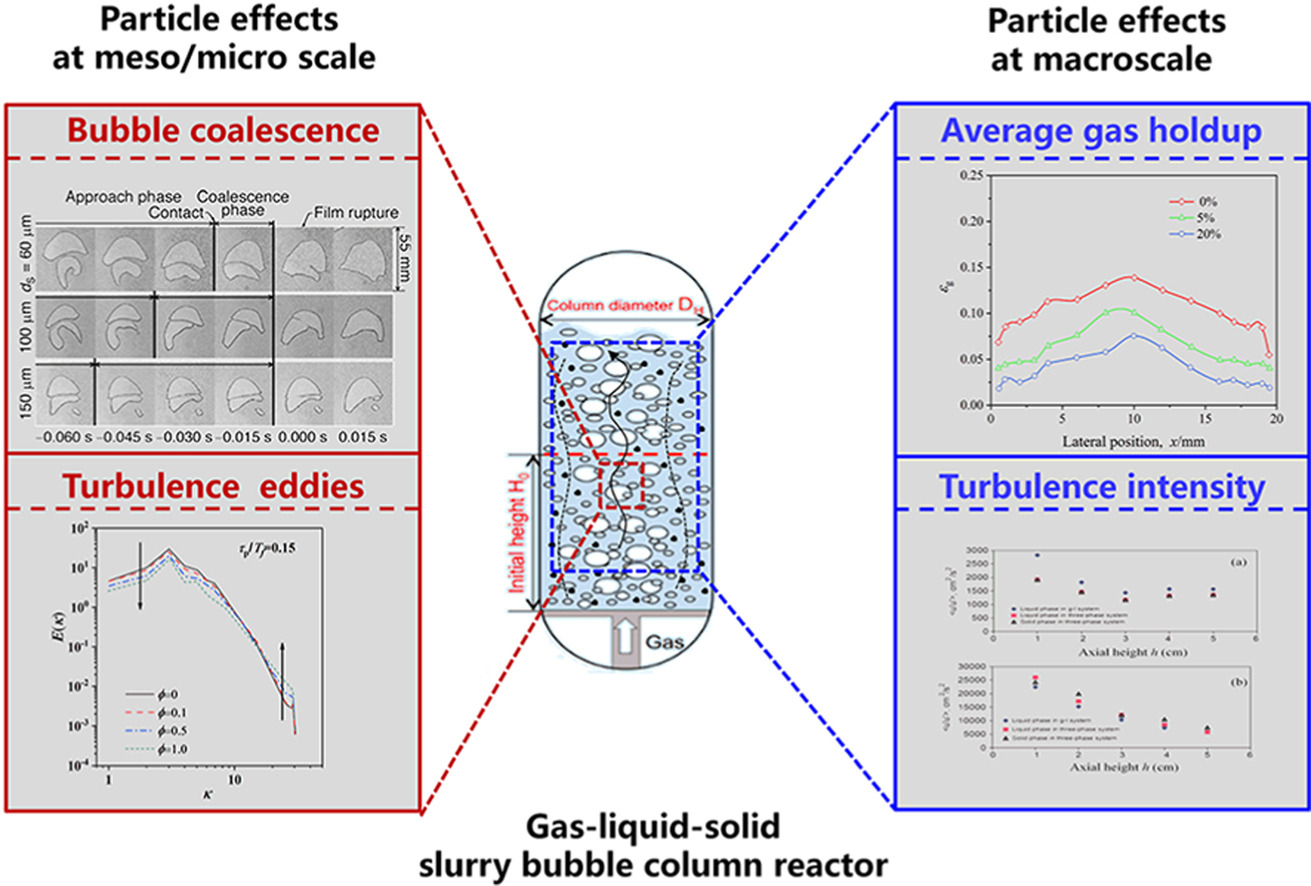
• Mechanisms of particle effects on hydrodynamics at multi scales are reviewed.
• Dimensionless groups for charactering particle effects are raised and compared.
• Increased slurry viscosity is the dominant effect of the tiny porous particle only.
• Entrained particles have a pivoting effect on the turbulence energy spectrum.
Particles can appear as catalyst, reactant or product in various gas-liquid-solid three-phase production processes. Slurry bubble column reactors (SBCRs), as a kind of three-phase reactors, are preferred for phase contacting and mixing. However, literature studies concerning the effects of particles on the hydrodynamics of SBCRs are manifold and inconsistent in conclusions. Essentially, the multiscale interactions between particles, turbulent eddies and bubbles determine the reactor performance. This review focuses on revealing the particle effects in SBCRs from the perspective of multiscale mechanisms. Macroscopic hydrodynamic changes due to particle effects in literature are summarized. Dimensionless parameters, including the Stokes number, the solid-to-liquid density ratio, the ratio of particle and liquid characteristic lengths, the contact angle and the particle volume fraction are adopted to evaluate the characteristics of gas-liquid-solid flows. The relationships between particle influencing mechanisms and these parameters are analyzed and determined. Inconsistent experimental results are explained by different ranges of these dimensionless parameters. Moreover, particle effects at the mesoscale and microscale, such as the influence on the bubble dynamics and the pivoting effect on the turbulence energy spectrum, are elaborated. Finally, progress in modeling the SBCRs with consideration of particles effects using the Euler method are introduced. This review aims to improve the overall understanding of the complex hydrodynamics in the SBCRs.