• Excellent electrochemical performance of the fluorine-doped carbon-coated LMFP composite cathode materials.
• LMFP cathode materials were prepared by a simple co-precipitation method.
• LMFP/C–F cathode materials showcasing exceptional multiplication rate performance and stability.
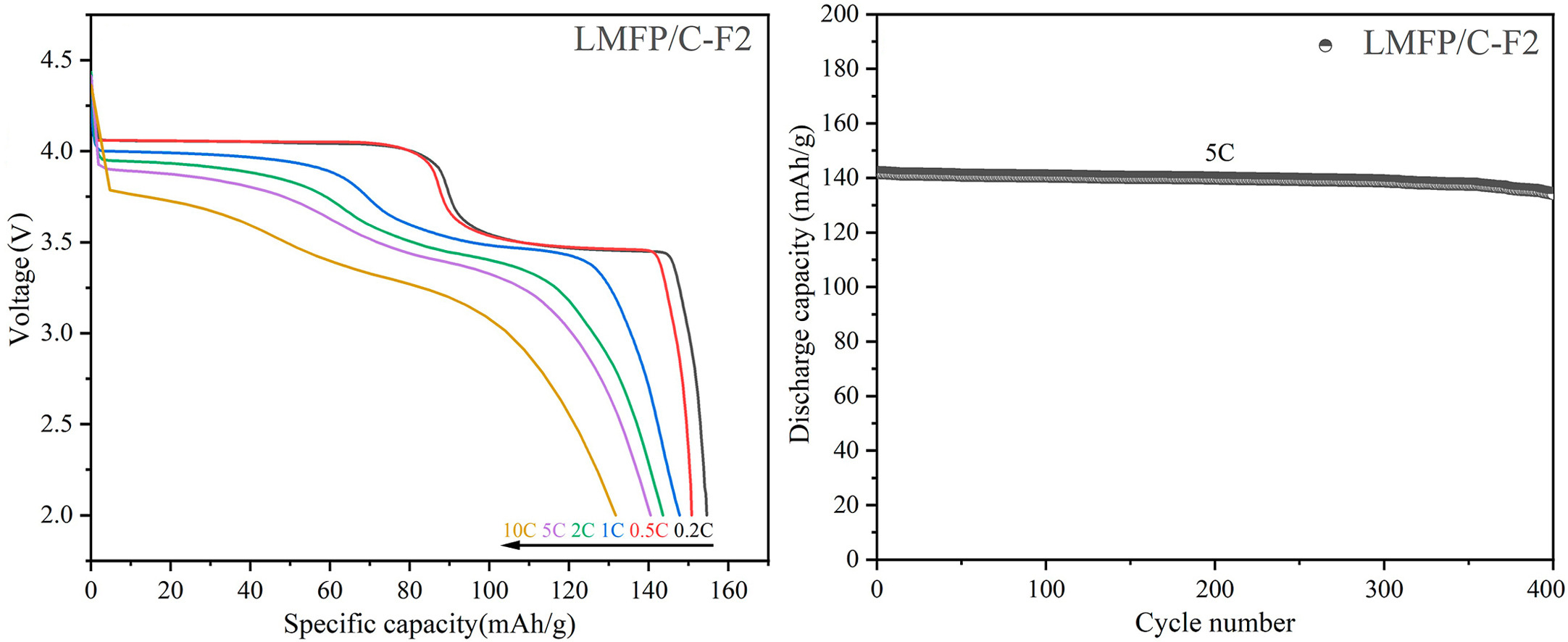
In this study, glucose and NH4F were utilized as sources of carbon and fluorine, respectively, for the synthesis of LiMn0.6Fe0.4PO4 (LMFP) nanoscales. These nanoscales were subsequently modified with varying levels of fluorine-doped carbon through co-precipitation and mechanical ball milling processes. The LMFP, incorporating carbon and varying levels of fluoride ions, exhibit higher specific discharge capacities at 0.2 Cand electrochemical characteristics compared to the original LMFP coated solely with carbon. The inclusion of fluorine-doped carbon in the composite material creates numerous pathways for expeditious electron transfer. Moreover, the partial formation of metal fluoride at the interface between the surface of LMFP and the layer of carbon coating doped with fluorine enhances the reduction in the charge-transfer resistance. The modified ferromanganese phosphate cathode material reveals an outstanding discharge capacity displaying a reversible discharge specific capacity value of 131.73 mA h g−1 at 10C and 154.6 mA h g−1 at 0.2C, due to its unique structure.