• Analyzed the effect of split drag rudder (SDR) on the transonic flutter characteristic of rigid NACA 64A010 through numerical simulations.
• The increase of the split angle has a positive influence on flutter speed in the subsonic state, where the flutter velocity increases by approximately 80% with a split angle increase in the range 0–10 deg.
• The SDR delays the shock wave shifting downstream, and the Mach number corresponding to reaching freeze region increases as the split angle increases, which leads to the delay in the occurrence of the transonic dip.
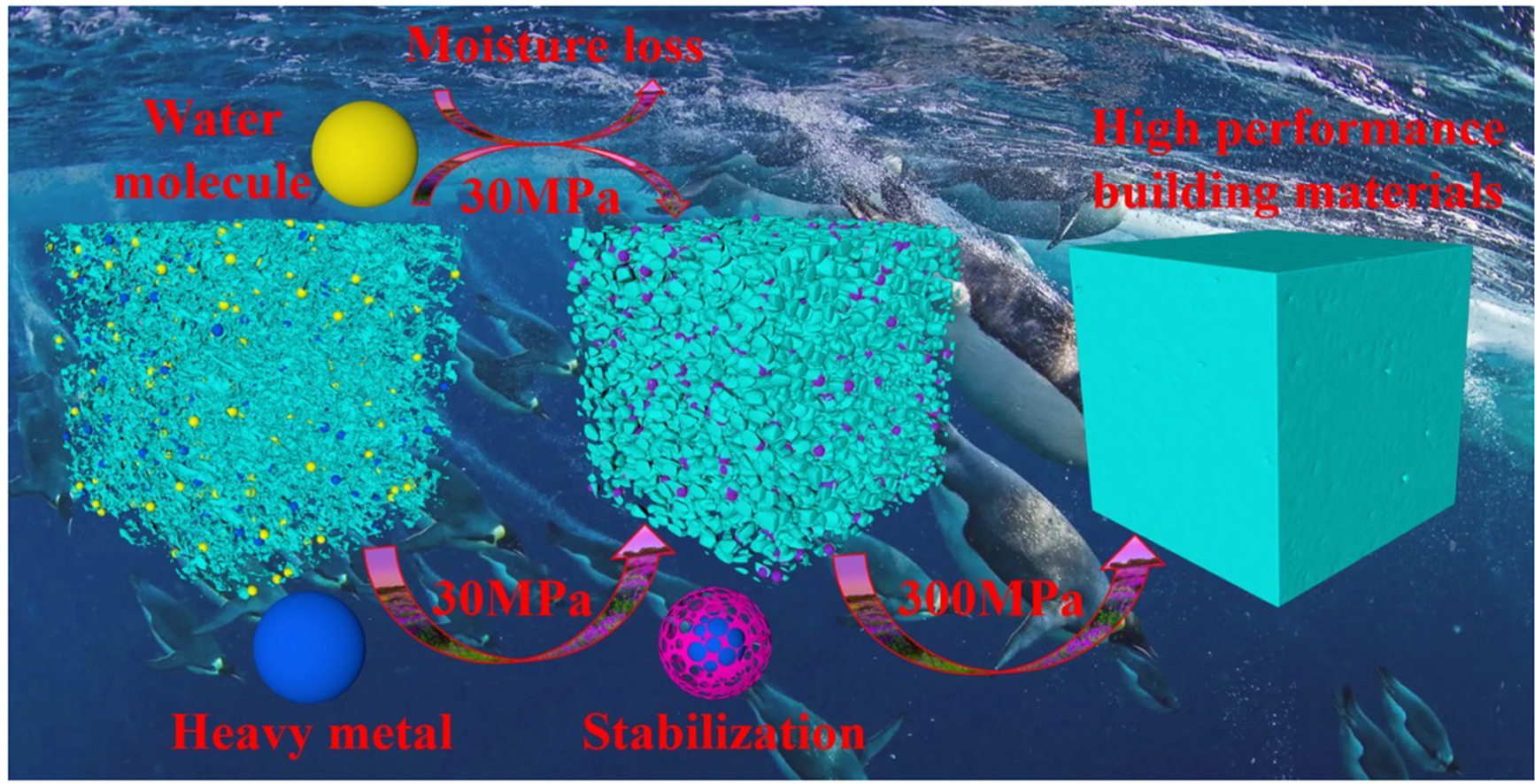
In order to improve the resource utilization rate of aluminum ash, high-quality building materials were prepared by replacing traditional cement with aluminum ash, and the performance of building materials under different conditions and factors was studied. The experimental results show that when the pressure was 300 MPa and the natural curing time was 3 days, the comprehensive performance of the brick reaches its optimum (compressive strength of 60 MPa, flexural strength of 1.3 MPa, and softening coefficient of about 0.9), far superior to other reported methods for preparing building materials. SEM-EDS, Particle size analysis and XRD confirmed that the crystal structure in aluminum ash undergoes a transformation under high-intensity mechanical pressure, forming cement-based active substances. This study not only obtained a new method for preparing building materials, but also further promoted the research on the resource utilization of aluminum ash, providing a new approach for the treatment and disposal of hazardous waste.