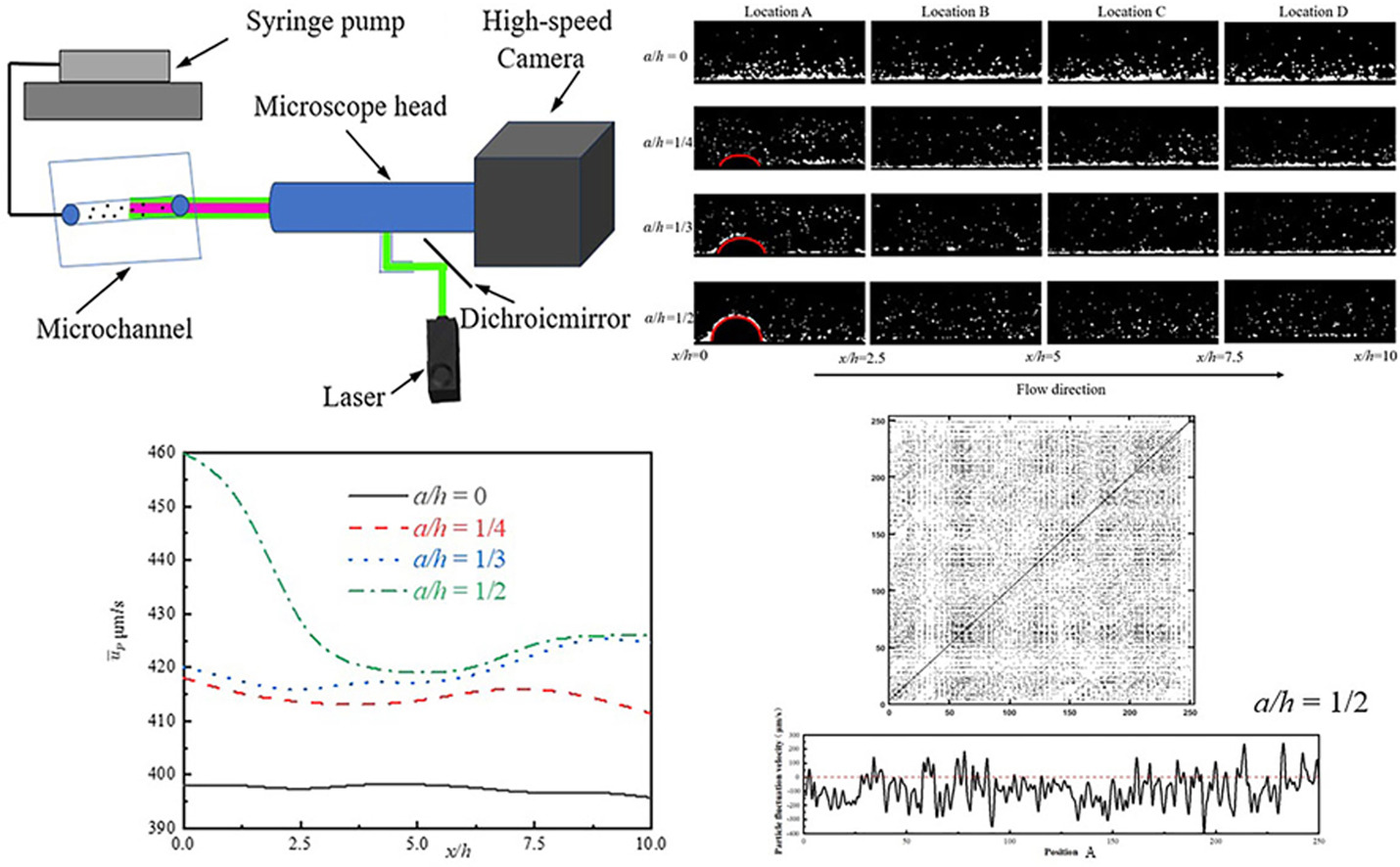
• Fan-shaped ribs mounted in microchannels to decrease particle deposition.
• Increasing the height of fan-shaped rib is more favorable to the diffusion of particles in the microchannel.
• Fan-shaped rib can increase particle flow velocity in the microchannel.
• Higher fan-shaped rib leads to stronger perturbation of particle flow in the microchannel.
Microchannels are widely used in electronic device cooling due to their efficient heat dissipation performance, but particle deposition is still a major challenge limiting their performance. To design and optimize efficient microfluidic devices, this paper proposes to introduce fan-shaped ribs within the microchannels to reduce particle deposition. The placement of fan ribs of different heights in the microchannel was first experimentally determined, and then the particle motion characteristics were further investigated by numerical simulations. The results show that the fan-shaped ribs can effectively reduce particle deposition and exhibit greater deposition inhibition with increasing rib height. The channel constriction induced by the rib structure promotes the radial diffusion of particles in the downstream, and at the same time significantly enhances the radial component of the particle flow, which is improved by 5.76 %, 7.98 %, and 10.86 %, respectively. In addition, recursive analysis revealed that the incorporation of fan-shaped ribs shifted the particle flow from a homogeneous, periodic mode to a more abrupt diffusion mode, which contributed to the improvement of particle dispersion. This study provides a new strategy without the use of surfactants, which provides a reference for the optimized design of microchannel cooling systems.