• Particle dynamics in varied nozzle structures and gas compositions explored.
• Non-convergence nozzles prolong fuel concentration, affecting divergence angles.
• Shorter throat lengths enhance early jet penetration and velocity dynamics.
• Hydrogen fluidization results in increased divergence angles and altered jet behavior.
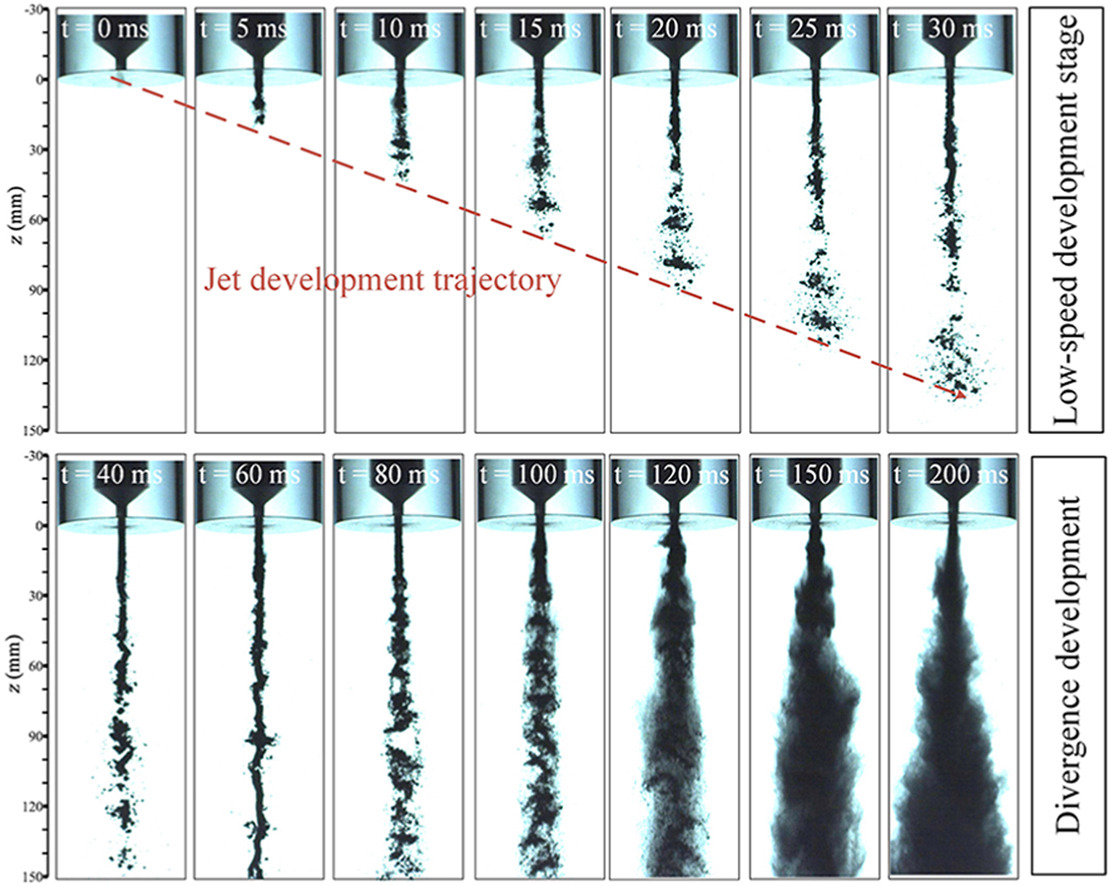
The interaction between nozzle design and fluidization gas composition significantly influences the dynamics within a powder fuel scramjet's combustion chamber. To investigate this relationship, an experimental study utilized high-speed shadow imaging technology to explore the macroscopic aspects of powder fuel injection. The investigation examined various convergence angles, nozzle throat lengths, and fluidized gas compositions. Key findings include: During jet development, powder fuel initially concentrates near the axis, with non-convergence angle nozzles exhibiting longer concentrated distribution periods than convergence angle conditions. Decreasing nozzle convergence angles lead to increased penetration distance, frontal velocity, and radial diffusion distance during the initial stages of jet development. Additionally, stable jet shapes show larger divergence angles as nozzle convergence angle decreases, with the largest divergence angle observed at α = 60°. In the initial 0–7 ms of jet development, the powder fuel jet demonstrates greater penetration distance and frontal velocity under certain conditions. Moreover, penetration distance and frontal velocity increase with throat length from 7 to 20 ms, accompanied by changes in divergence angles. Specifically, at a throat length (l) of 2 mm, the near-field divergence angle measures 46.50°, and the far-field divergence angle is 22.25°. Conversely, at Ι = 8 mm, the near-field divergence angle is 33.49°, and the far-field divergence angle is 23.21°. The fluidization gas composition minimally affects jet penetration distance and frontal velocity during the initial 0–3 ms. However, due to hydrogen's low density, hydrogen/powder fuel jets exhibit shorter distances and velocities compared to nitrogen/powder fuel jets. Hydrogen fluidization also results in larger divergence angles, particularly in the near field. These findings underscore the importance of nozzle design and fluidization gas composition in optimizing scramjet performance and efficiency.