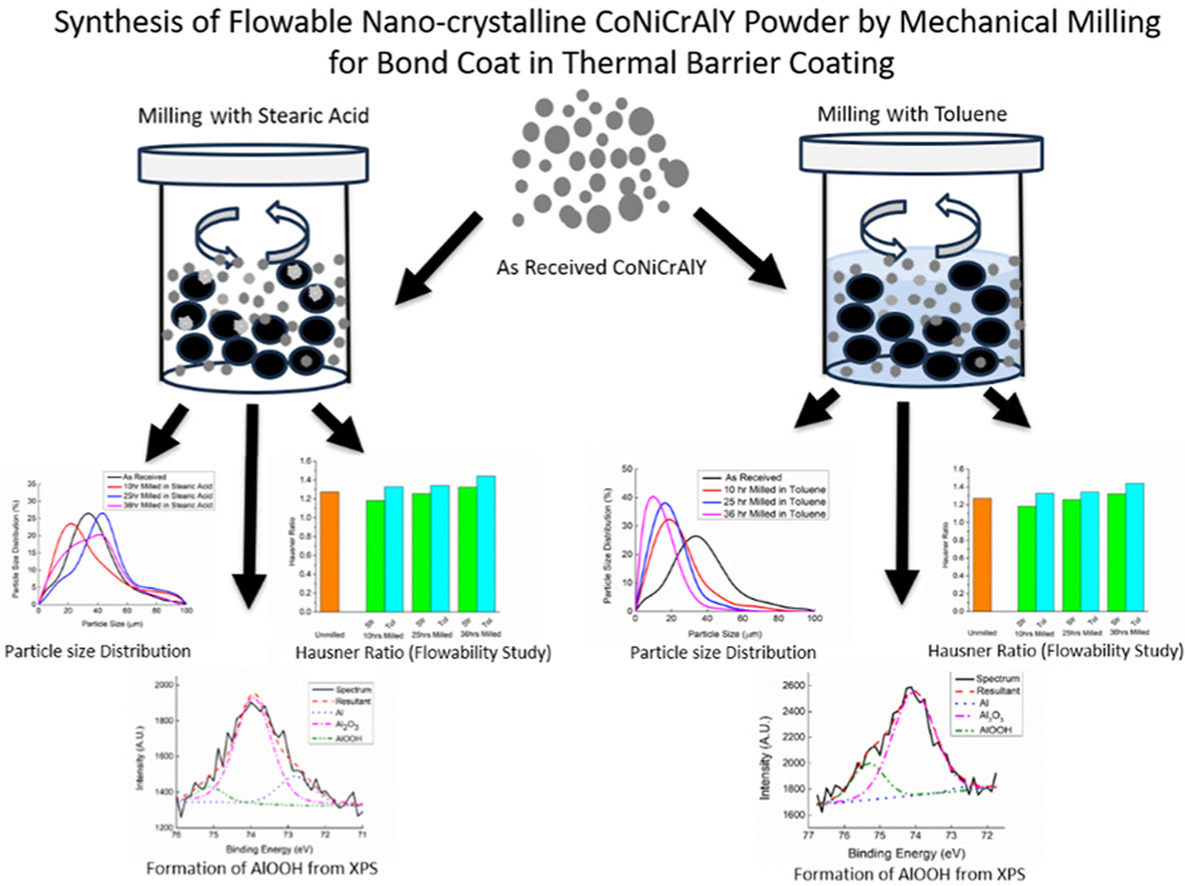
• Characteristics of mechanical milled CoNiCrAlY powder in toluene and stearic acid medium.
• Particle size and crystallite size are smaller in toluene medium as compared to stearic acid medium.
• Flowability is higher when stearic acid is used as medium than toluene medium.
• Mechanism of milling in both the medium has been established.
The present study concerns understanding the effect of process parameters on the characteristics and flowability of nanocrystalline CoNiCrAlY powder synthesized by mechanical milling. Mechanical milling has been conducted in a planetary ball mill with tungsten carbide (WC) ball, with ball to powder ratio of 10:1 at 300 rpm speed, using 1% stearic acid and toluene as process control agent (PCA) with time varying from 10 h to 36 h. The synthesized nanocrystalline powder were characterized by Scanning Electron Microscopy, X-ray Diffraction technique, X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, and Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Subsequently, flowability in terms of Hausner ratio was assessed by Tap Density Tester. Average particle size of the powder was found to decrease from 33 μm to 22 μm after 10 h of milling and further increases to 43 μm and 38 μm after 25 and 36 h of milling, respectively, in stearic acid medium. However, in toluene medium particle size continuously decreases from 33 μm to 9.7 μm with increasing milling time. The particle morphology changes from spherical to platelet shape at low milling hours in both of the media. After 25 h of milling, the shape of the particles is nearly spherical for stearic acid and irregular for toluene used as a PCA. Crystallize size was found to decrease with increasing milling time from 147 nm to 7.7 nm and to 6.4 nm in stearic acid and toluene media, respectively. There was presence of γ, γʹ, β, hcp-Co, Al2O3 and AlOOH phases on the powder particles milled in both the medium. The measured Hausner ratio of the powders was found to vary from 1.18 to 1.32 in stearic acid medium, and was found to increase with increasing milling time. On the other hand, in toluene media flowability decreases (Hausner ratio increases from 1.33 to 1.44) with increasing milling time.