- Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
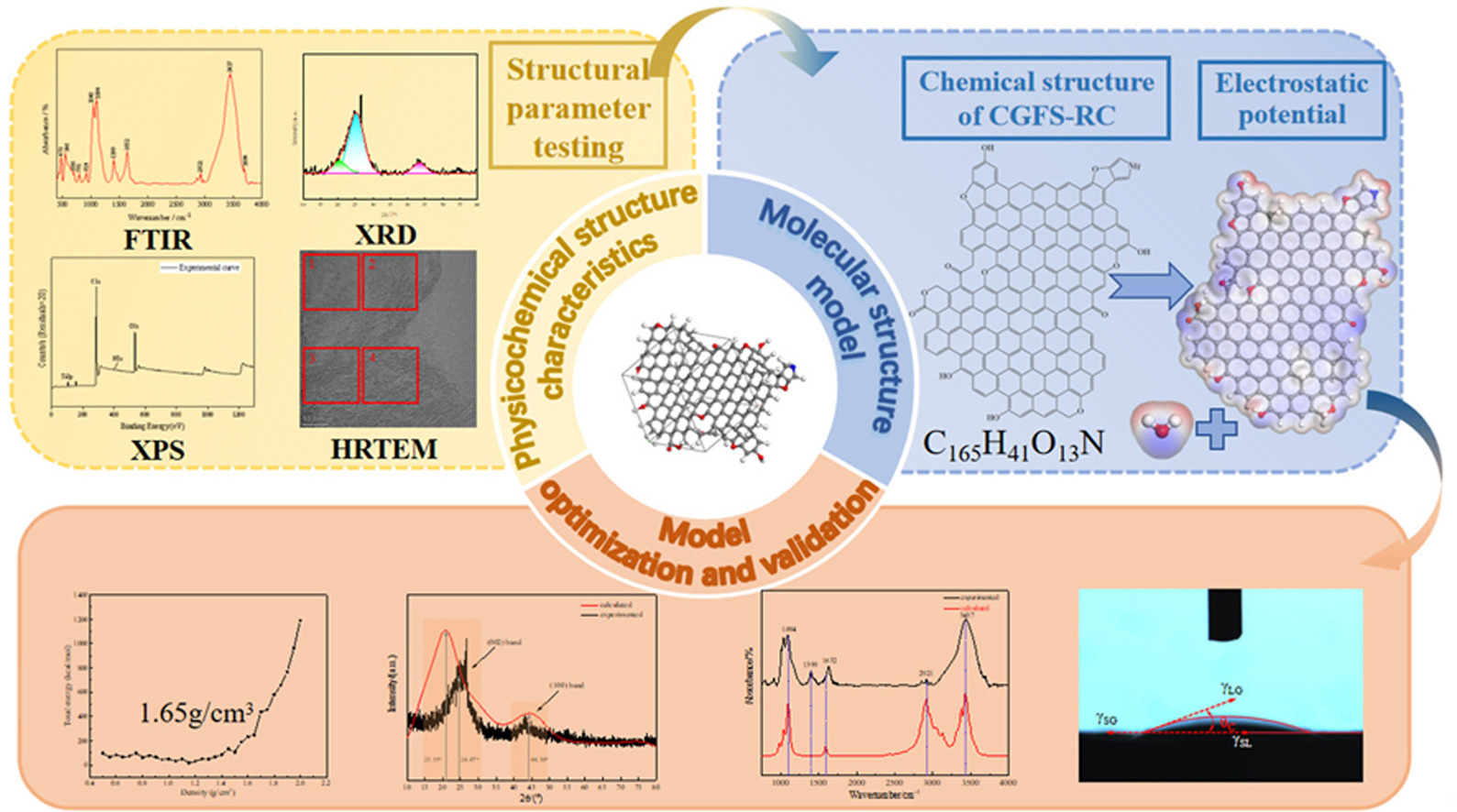
• Molecular composition of residual carbon contained in coal gasification fine slag (CGFS-RC) was obtained using HRTEM.
• CGFS-RC molecular modeling method was realized and its validity was confirmed.
• In CGFS-RC, C exists as aromatic, O as ether-oxygen bonded, and N as pyrrole.
• Molecular formula, 2D and 3D models of CGFS-RC were obtained by simulation.
• Wetting property of the CGFS-RC surface was revealed from the molecular level.
The residual carbon contained in coal gasification fine slag (CGFS-RC) is a valuable resource with great potential for application, and the elucidation of the macromolecular structural model of CGFS-RC is an important basis for its recovery and utilization. In this paper, CGFS-RC was comprehensively characterized by proximate, ultimate, FTIR, XRD, XPS, and HRTEM analyses, and the macromolecular geometric model of CGFS-RC was constructed and optimized using Materials Studio software. The results show that carbon atoms in CGFS-RC mainly exist in the form of aromatic carbons with a high percentage of 90.7 %, and the ring number of condensed aromatic rings is mainly 3–5. The aliphatic carbon side chain structure on the benzene ring is mainly dominated by cycloalkanes. Among the heteroatoms, oxygen atoms are mainly present in the form of ether-oxygen bonds, (phenolic) hydroxyl groups, carbonyl groups and carboxyl groups, while nitrogen atoms are mainly present in the form of pyrroles. The molecular formula of CGFS-RC can be expressed as C165H41O13N, and the density of its geometrical configuration was calculated to be 1.65 g/cm3. The XRD and FTIR simulation confirmed the reasonableness of the constructed model, and the electrostatic potential simulation revealed the hydrophilic properties of CGFS-RC at the molecular level. This study opened up the molecular structure analysis and modeling process of CGFS-RC, which can provide fundamental basis for the reagent design in the flotation recovery of CGFS-RC as well as the resource utilization of CGFS-RC.