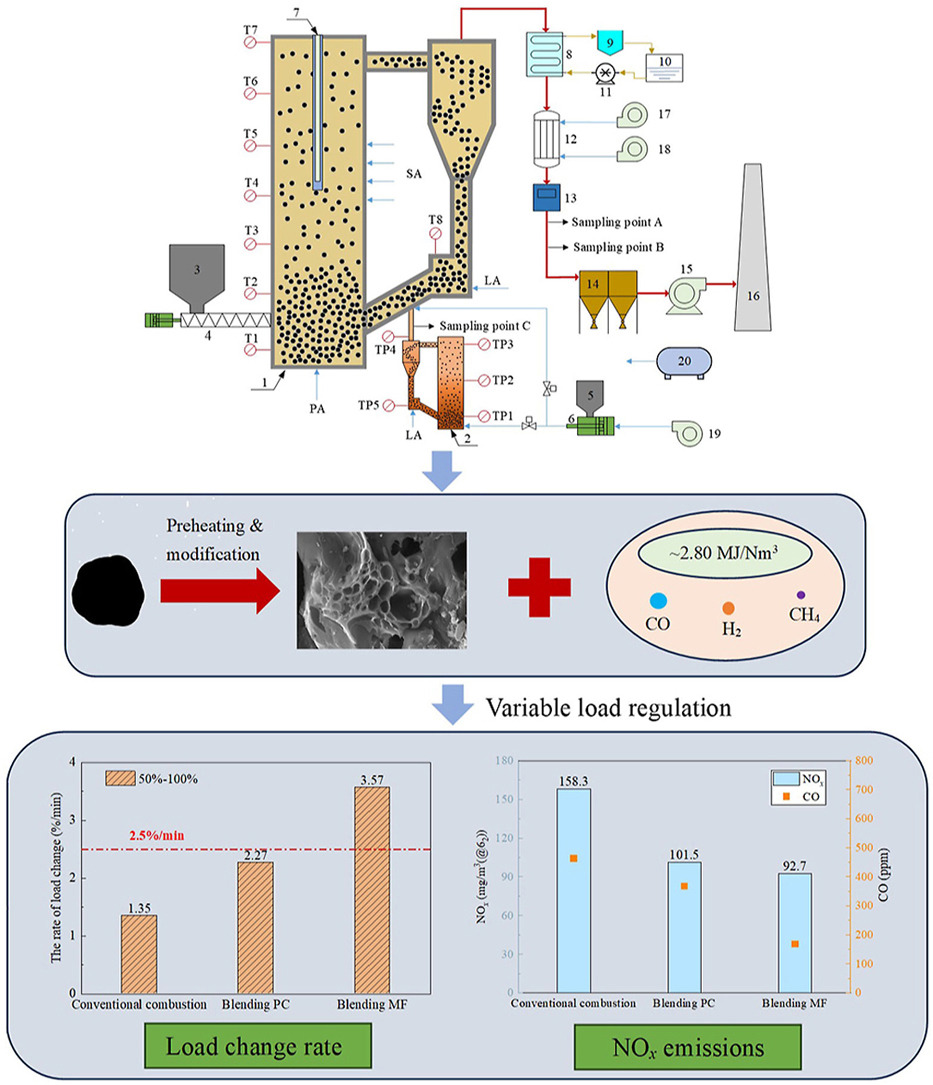
• The modified char has the finest particle size, the richest pore results and the highest reactivity.
• Modified char and coal gas with high sensible heat play an active role in rapid load change of CFB.
• Blending modified fuel can increase load change rate by 164.4% in range of 50%–100% load.
• Combustion of modified fuel reduces NOx emission of CFB at 100% load by 41.4%.
The circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boiler is an essential option, serving as a flexible power source. However, it is notable that CFB boilers exhibit noticeable limitations in rapid load changes. This study delved into the impact of fuel characteristics on CFB load change rate, combustion efficiency, and original NOx emissions using a 2 MW CFB experimental platform. The findings revealed that blending pulverized coal or modified fuel positively influenced the improvement of CFB load change rate, with blending modified fuel showing a more significant effect. Blending the modified fuel and pulverized coal increased the load change rate within the 50%–100% range by 164.4% and 57.3%, respectively. Additionally, blending pulverized coal and modified fuel significantly reduced NOx emissions, although there remained room for improvement in combustion efficiency. Compared to conventional combustion, blending pulverized coal and blending modified fuel decreased NOx emissions by 35.9% and 41.4% at 100% load, respectively.