-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 94
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
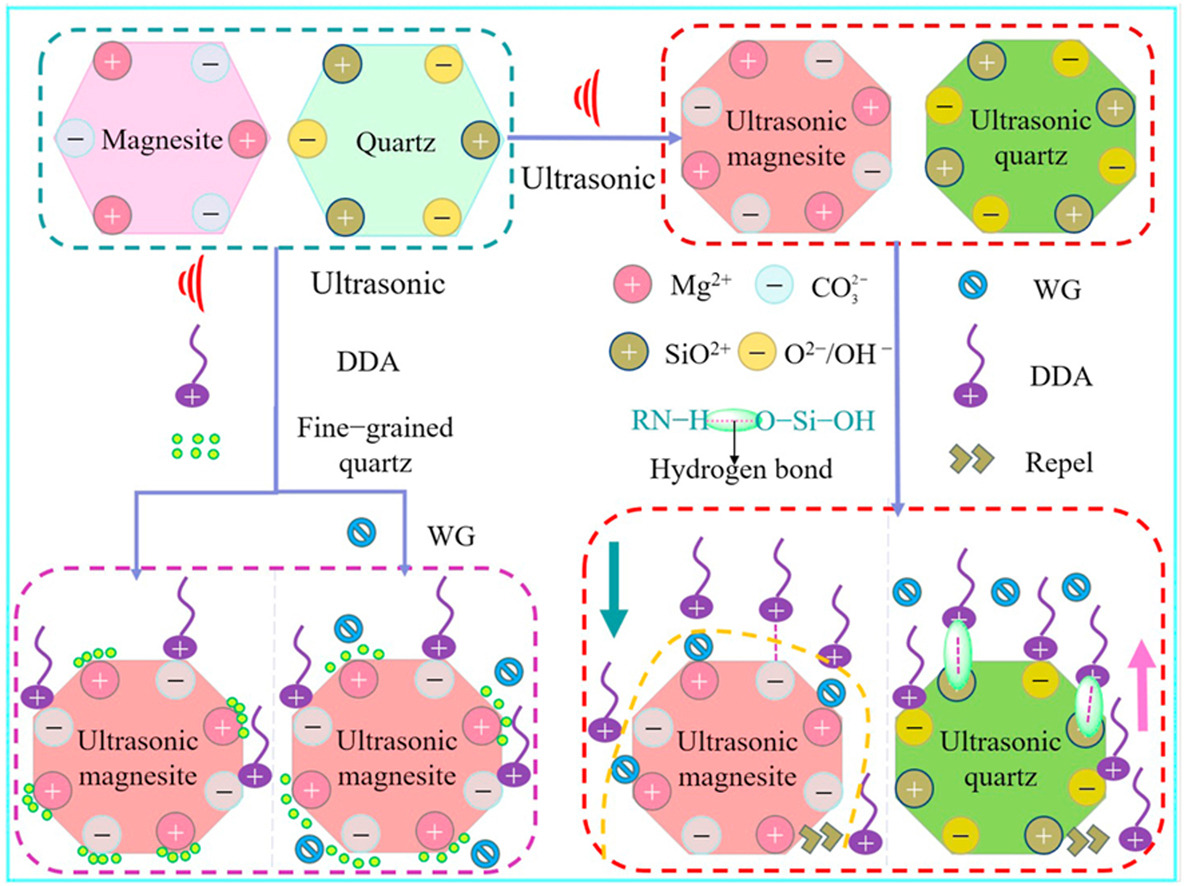
• Ultrasonic treatment increases the surface roughness and active sites of magnesite and quartz.
• Ultrasonic treatment reduces the flotation recovery of magnesite and quartz in DDA system.
• Ultrasonic treatment enhances the mutual attraction energy between magnesite and fine quartz particles.
Ultrasonic treatment, as an important surface modification method, profoundly affects the flotation behavior of minerals. This study examined the impact of ultrasonic treatment on the surface properties and flotation performance of magnesite and quartz in a dodecylamine (DDA) flotation system. Atomic force microscope detection results revealed that the surface roughness and roughness size of both magnesite and quartz increased after ultrasonic treatment. Flotation tests indicated that the recovery rates of magnesite and quartz were lower after ultrasonic treatment. At pH of 10 and DDA of 75 mg/L, ultrasonic treatment led to a 0.66%, 3.46%, and 0.33% decrease in the flotation recovery rates for three different magnesite particle sizes. Following ultrasonic processing, the flotation recovery rates for three different quartz particle sizes decreased by 8.48%, 30.76%, and 43.69%, in that order. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy detection results showed an increased presence of characteristic Mg and Si sites on the surfaces of magnesite and quartz following ultrasonic treatment. DDA acted on the surfaces of the two minerals through electrostatic adsorption and hydrogen bonding adsorption and repelled the flotation of minerals owing to the same charge as characteristic sites, thereby reducing flotation recovery. Adsorption capacity tests and contact angle measurements demonstrated a decrease in DDA adsorption and contact angle on the surfaces of magnesite and quartz after ultrasonic treatment, explaining the reduced floatability. Extended Derjaguin–Landau–Verwey–Overbeek theoretical calculations indicated that before ultrasonic treatment, there was a repulsive energy between magnesite and fine-grained quartz particles. After ultrasonic treatment, the interaction energy between magnesite and fine quartz particles is mutual attraction.