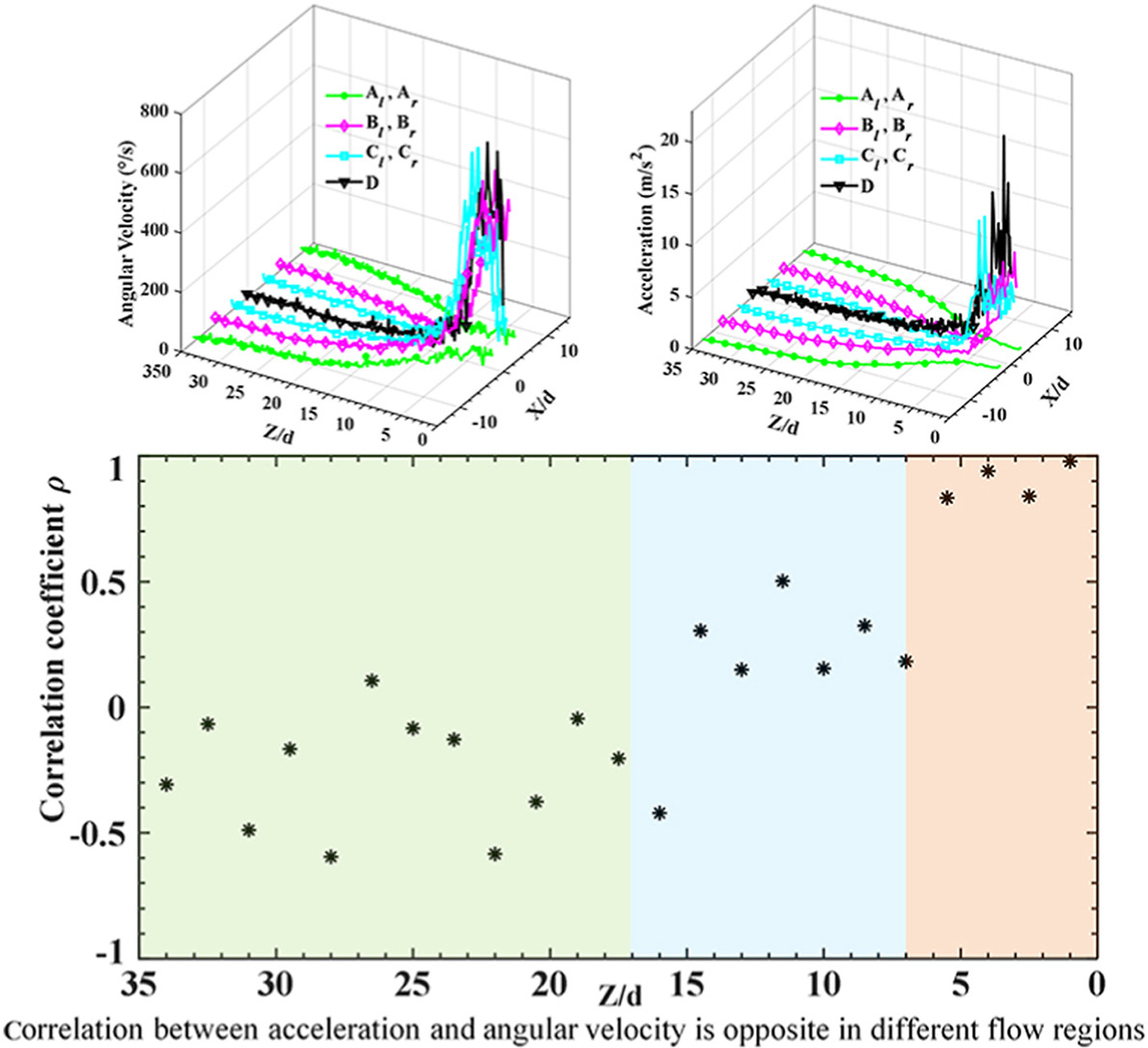
• The angular velocity distribution satisfies with log-normal function.
• Acceleration of particles is the largest in the center of silos.
• Correlation between acceleration and angular velocity is opposite in various regions.
Accurate measurement of the three-dimensional (3D) movement of discrete particles is crucial for comprehending complex granular rheology in silos. In this paper, the acceleration and angular velocity of particles in 3D silos are measured by using a spherical detector based on inertial technology and magnetic positioning technology. The acceleration of particles is the largest in the center of silos, which suggest that the resistance generated by friction and extrusion is the smallest. Surprisingly, the angular velocity distribution follows lognormal function except for particles near the outlet. The correlation between acceleration and angular velocity is opposite in different flow regions. It reveals for the first time that the extent to which the resultant force on the particles affects their rotational motion is related to the flow pattern. These results have practical significance for regulating the granular flow pattern and optimizing the structural design of silos.