-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 94
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
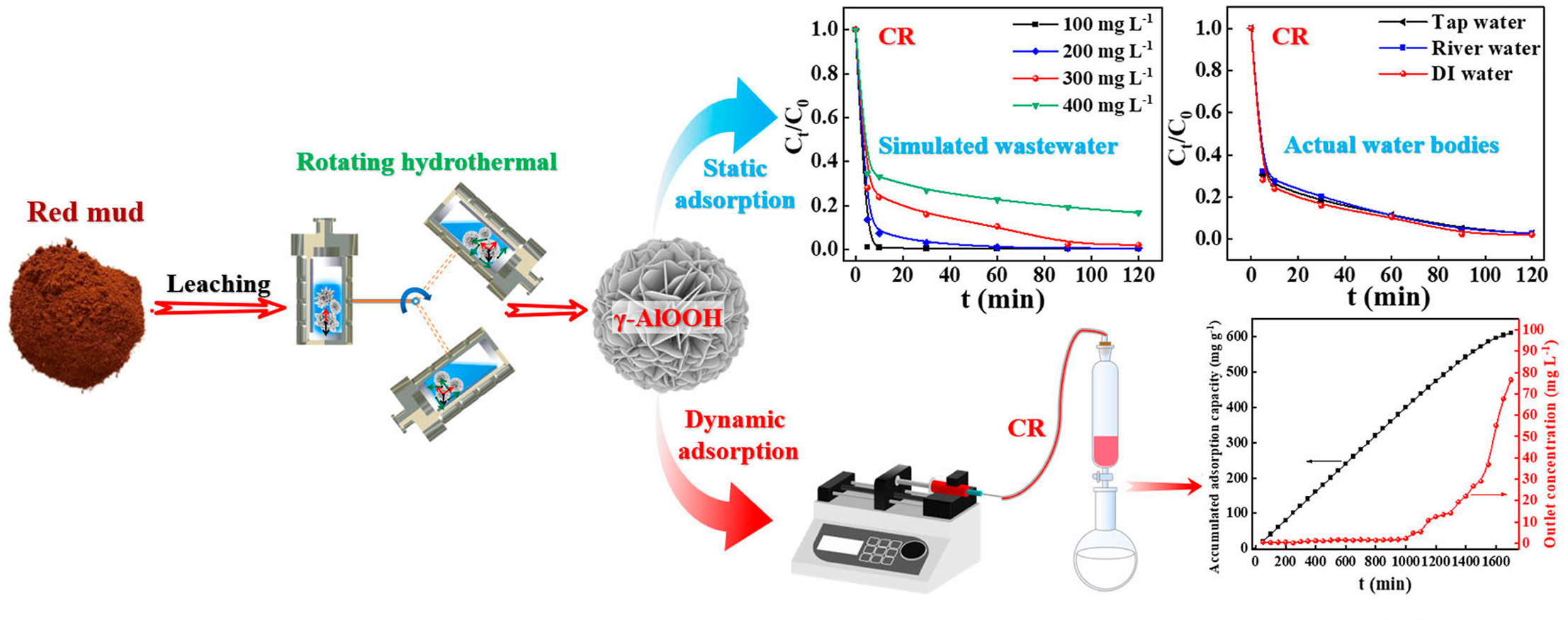
• Rotating hydrothermal route is developed to red mud derived γ-AlOOH microspheres.
• The γ-AlOOH microspheres exhibit distinctly narrow diameter distribution and small average diameter.
• Effect of rotation and rotating force analysis on the formation mechanism are uncovered.
• The γ-AlOOH microspheres exhibit high adsorption capacity for CR (602.4 mg g−1) and MB (1208.7 mg g−1).
• Static DI, dynamic flowing and actual water bodies simulated wastewater are tested.
Towards increasingly severe worldwide pollution of industrial solid waste red mud (RM) released from aluminum industry, constitutional valuable element Al has been successfully separated for a novel mild rotating hydrothermal synthesis (150 °C, 12 h, 5 Hz) of the uniform hierarchical porous flowerlike boehmite (γ-AlOOH) microspheres in the presence of appropriate urea, which exhibit distinctly small average diameter (1.52 μm) and narrow particle size distribution (PSD: 1.12–1.97 μm), as well as high specific surface area (129.37 m2 g−1). On the one hand, the rotating hydrothermal synthesis promotes the mass and heat transfer, enabling γ-AlOOH microspheres at a lower temperature within a shorter time. On the other hand, moderate rotation provides predominant shear force, rendering the uniform γ-AlOOH microspheres with small average diameter and narrow PSD. The optimal AlOOH–U2M-R5Hz microspheres demonstrate satisfactory adsorption performance for Congo Red (CR) and Methyl Blue (MB), with the maximum adsorption capacities of 602.4 and 1208.7 mg g−1, respectively. Various isotherm models of Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich are utilized, adsorption kinetics are analyzed, adsorption mechanism is uncovered based on hydrogen bonding and electrostatic attraction. The increase in the temperature or the presence of coexisting cations facilitates the adsorption of CR, whereas coexisting anions weaken the adsorption of CR on the AlOOH–U2M-R5Hz microspheres. Furthermore, the excellent recycling performances and especially dynamic adsorption (retainment of removal efficiency of approx. 99.0% within 1000 min) as well as authentic water bodies (e.g. tap water and river water) simulated wastewater treatment undoubtedly indicate great practical applications of the AlOOH–U2M-R5Hz microspheres, towards cleaner aluminum production and cost-effective sustainable solution to anionic dye-bearing wastewater.