- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
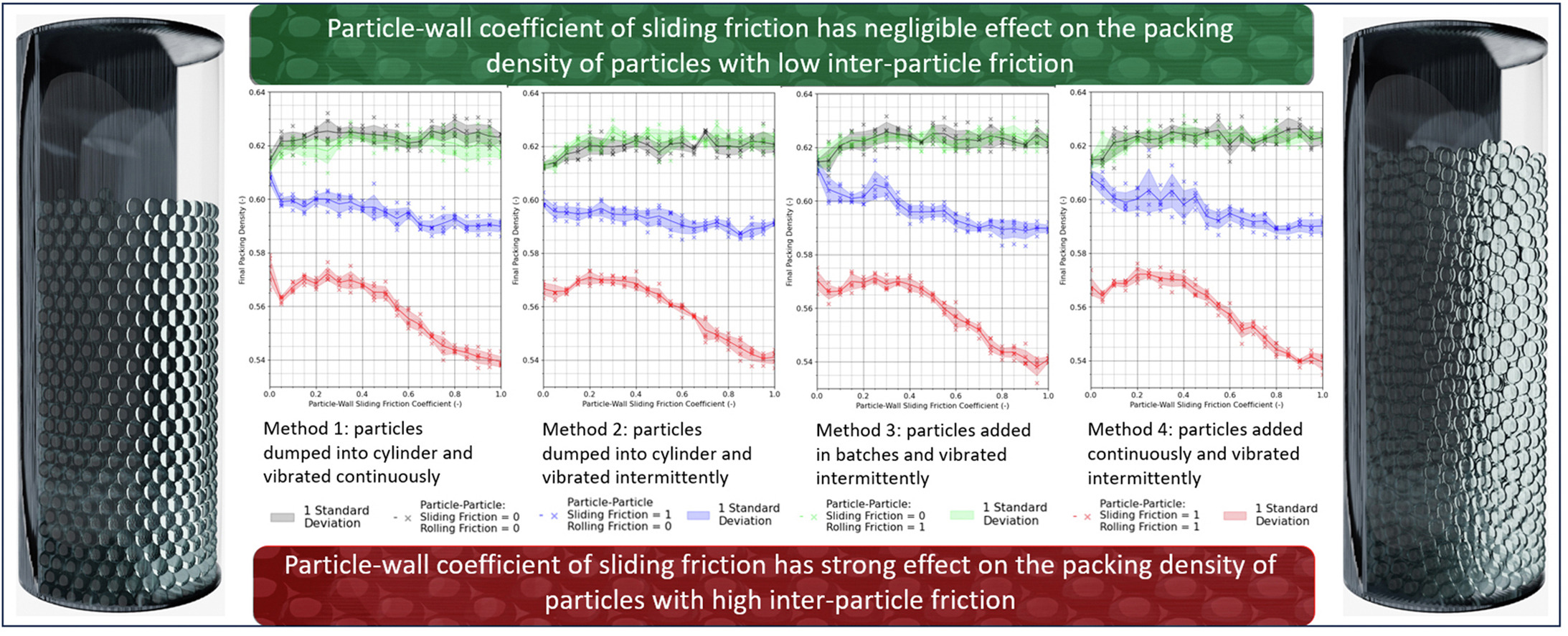
• Investigated wall effects on packing of 3D-vibrated particles.
• Packing density unaffected by wall parameters for low-friction particles.
• Packing reduced by particle-wall sliding friction for high-friction particles.
• Packing unaffected by particle-wall restitution for high-friction particles.
• Packing unaffected by particle-wall rolling friction for high-friction particles.
Achieving densely packed particles is desirable within the industries of ceramics, pharmaceuticals, defence and additive manufacturing. In this work, we use the discrete element method (DEM) to determine the effect of wall parameters on the final packing density of mono-disperse spheres subject to 4 varying three-dimensional vibration and fill conditions. We focus specifically on the impact of the container wall parameters on the particles' final packing density. Following on from the validation of the DEM simulation the particle-wall coefficient of restitution, the particle-wall coefficient of rolling friction and the particle-wall coefficient of sliding friction were varied individually and the effect on the final packing density analysed. For relatively low particle-particle friction glass beads, the effect of these wall properties had no discernible effect on the final packing density achieved. Following on from these findings the particle-wall properties were varied at the extreme values of particle-particle coefficient of rolling friction and particle-particle coefficient of sliding friction. For a particle-particle coefficient of sliding friction = 1, increases in particle-wall coefficient of restitution resulted in a minor increase in the final packing density of particles though this was not statistically significant. For a particle-particle coefficient of sliding friction = 1, increases in particle-wall coefficient of rolling friction resulted in a minor decrease in the final packing density of the particles though again not to a degree where the trend can, with complete certainty, be distinguished from the random error across the repeats. Finally, when the particle-particle coefficient of sliding friction = 1, increases in particle-wall coefficient of sliding friction resulted in a significant decrease in the final packing density of particles. This decrease was attributed to the propagation of force chains throughout the packing. The significant decrease in final packing density with particle-wall coefficient of sliding friction highlights the need to choose appropriate vessel materials to optimise packing of particles with a high particle-particle coefficient sliding friction. Conversely, for particles with minimal particle-particle friction, the particle-wall friction coefficient has no effect on the final packing density of particles - a potentially valuable finding for certain industrial applications. All simulations were run using the open-source DEM package LIGGGHTS on the University of Birmingham's high-performance computer: BlueBEAR. All the code files used within this paper can be found on Github: https://github.com/Jack-Grogan/DEM-Vibropacking-Wall-Effects.