• F-doped cathode materials are prepared by co-precipitation method combining with two-stage calcination process.
• F-doped cathode materials possess preferable microstructures and satisfactory electrochemical performances.
• This study provides a valuable reference for researches of anion doping in other layered cathode materials.
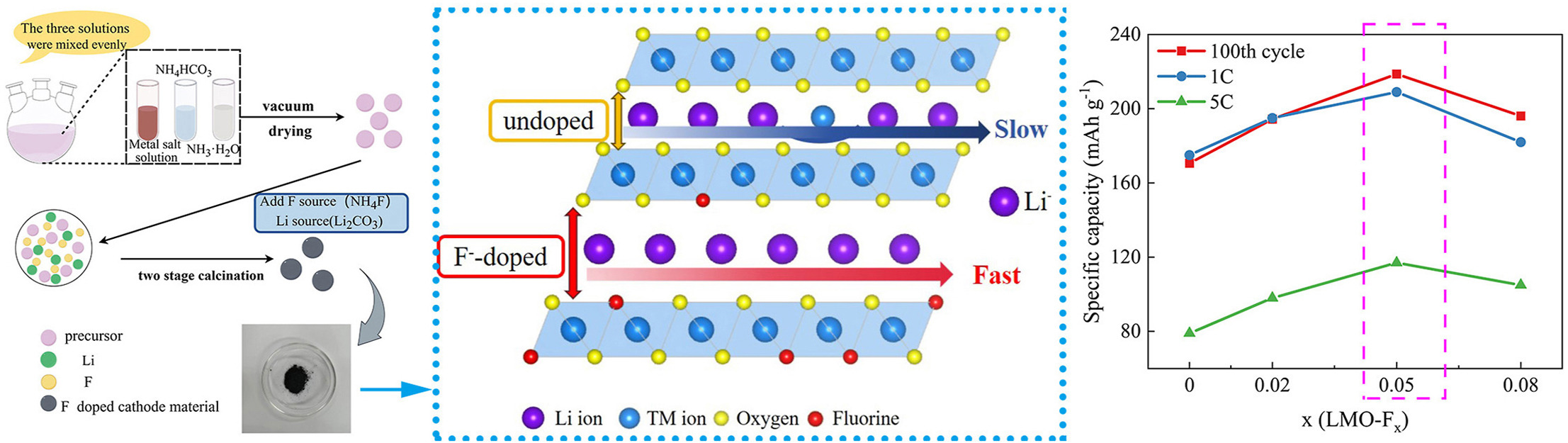
Lithium-rich manganese-based (Li-rich Mn-based) cathode materials possess high specific capacity, low self-discharge rate and steady working voltage, but cycle performance and rate performance need to be further improved. In this study, cathode materials Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2-xFx (x = 0, 0.02, 0.05, 0.08) are synthesized by the co-precipitation method with the two-step calcination process. And the F-doping effects on the microstructure and the electrochemical performance are investigated in the cathode materials Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2. The results indicate that among all the F-doped cathode materials, the crystal lattice parameters are increased, order degree and stability of the layered structure are improved. As for x = 0.05, cathode material Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O1.95F0.05 (LMO-F0.05) shows the best cycle performance and rate performance with its capacity retention rate 87.7% after 100 cycles at 0.2 C and discharge capacity 117 mAh g−1 at 5 C high power. It can be seen that F doping is a simple and crucial strategy to promote the Li ion diffusion and develop high performance layered cathode materials.
F-doped; Li-rich Mn-Based cathode material; Microstructure; Cycling performance; Rate performance
