• A novel rotary kiln with three different types of lifters is designed.
• Particle motion and heat transfer are studied by experiment and simulation.
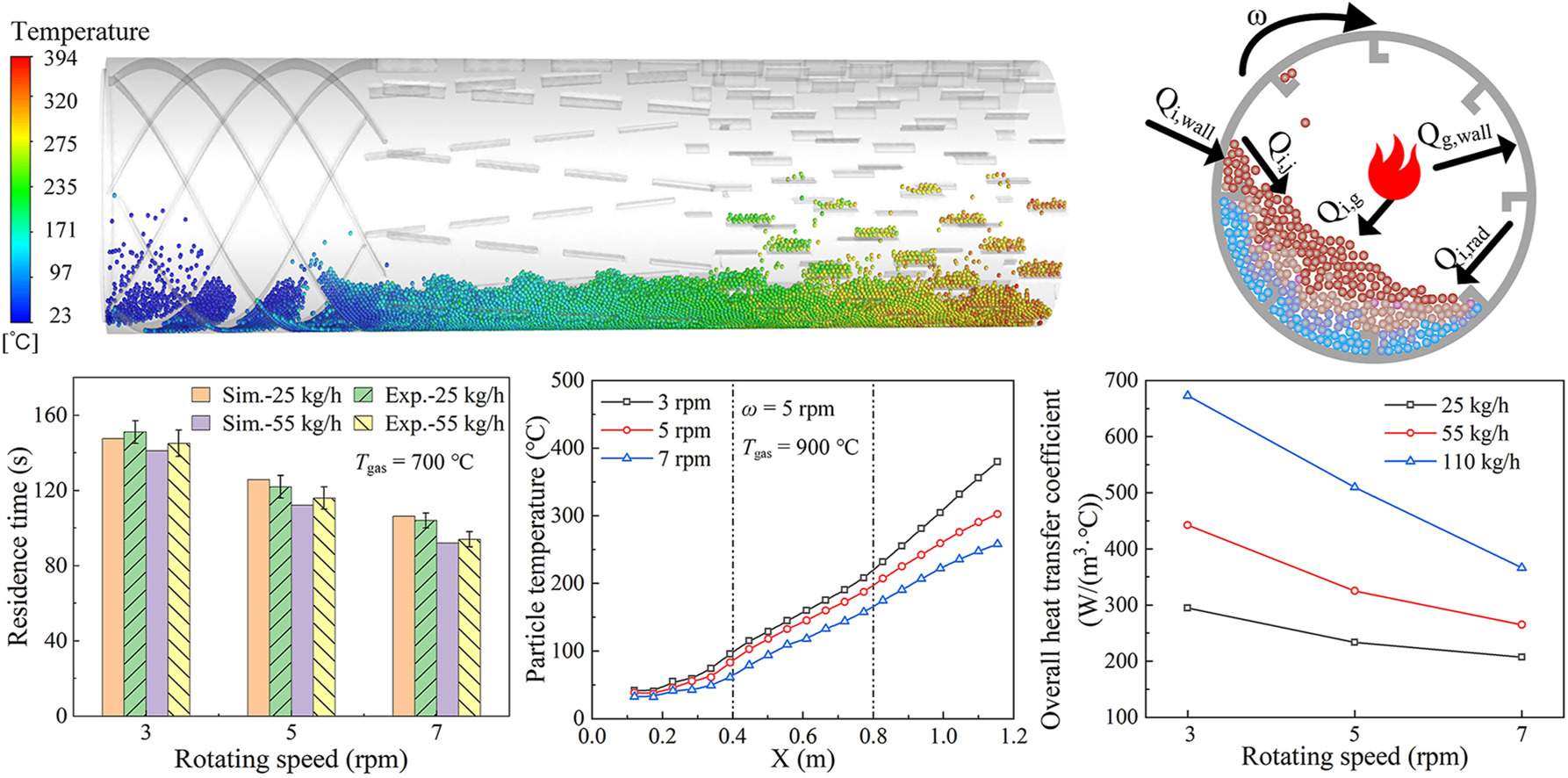
• Effect of operation parameters on the outlet particle temperature are analyzed.
• Overall volumetric heat transfer coefficient of kiln is from 200 to 700 W/(m3 °C).
Rotary kiln is widely used for thermal disposal of solid waste due to its effectiveness and high efficiency in recent years. To further improve the processing efficiency, a newly designed rotary kiln with three-section structure is proposed, and the behaviours of particle motion and heat transfer are investigated. Firstly, a lab-scale rotary kiln is manufactured, and experiments are carried out. Verified by experimental data, a CFD-DEM numerical model is developed to analyze the particle motion and heat transfer characteristics with the effects of inlet flue gas temperature, feeding rate and rotating speed. The results show that the outlet temperature increases linearly with the flue gas temperature, while it is negatively correlated with the feeding rate and rotating speed. In addition, the volumetric heat transfer coefficient in this complex rotary kiln is analyzed, the overall heat transfer coefficient is between 200 and 700 W/(m3 K).