-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 94
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
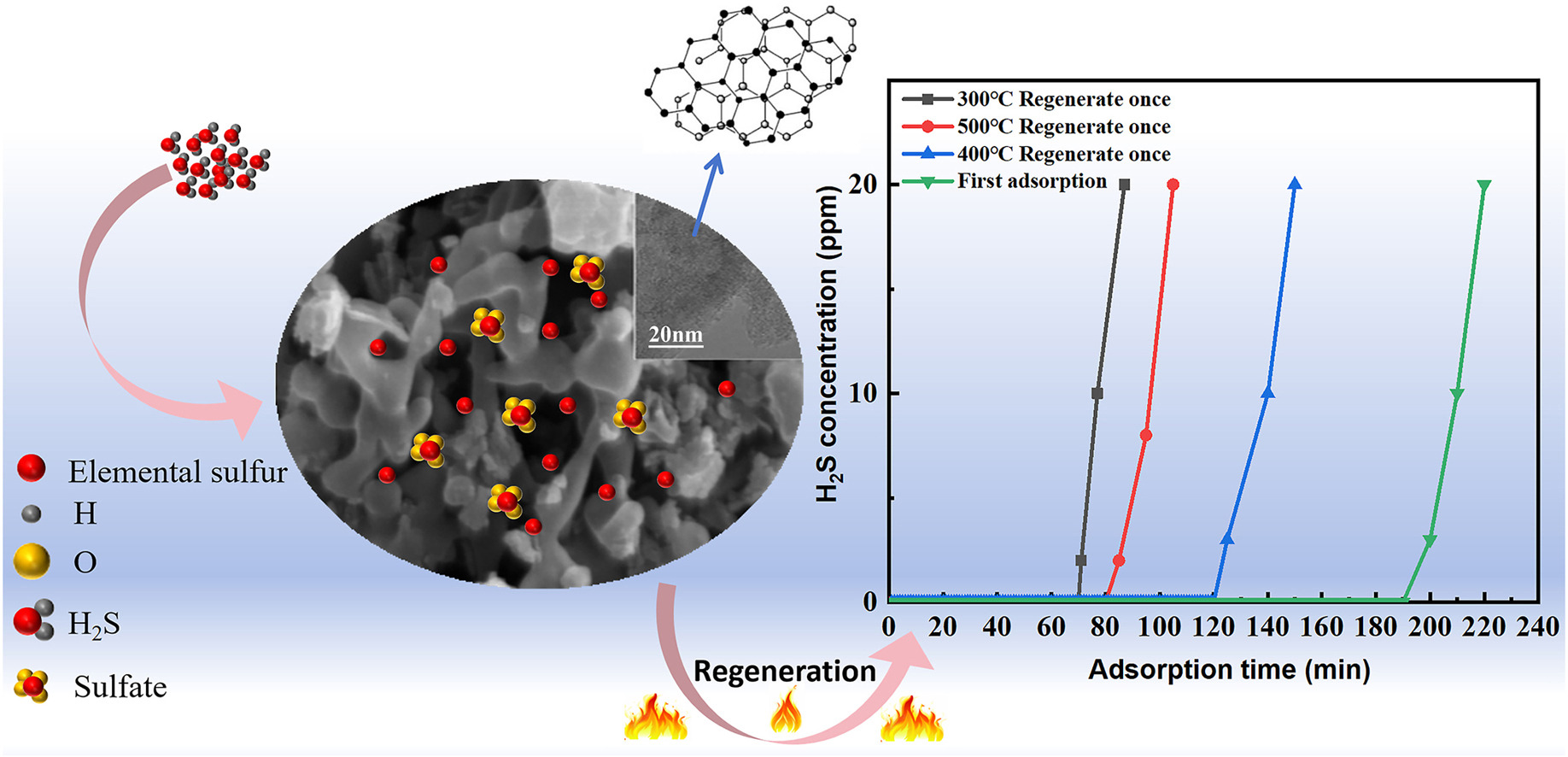
• We prepared lignin carbon by direct pyrolysis for H2S adsorption.
• KOH modification increased the specific surface area of lignin carbon but decreased its degree of graphitization.
• The modified lignin carbon shows a high specific surface area of 1672.9 m2/g and a sulfur capacity of 67.1 mg/g.
• Heating can regenerate lignin carbon saturated with adsorbed H2S, allowing two cycles of reuse.
In pursuit of effective adsorption materials for malodorous gases such as H2S and to broaden the utilization avenues of lignin waste, this study employed the direct pyrolysis method to synthesize three types of alkali lignin graphitized carbons, namely C-800, KC-700, and KEC-700. Among them, KEC-700 exhibits a high specific surface area of 1672.9 m2/g, significantly superior H2S adsorption performance compared to other materials, an adsorption breakthrough time of up to 220 min, and a sulfur capacity of 67.1 mg/g. Structural analysis showed that the more oxygen-containing functional groups of lignin charcoal and the larger specific surface area facilitated the adsorption of H2S. After reaching adsorption saturation, the degree of graphitization of lignin carbon diminishes. The H2S adsorption products primarily manifest as elemental sulfur and sulfate within the pores of lignin carbon measuring less than 2 nm. Through thermal regeneration, the charcoal effectively eliminates the elemental sulfur adsorption product. Nevertheless, sulfate removal proved unsatisfactory, as the adsorption efficiency of KEC-700 following two thermal regenerations was approximately 41% of that observed for fresh samples.