-
Volumes 96-107 (2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volume 105
-
Volume 104
-
Volume 103
Pages 1-314 (August 2025)
-
Volume 102
Pages 1-276 (July 2025)
-
Volume 101
Pages 1-166 (June 2025)
-
Volume 100
Pages 1-256 (May 2025)
-
Volume 99
Pages 1-242 (April 2025)
-
Volume 98
Pages 1-288 (March 2025)
-
Volume 97
Pages 1-256 (February 2025)
-
Volume 96
Pages 1-340 (January 2025)
-
Volume 106
-
Volumes 84-95 (2024)
-
Volume 95
Pages 1-392 (December 2024)
-
Volume 94
Pages 1-400 (November 2024)
-
Volume 93
Pages 1-376 (October 2024)
-
Volume 92
Pages 1-316 (September 2024)
-
Volume 91
Pages 1-378 (August 2024)
-
Volume 90
Pages 1-580 (July 2024)
-
Volume 89
Pages 1-278 (June 2024)
-
Volume 88
Pages 1-350 (May 2024)
-
Volume 87
Pages 1-338 (April 2024)
-
Volume 86
Pages 1-312 (March 2024)
-
Volume 85
Pages 1-334 (February 2024)
-
Volume 84
Pages 1-308 (January 2024)
-
Volume 95
-
Volumes 72-83 (2023)
-
Volume 83
Pages 1-258 (December 2023)
-
Volume 82
Pages 1-204 (November 2023)
-
Volume 81
Pages 1-188 (October 2023)
-
Volume 80
Pages 1-202 (September 2023)
-
Volume 79
Pages 1-172 (August 2023)
-
Volume 78
Pages 1-146 (July 2023)
-
Volume 77
Pages 1-152 (June 2023)
-
Volume 76
Pages 1-176 (May 2023)
-
Volume 75
Pages 1-228 (April 2023)
-
Volume 74
Pages 1-200 (March 2023)
-
Volume 73
Pages 1-138 (February 2023)
-
Volume 72
Pages 1-144 (January 2023)
-
Volume 83
-
Volumes 60-71 (2022)
-
Volume 71
Pages 1-108 (December 2022)
-
Volume 70
Pages 1-106 (November 2022)
-
Volume 69
Pages 1-122 (October 2022)
-
Volume 68
Pages 1-124 (September 2022)
-
Volume 67
Pages 1-102 (August 2022)
-
Volume 66
Pages 1-112 (July 2022)
-
Volume 65
Pages 1-138 (June 2022)
-
Volume 64
Pages 1-186 (May 2022)
-
Volume 63
Pages 1-124 (April 2022)
-
Volume 62
Pages 1-104 (March 2022)
-
Volume 61
Pages 1-120 (February 2022)
-
Volume 60
Pages 1-124 (January 2022)
-
Volume 71
- Volumes 54-59 (2021)
- Volumes 48-53 (2020)
- Volumes 42-47 (2019)
- Volumes 36-41 (2018)
- Volumes 30-35 (2017)
- Volumes 24-29 (2016)
- Volumes 18-23 (2015)
- Volumes 12-17 (2014)
- Volume 11 (2013)
- Volume 10 (2012)
- Volume 9 (2011)
- Volume 8 (2010)
- Volume 7 (2009)
- Volume 6 (2008)
- Volume 5 (2007)
- Volume 4 (2006)
- Volume 3 (2005)
- Volume 2 (2004)
- Volume 1 (2003)
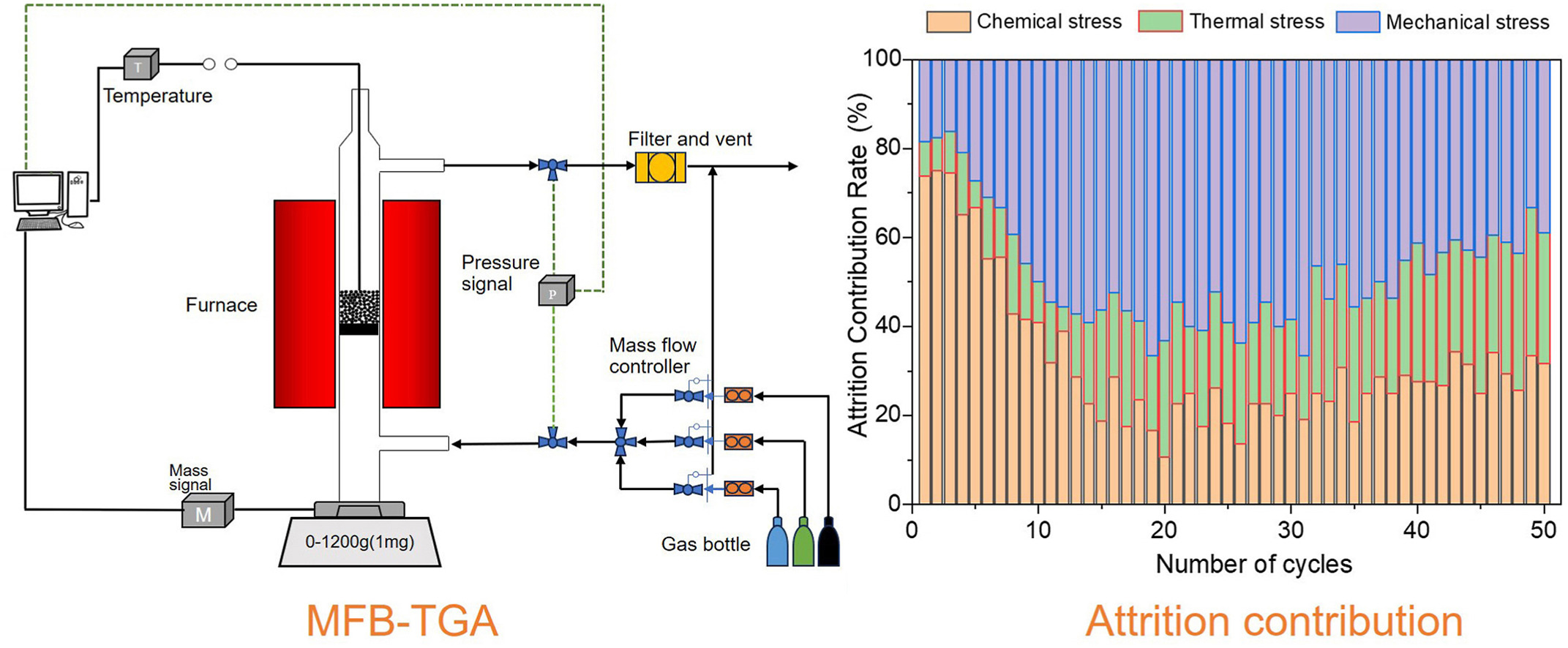
• Micro fluidized bed thermogravimetry was proposed to obtain attrition rate.
• Attrition behaviors of Ilmenite,iron ore,and laterite ore were investigated.
• Contributions of chemical,thermal,and mechanical stresses were revealed.
• This work provides a tool to determine attrition behavior of oxygen carrier in lab.
It is evident that oxygen carriers play a pivotal role in the chemical looping combustion. Although the majority of studies have concentrated on enhancing the high-temperature thermal stability and reactivity of oxygen carriers,it is imperative to study the attrition behaviors of oxygen carriers precisely. In this work,a micro fluidized bed thermogravimetric analysis (MFB-TGA) was developed to obtain the attrition properties through real-time measurement of weight changes during the redox reactions. Ilmenite, iron ore, and laterite ore were selected as the oxygen carriers, and the contributions of mechanical, thermal, and chemical stresses to oxygen carrier attrition were investigated. It was found that ilmenite and iron ore started stable attrition just after the 20th and 5th cycles due to the activation phenomenon. Laterite ore suffered a fast attrition stage with a rate of 0.37 % h−1 before the 20th cycle, after that, the attrition rate changed to be slow. At the end of activation, ilmenite and iron ore attrition was led by mechanical stress with the proportion of ∼40 %, while chemical stress was the predominant factor of laterite ore attrition with the proportion of ∼57.6 %. The proposed micro fluidized bed thermogravimetric method provides an effective and convenient pathway to determine,evaluate,and compare the attrition behavior of oxygen carriers in laboratory.