- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
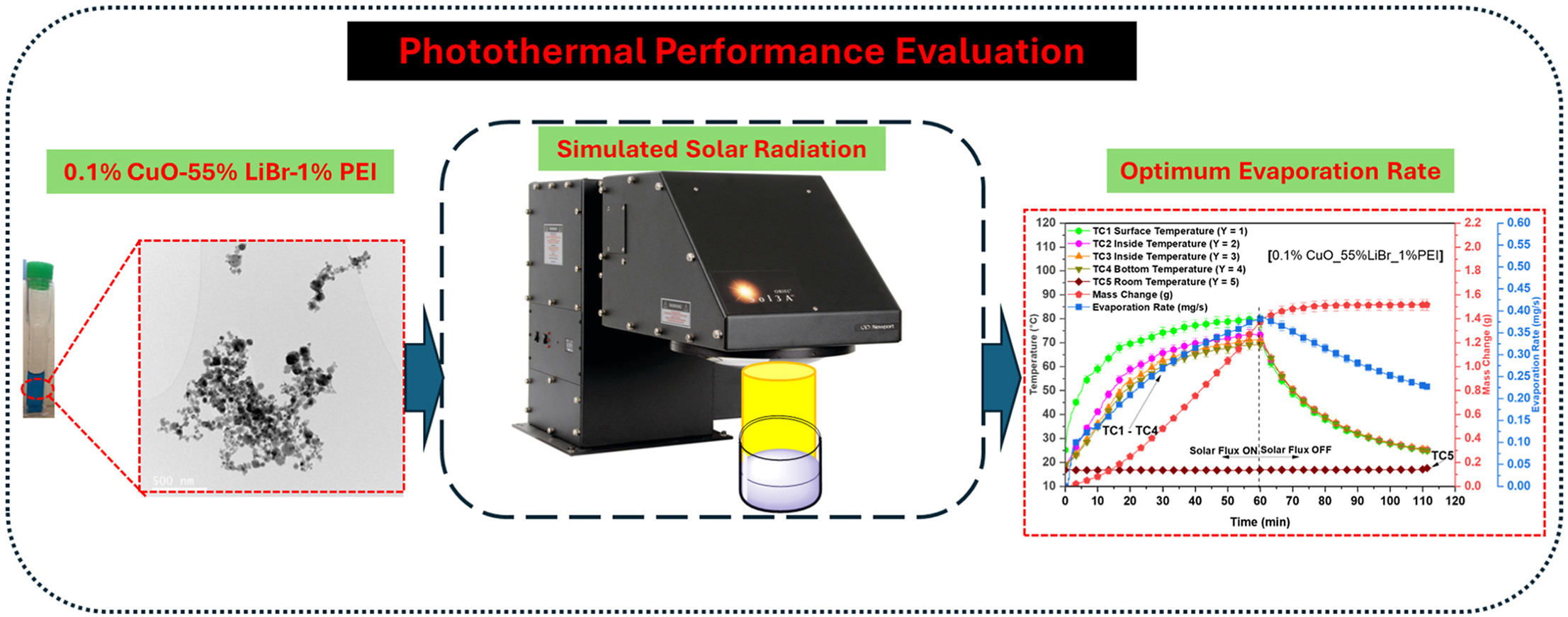
• A highly stable functionalised CuO nanofluid in 55 wt% LiBr for solar absorption refrigeration has been developed.
• Increased bulk temperature and evaporation rates under solar radiation were demonstrated.
• Notable boost in the latent and sensible heat has been observed which enhanced steam evaporation efficiency.
• CuO nanofluid's potential for eco-friendly,energy-efficient solar refrigeration has been showcased.
Multiphase flow and heat transfer processes are involved in various applications, such as water desalination, sterilisation, and power generation. Environmentally friendly and sustainable system operation can be ensured through the utilisation of renewable energy resources. Furthermore, the thermal efficiency of these systems can be enhanced by using nanofluids. This study reports an experimental investigation of the photothermal conversion properties of polyethylenimine (PEI) functionalised Copper oxide (CuO) nano particles used in Lithium Bromide (LiBr) salt solutions. The nano particles were characterised by the dynamic light scattering (DLS), transmission electron microscope (TEM), ultraviolet visible (UV–Vis) spectrophotometer. The long-term stability of the prepared nanofluid was evaluated using a high-speed centrifuge analyser. The instability index of 0.071 ± 0.002 indicated low agglomeration and sedimentation tendencies. Photothermal conversion efficiency for different concentrations of CuO was experimentally investigated under a solar simulator. The experiments were conducted with nanofluids containing 55 wt% of LiBr and PEI functionalised nanoparticles, with loading ranging from 0.05 to 0.15 wt%. The addition of nanoparticles resulted in an increase in surface temperature, up to 90.69 ± 2.7 % higher than the base case tested with deionised water (DIW). Experimental results further confirms that the nanofluid tested in this study has the potential to significantly increase solar energy trapping efficiency and evaporation rate due to a localised solar energy harvesting by the surface of nanofluid. It was found that a 0.1 wt% CuO NP concentration is the optimum nanofluid concentration in terms of stability for enhanced sensible and latent heat efficiencies.