-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 94
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
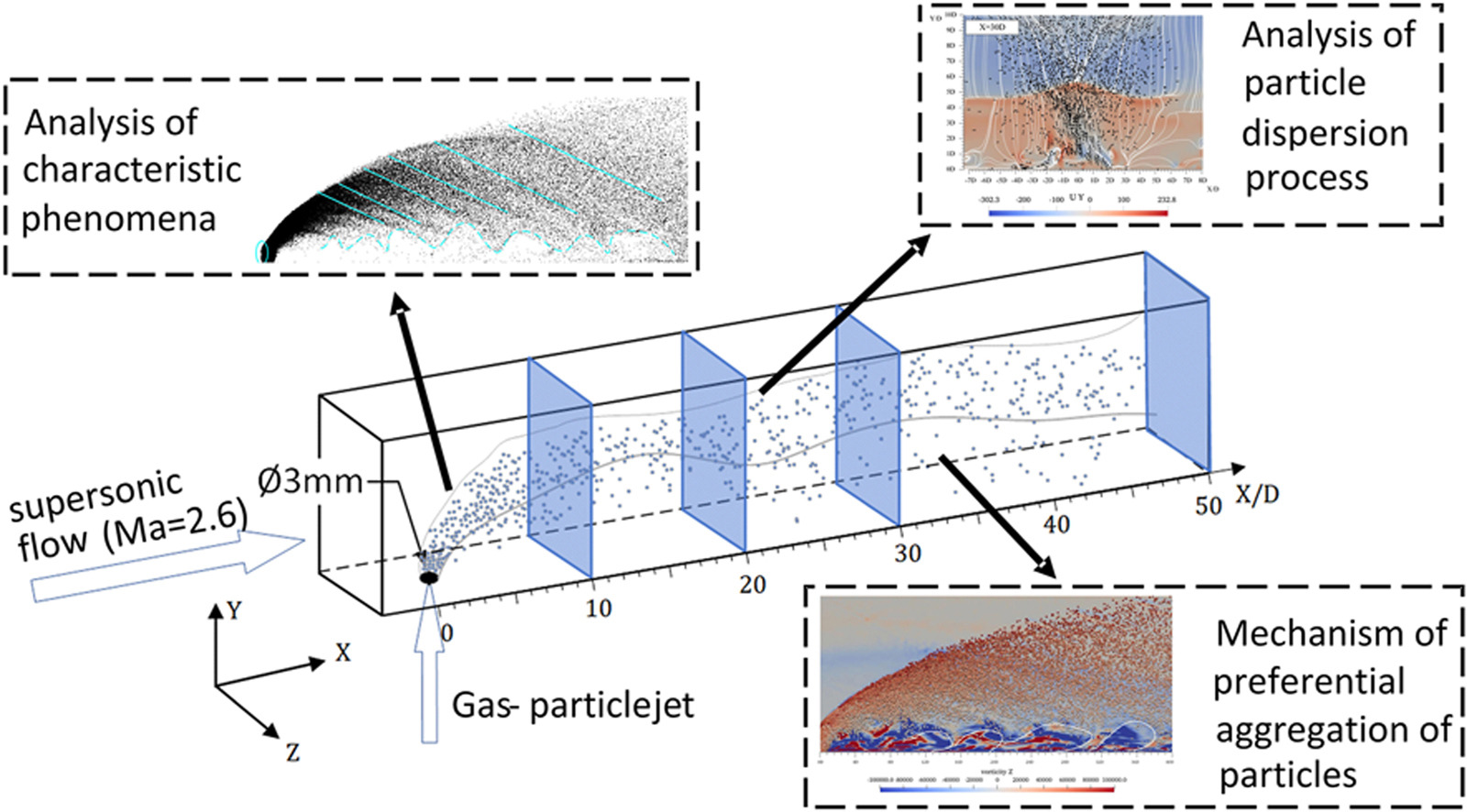
• Experiments and numerical simulations of supersonic gas-particle transverse jets were conducted.
• Numerical simulations reproduced three characteristic phenomena found in experiments.
• Particles tend to aggregate in regions of high density and low vorticity.
• There is a particle size range that is the influence limit of gas density.
The supersonic gas-particle two-phase transverse jet is a typical flow process in many applications, such as solid rocket scramjet. This study carried out experimental tests as well as Large Eddy Simulation (LES) to investigate the evolution process of transverse gas-particle two-phase jets in supersonic crossflow, especially focusing on the phenomena called preferential concentration. The simulation is based on the Eulerian-Lagrangian method, which successfully reproduces the characteristic phenomena observed in experiments. The particle cloud forms three different characteristic distribution patterns: tooth-like waves near the jet port, quasi-ordered structures near counter-rotating vortex pairs (CVP), and filamentous clouds in the upper part. The turbulence and small unstable shock play a suppressing role in mixing small-diameter particles, which tend to aggregate in regions of high density and low vorticity. Furthermore, it is found that there exists a specific range of particle sizes, as particles' sizes approach this specific range, the influence of compressibility of the airflow on particle distribution becomes increasingly prominent. Overall, this study shed some light on the understanding of the complex and intricate nature of the supersonic gas-particle two-phase transverse jet.