-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 94
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
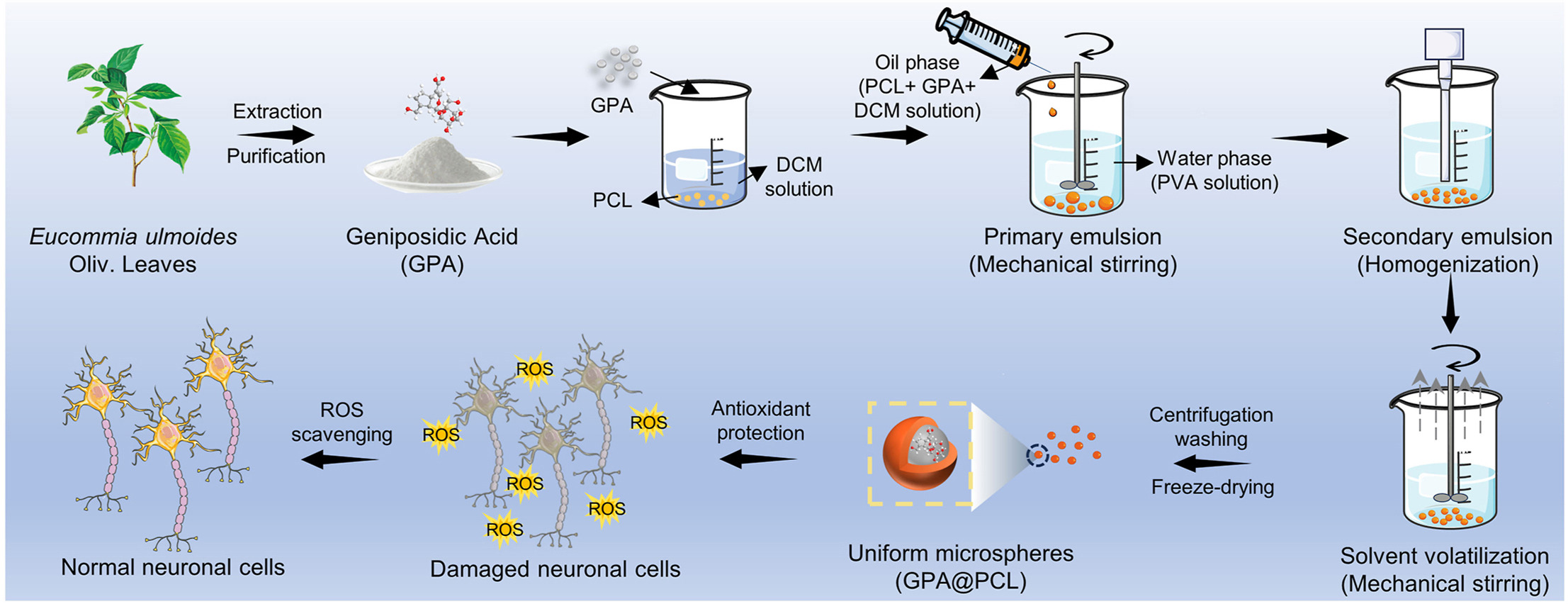
• Developed a two-step emulsification method that produces more uniform microspheres compared to traditional methods.
• Encapsulating GPA in PCL microspheres protects it from degradation, thereby enhancing its efficacy.
• PCL microspheres efficiently load GPA and provide sustained release in vitro.
• GPA-loaded PCL microspheres are biocompatible and protect neuronal cells from oxidative damage by scavenging ROS.
The mortality rate of neurological disorders is increasing globally, and natural antioxidant geniposidic acid (GPA) holds great potential in the treatment of neuronal oxidative damage. Nevertheless, its inherent instability constrains its pragmatic utilization. Herein, we introduced a drug delivery system capable of protecting unstable natural active compounds from degradation. Among the various methods for preparing drug-loaded microspheres, the emulsification-solvent evaporation technique is one of the most commonly employed due to its efficiency and simplicity. Nevertheless, this method results in microspheres with heterogeneous particle sizes. To address this limitation, we developed a two-step emulsification method involving stirring and homogenization. Using the biocompatible, synthetic, biodegradable polymer polycaprolactone (PCL) as the drug delivery carrier, we prepared GPA-loaded PCL microspheres via the two-step emulsification method. The results demonstrated that the microspheres possessed uniform particle size (polydispersity index = 0.12), excellent drug loading capacity (∼4.86%), sustained drug release profiles (∼68.55% in 264 h), and biocompatibility (cell viability >85%). The in vitro tests showed that the microspheres exerted antioxidant effects by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced by oxidative stress, thereby protecting neuronal cells from oxidative damage. This work presents a promising new approach for the treatment of neuronal oxidative damage.