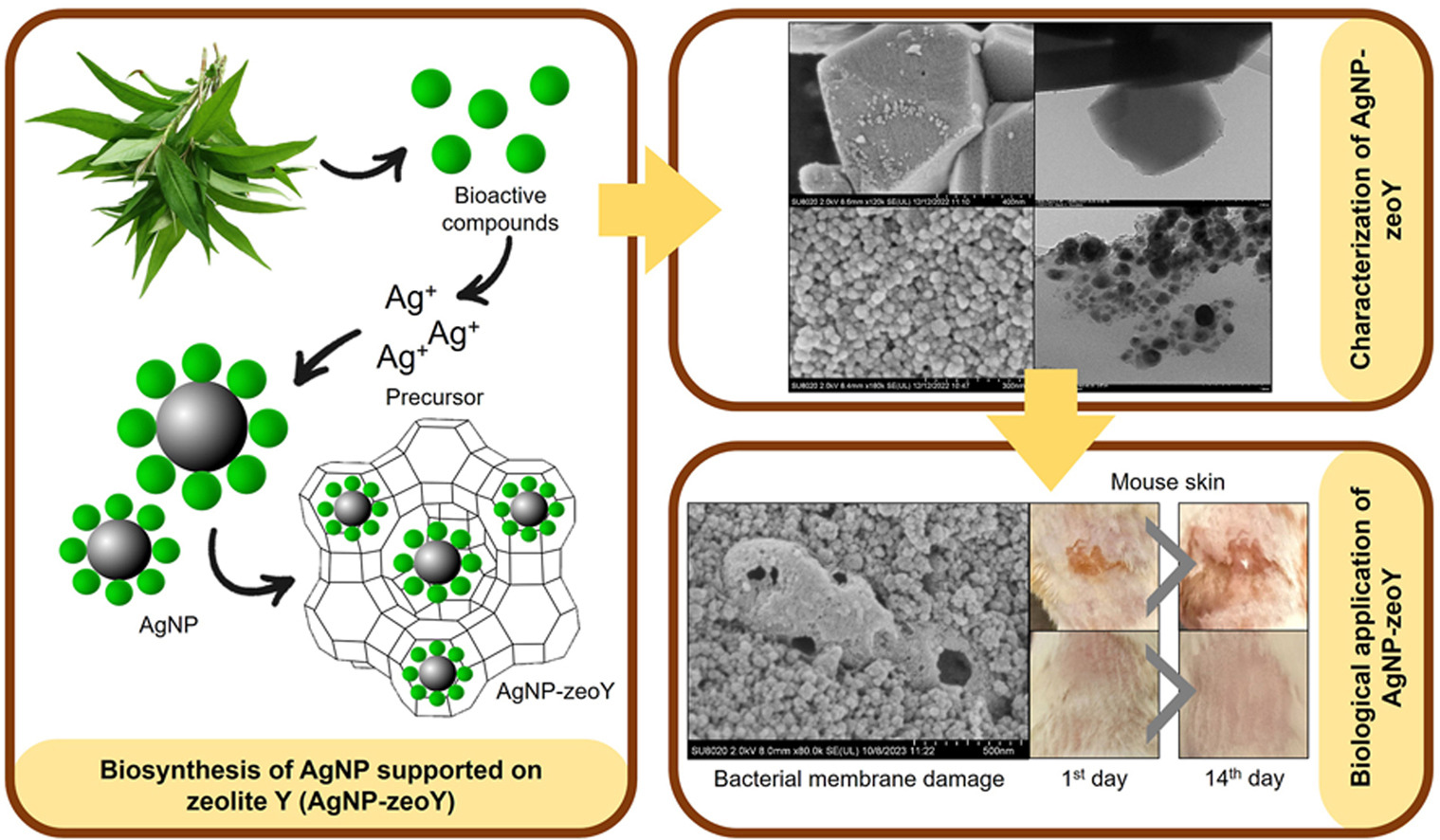
• Phytochemical compounds responsible for the reduction and stabilization of AgNP.
• Incorporation of AgNP into zeolite Y as a porous support system.
• Release of AgNP from zeolite Y induces bacterial membrane damage.
• Biocompatibility of AgNP released from zeolite Y towards fibroblast cells and mice skin.
Conventionally synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNP) imposed an alarming effect on the environment and caused toxicity to humans. However, the use of zeolite (zeoY) as a support system could increase its biocompatibility and reduce its toxicity. Hence, green synthesis of AgNP using Persicaria odorata leaves extract supported on zeolite Y has been prepared by an in situ synthesis technique. The phytochemical compounds in the optimized leaf extract concentration of 1% and volume of 0.9 mL reduced the silver ions to AgNP within the zeolite Y pores. Morphological observation revealed the incorporation of AgNP in the zeolite Y (average size: 18.51 nm). The release of AgNP exhibited antibacterial activity on C. acnes at a concentration lower than 1 g L−1 which is also dependent on the electrolyte. AgNP-zeoY promoted cell proliferation in vitro and it has a non-irritating effect when tested in the in vivo skin irritation model.