-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 94
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
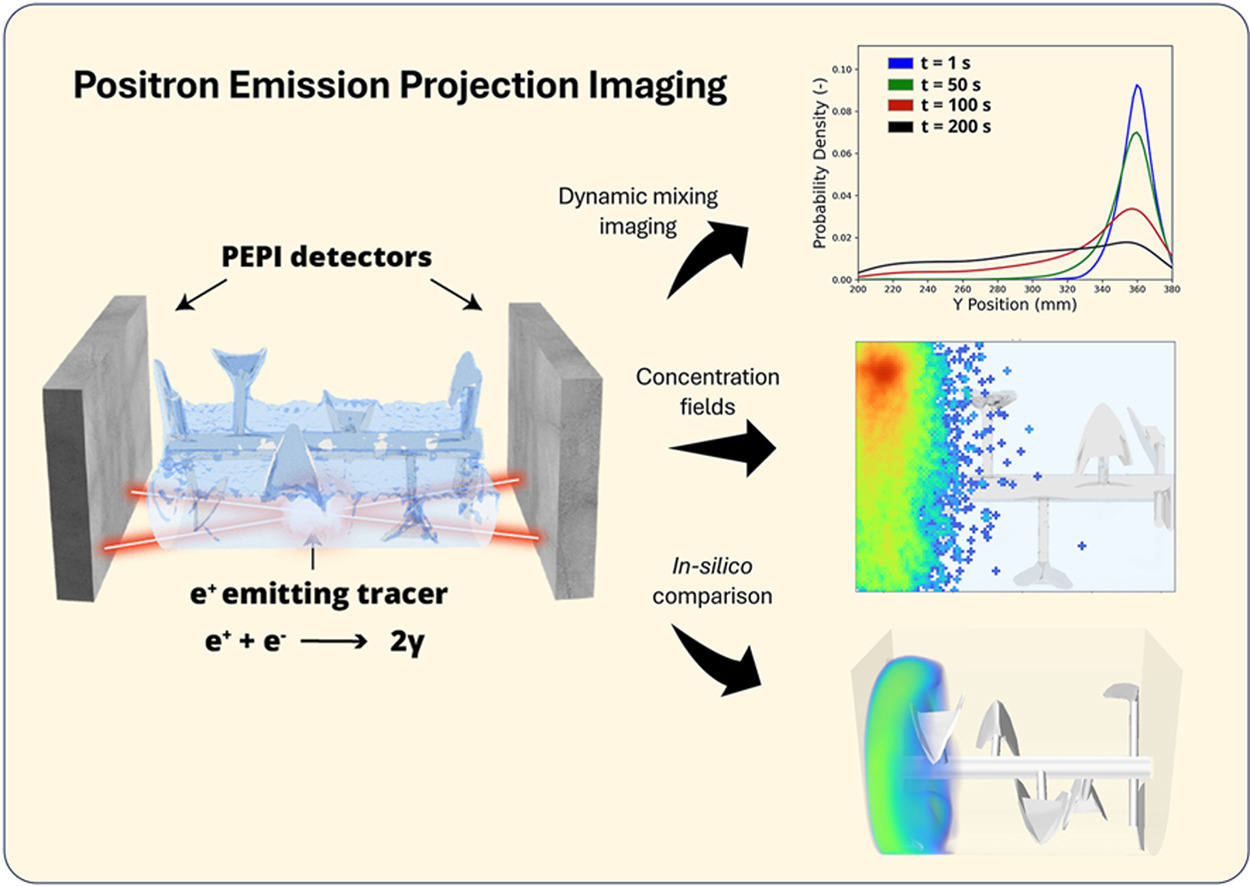
• New PEPI algorithm enhances spatial and temporal resolution for imaging.
• Validated using synthetic data from a PET scanner digital twin.
• Applied PEPI to image laminar flow mixing in a ploughshare mixer.
• PEPI effectively validates CFD models for industrial processes.
• Future: refine algorithm and expand industrial applications of PEPI.
A novel Positron Emission Projection Imaging (PEPI) algorithm designed to compute the plane-projected spatial distribution of radiolabelled materials without the need for collimation is introduced. By leveraging improved data efficiency, we have achieved a technique with enhanced spatial resolution and temporal resolution compared to previous PEPI algorithms. Validation of this algorithm was conducted using synthetic data generated from a digital twin of a PET scanner, demonstrating its accuracy for practical applications. The industrial advantage of this novel algorithm was applied in the imaging of laminar flow mixing within a ploughshare mixer, with the experimental results compared against those obtained from validated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models. This comparison highlights an important use case for PEPI as a robust validation tool for CFD simulations, crucial for enhancing industrial processes. PEPI, which uses deeply penetrating gamma-photons, is now capable of imaging opaque fluids and solids in industrial casing. Future directions for this work include further algorithmic refinements and expanding its application across various industrial systems, establishing PEPI as a robust tool for in-depth industrial process analysis. The advancements presented here allow for optimized mixer design and enhanced process efficiency, extending the frontiers of tomographic imaging in industrial applications.