Sijia Wang a, Liang He a, Mengting Wang a, Xingtong Guo a, Xiangyun Qiu b, Shoudong Xu c, Petr Senin d, Ting Bian a, Tao Wei a *
• SCEs based on PVDF-HFP/PMMA matrix containing MOFs and LiTFSI were designed and synthesized.
• PMMA was firstly used in polymer-based solid-state electrolyte.
• Use of PMMA can obtain good interfacial stability and low interfacial impedance with lithium metal electrodes.
• Synergistic effect of MOFs and PMMA enables satisfying electrochemical performances.
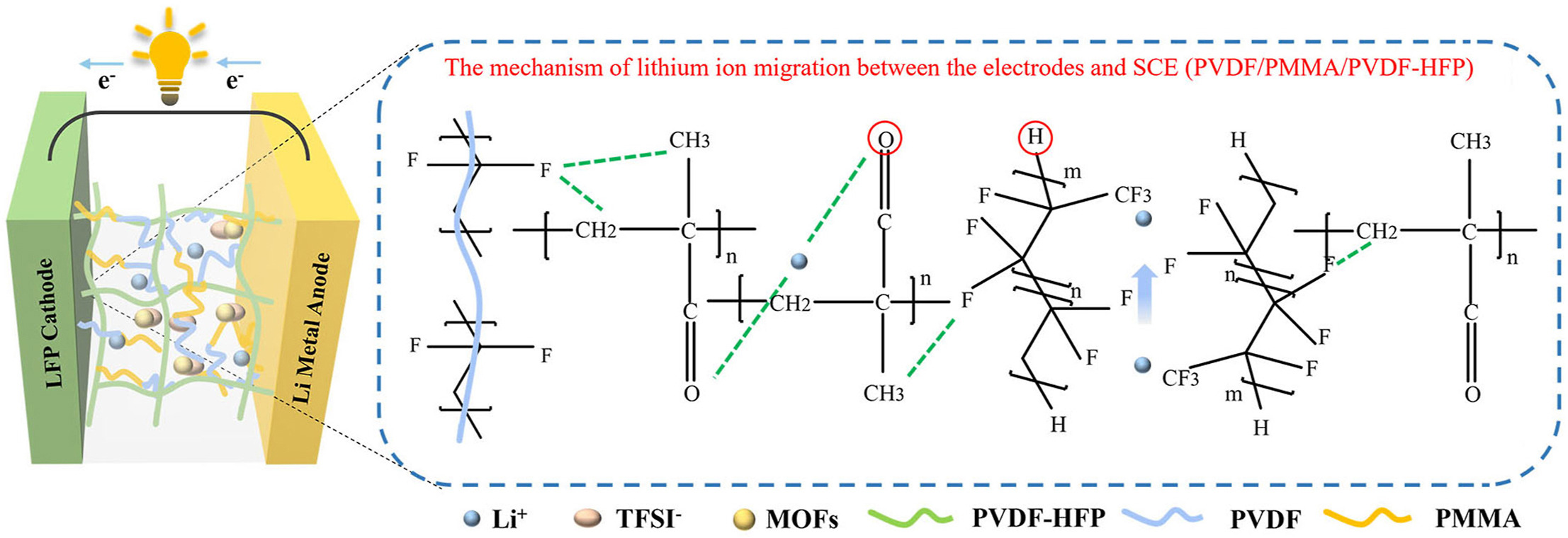
For all-solid-state lithium batteries (ASSLBs), polymer-blended solid composite electrolytes (SCEs) have drawn wide interest owing to their significance in improving the interfacial solid-solid contacts and inhibiting the growth of lithium dendrites. In this work, SCEs based on PVDF-HFP/PMMA matrix containing MOFs (NH2-MIL-53(Al)) and LiTFSI were designed and synthesized employing an easy solution casting method. The synthesized samples were examined by XRD, SEM, EDS, and electrochemical tests. It was found that MPP-2 SCE not only has excellent ionic conductivity at 60 °C of 5.54 × 10−4 S cm−1, but also exhibits superior interfacial compatibility in Li||Li symmetric batteries, which can constantly cycle for about 800 h at 0.1 mA cm−2 with no short-circuiting. The assembled Li|MPP-2|LiFePO4 cell exhibited a first discharge specific capacity of up to 157.1 mAh g−1 at 60 °C and 0.2 C. This work may help to further advance the progress of ASSLBs in the future.