-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volume 105
-
Volume 104
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
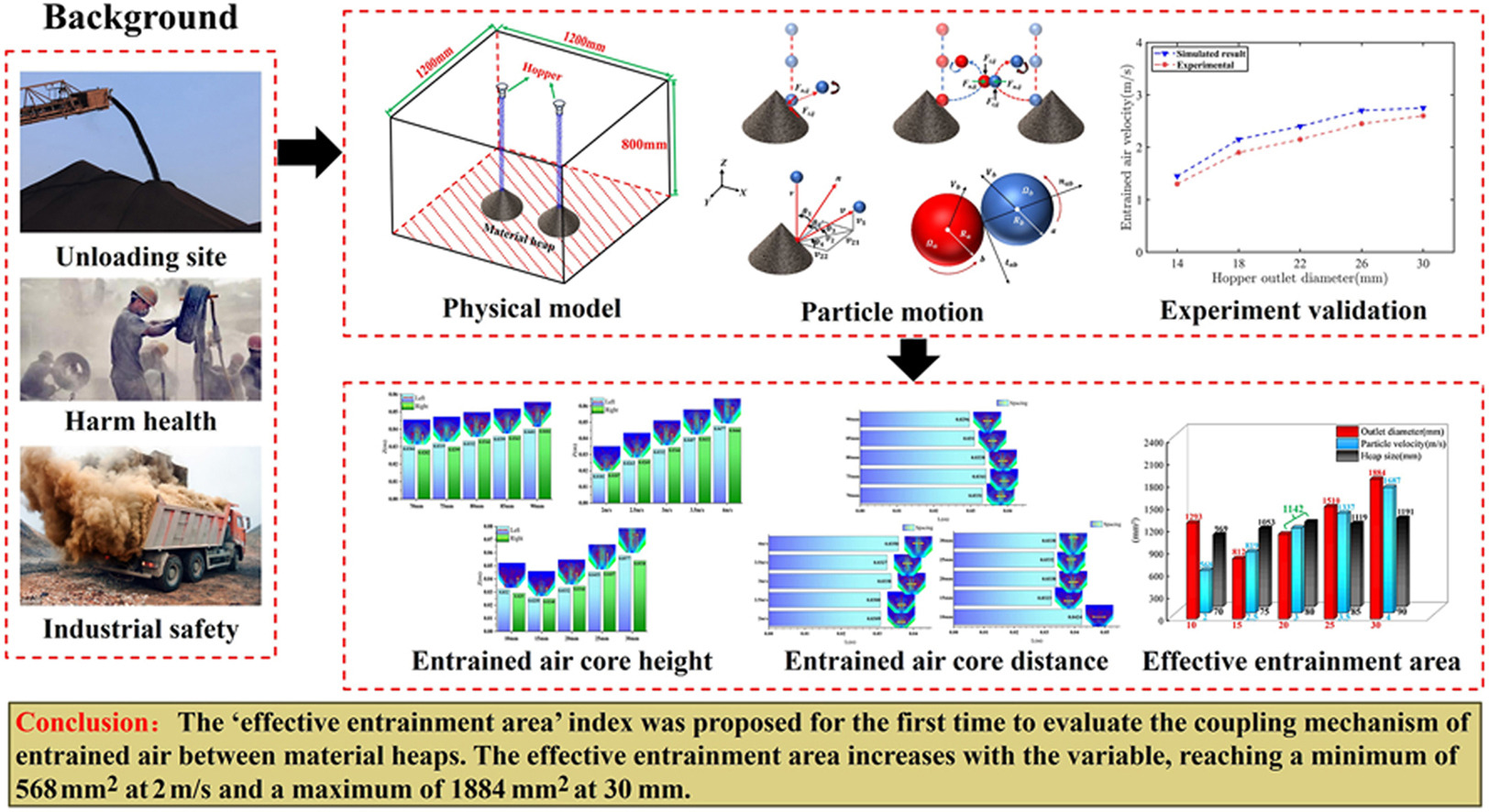
• The mathematical-physical model of double material heap simultaneous unloading process was developed.
• Effects of material heap height, particle velocity and hopper outlet diameter on entrained air characteristics were analyzed.
• The effective entrainment area index was proposed to evaluate mechanism of entrained air coupling between material heaps.
The simultaneous unloading of double material heaps is a common occurrence in industrial workshops. This process causes dust escape to increase due to the interaction of entrained air between material heaps. In order to understand the coupling mechanism, a mathematical and physical model of the simultaneous unloading process of double material heaps is established in this paper. The DEM-CFD coupling method was validated using experimental data. The effects of material heap height, particle velocity and hopper outlet diameter on the entrained air characteristics of double material heap unloading process are analyzed. The “effective entrainment area” index was proposed for the first time to evaluate the coupling mechanism of entrained air between material heaps. The results indicate that: as the height of the material heap increases, the maximum velocity of the entrained air after collision of particles in different cross-sections gradually decreases from 1.4 to 1 m/s. With the increase in particle velocity and hopper outlet diameter, the maximum velocity of the entrained air generated between the material heaps increases. As the heap height, particle velocity, or hopper outlet diameter increases, the rate of change in entrained air velocity gradually decreases. The diameter of the hopper outlet has the greatest effect on the velocity of entrained air at the vertical axis between material heaps. The diameter of the hopper outlet has the most obvious effect on the height of the vortex core, with a maximum height difference of 33 mm. The effective entrainment area increases with heap height, particle velocity, or hopper outlet diameter, reaching a minimum of 568 mm2 at 2 m/s and a maximum of 1884 mm2 at 30 mm.