-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 94
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
• Rotating particle collisions in 3D.
• Numerical model to predict particle rebounds.
• Out of plane particle rebound.
• Particle-wall collision and induced rotation.
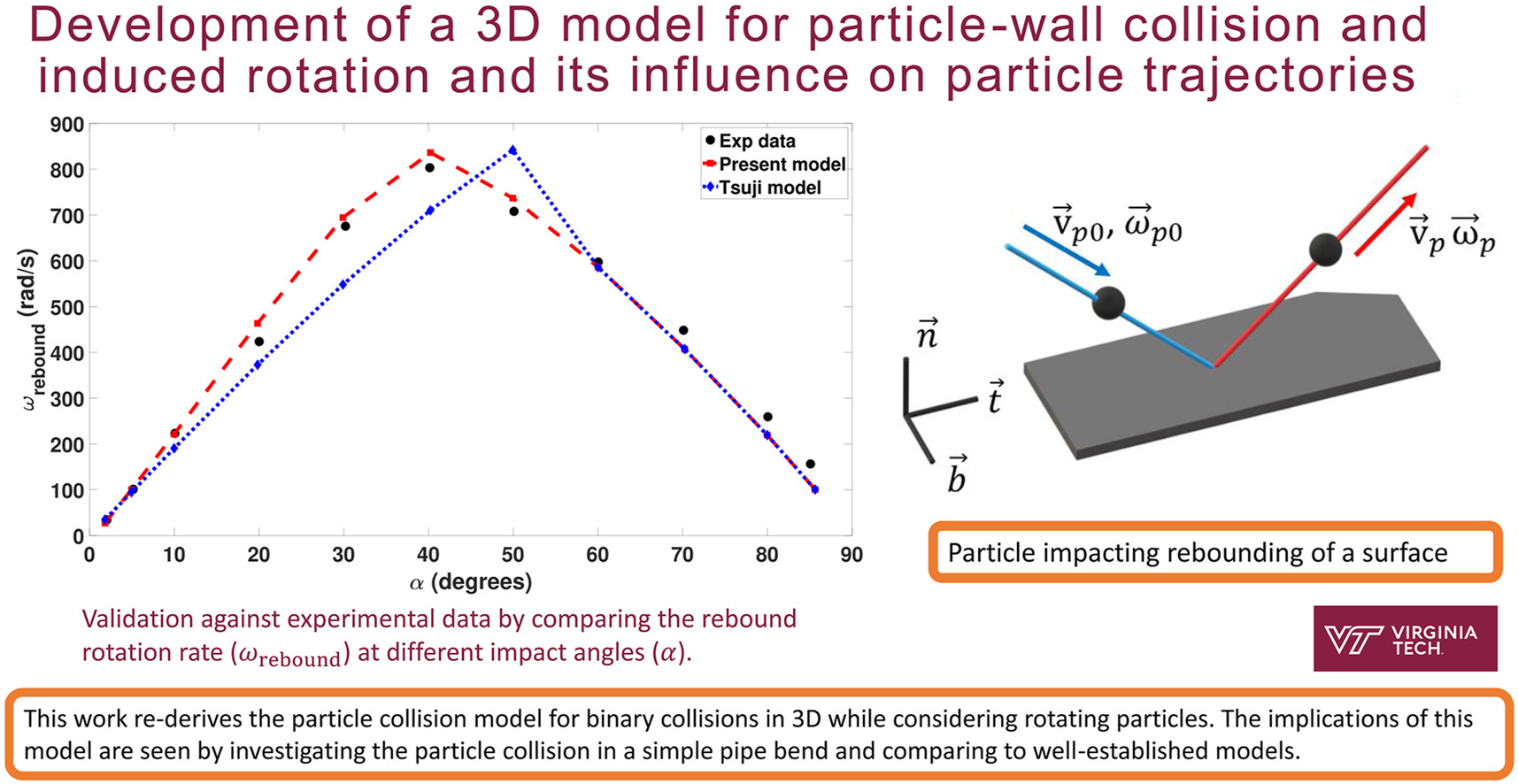
The present research focuses on improving the prediction of rotating particle collisions. Current particle-surface collision models do not accurately predict the particle rebound when taking rotation into account. Experimental data, such as the studies by Gorham and Kharaz (2000), Buck, Tang, Heinrich, Deen and Kuipers (2017), and Dong and Moys (2006) show that the Tsuji, Oshima and Morikawa (1985) model is inaccurate due to the incorrect tangential coefficient of restitution assumption. Hoomans, Kuipers, Mohd Salleh, Stein, and Seville (2001) introduced a similar model to the work by Tsuji et al. (1985) which includes a tangential coefficient of restitution but is only in two dimensions and does not consider out of plane rebounds. This work re-derives the particle collision model from the impulse equations for binary collisions in 3D while considering rotating particles. The derived equations in this work compares well to experimental particle-surface impact studies. The implications of this model are seen by investigating erosion due to particle collision in a simple pipe bend. It is shown that Tsuji et al. (1985) over predicts the erosion. These small differences in particle trajectories between the present model and the Tsuji et al. (1985) model will grow in complex flows with multiple close range particle impacts leading to inaccurate erosion predictions which will negatively impact the design of turbomachinery and pneumatic pipes.