- Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Changing the atmosphere has a big impact on fluidized bed combustion of Al particles.
• The order of promotion effects is CO2>H2O > O2.
• The surface crystalline structures of Al were discussed.
• The scanning electron microscope of the combustion products was investigated.
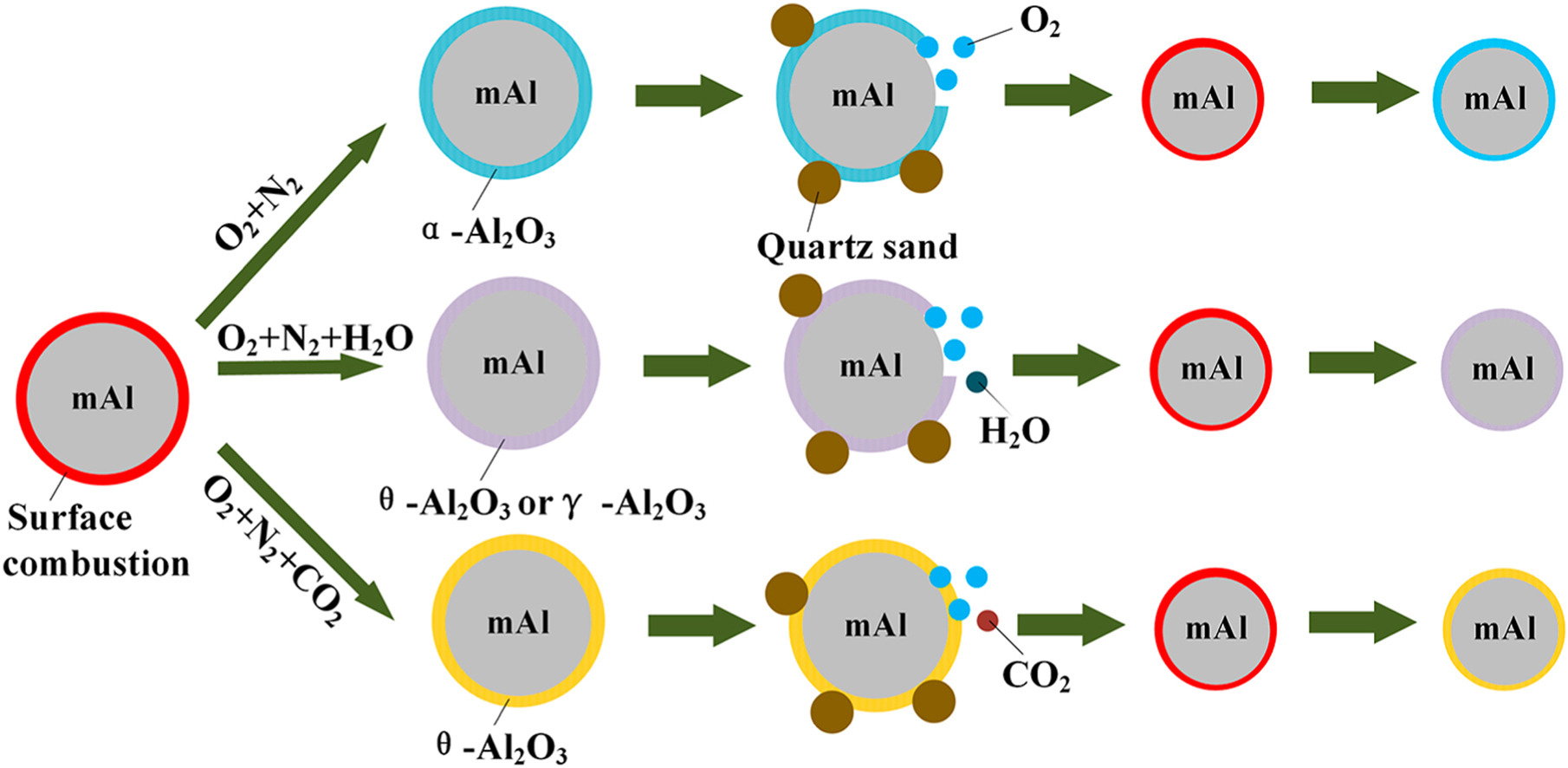
Aluminum is an attractive alternative fuel, but it burns very inefficiently due to the formation of a dense Al2O3 layer which prevents O2 from diffusion to the surface of Al particles. In previous experiments, the combustion of millimeter-sized Al (mAl) particles in the fluidized bed has achieved a substantial increase in the combustion efficiency, but further improvements are still needed. In this study, the effects of reaction atmosphere on the fluidized combustion of mAl particles were investigated. The experiments with different O2/H2O/CO2 concentrations were conducted. The experimental results indicate that the combustion efficiency of mAl particles in fluidized bed increases as the mole fraction of O2, H2O or CO2 increases, and the highest combustion efficiency can reach 38.7%. After the analysis of the oxide film on the surface of aluminum particles, it was found that it is easier to generate the unstable θ-Al2O3 under CO2 atmosphere, and it is easier to generate the unstable γ-Al2O3 and θ-Al2O3 under H2O atmosphere. The unstable Al2O3 film is more likely to be abraded in the fluidized bed, which leads to the effective improvement of the combustion efficiency.