- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
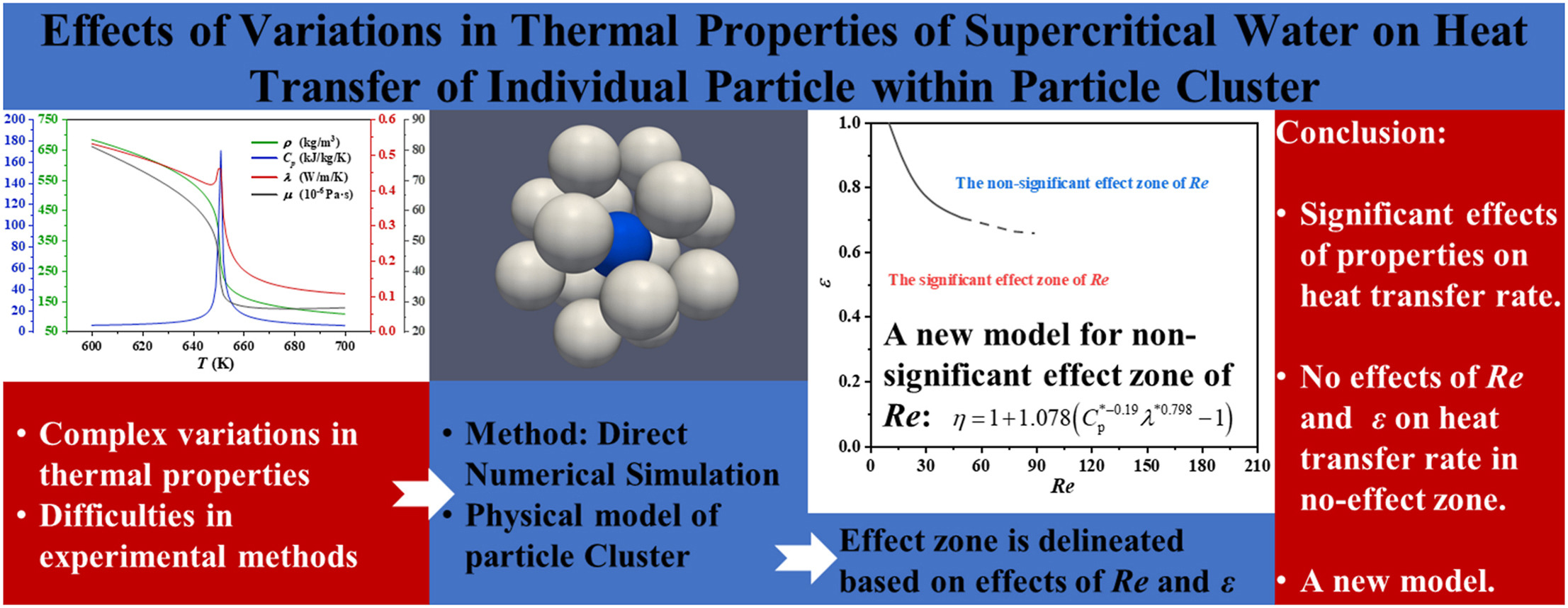
• Control mechanism of spatial factors and property factors on Nusselt number.
• Effect mechanism of spatial factors and property factors on heat transfer rate.
• Preliminary division of influence zones.
• Model establishment for heat transfer rate exponent.
The complex physical properties of supercritical water (SCW) make the heat transfer characteristics of particles within a particle cluster complicated. The heat transfer characteristics of single particle within a particle cluster in SCW, influenced by surrounding particles, have not been effectively explored. The numerical simulations were conducted to investigate the heat transfer characteristics of particle clusters in SCW under different conditions. The results were compared and analyzed with those from constant property flow. It was found that Reynolds number (Re) and the void fraction of particle cluster have no special effects on the variation trends of Nusselt number (Nu) for the focused particle. However, the particle temperature had a significant effect on the variation trends of Nu. The effect of Re on the heat transfer rate exponent (η) of the focused particle can be divided into two zones: a significant effect zone and a non-significant effect zone. The effect of void fraction on η in the non-significant effect zone was minimal. Within the non-significant effect zone, η decreased with the increasing particle temperature. In the significant effect zone, the variation trends of η became more complex. The fundamental reason for this series of phenomena is the changes in distribution of physical properties. A model for η was developed for the non-significant effect zone. This model can filter out the effects of Re and certain particle cluster spatial configurations, and it demonstrates good predictive performance.